| A | B |
|---|
| In prokaryotic DNA, a sequence of nucleotides near the start of an operon to which an active repressor can attach, preventing the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter (which prevents transcription). | operator (the yellow part of the operon below) p352,  |
| A promoter, an operator, and the genes they control make up a(n) _______. | operon p352,  |
| In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, gene expression is most often regulated at the stage of _______. | transcription p351,  |
| DNA wraps around ________ to form chromatin. | histone proteins p320, 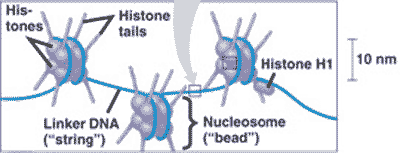 |
| During development of multicellular organisms, cells undergo a process of becoming specialized in form and function in a process called ________. | cell differentiation (this involves activating certain genes and permanently silencing others, such as genes for liver proteins in a pancreas cell) p367 |
| What affect does the acetylation of histone tails have on the ability of DNA to be transcribed? | makes it easier (because the acetyl group -COCH3 neutralizes the positive charge of the histone protein, loosening the grip of the histone on the negatively charged DNA. It also loosens their attraction to neighboring nucleosomes) p357, 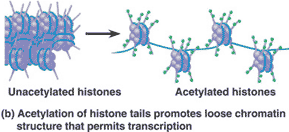 |
| What affect does the methylation of histone tails have on the ability of DNA to be transcribed? | makes it harder p357 |
| Segments of non-coding DNA that help regulate transcription by binding certain proteins are called ______. | control elements p358,  |
| The Epstein-Barr virus, Human papillomavirus (HPV) and HTLV-1 virus have all been identified as ____ viruses that cause ______. | tumor viruses, cancer p377 |
| Cancer causing genes are called _____. | oncogenes (the normal version of these cellular genes are called proto-oncogenes. They are usually involved with normal stimulation of cell growth and division. These genes are ones that commonly mutate to form oncogenes) p373 |
| ______ code for proteins that stimulate normal cell growth and division, but can be turned into a cancer-causing gene by mutations. | proto-oncogenes p373 |
| An individual ______ an oncogene or mutant allele of a tumor-suppressor gene is one step closer to accumulating the necessary mutations for cancer to develop by the _____ model of cancer development. | inheriting, multistep p376, 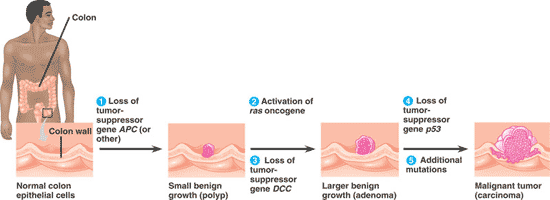 |
What is "A" pointing to in the picture below?, 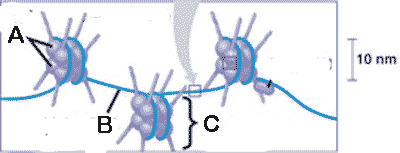 | histone proteins p357,  |
| A gene found in viri or as a mutated form of normal gene that is normally involved with regulating the cell cycle, but now is involved in triggering cancerous characteristics. | oncogene p373 |
| The guardian angel of the genome, this gene is expressed when a cell's DNA is damaged. Its product is a transcription factor that transcribes proteins whose job it is to keep mutated cells from dividing or help repair damaged DNA. | p53 gene p376, 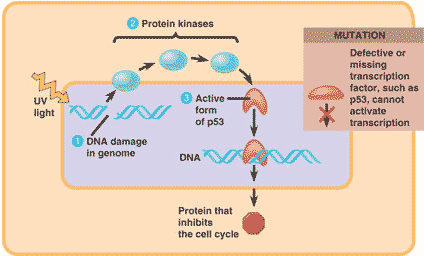 |
| A segment of noncoding DNA that helps regulate transcription of a gene by binding proteins called transcription factors. | control element p358,  |
| Expression of different sets of genes by cells with the same genome is called _____. | differential gene expression p356 |
| A normal cellular gene corresponding to an oncogene; a gene with the potential to cause cancer, but that requires some alteration to become an oncogene. | proto-oncogene p373 |
| HPV, the human papillovavirus, is a virus that is often sexually transmitted and is associated with _____ in females and ____ in males. | cervical cancer, genital warts (This is a type of virus with many different forms. It is usually transmitted sexually and can lie dormant without producing symptoms for years. Yet it can still be transmitted while asymptomatic. The strains that cause genital warts (in men and women) are not the same ones that increase the risk of cervical cancer. It is estimated that around 3/4ths of older adults carry this virus. Young adults are now able to get vaccinated against the most common and dangerous forms of the virus) p377 |
| The end of an animal that is near the head is called the _______ end. | anterior p370 |
| The end of an animal that is near the tail is called the _______ end. | posterior p370 |
| The belly of an animal is said to be on the ______ side of the body. | ventral p370 |
| The back of an animal is said to be on the ______ side of the body. | dorsal (Think about the dorsal fin of a shark sticking out of the water) p370 |
| Maternal substances in the egg that influence the course of early development are called ___________. | cytoplasmic determinants p367 |
| In Drosophila, bicoid mRNA is an example of a __________. | cytoplasmic determinant (The term "morphogen" can also apply because the bicoid mRNA forms a gradient that helps establish the developmental axes. The term "Bicoid" by itself refers to the protein product of bicoid m-RNA that gets translated once the egg is fertilized. Bicoid is also a morphogen, but is not a cytoplasmic determinant, because it did not enter the egg from the mother's cells), 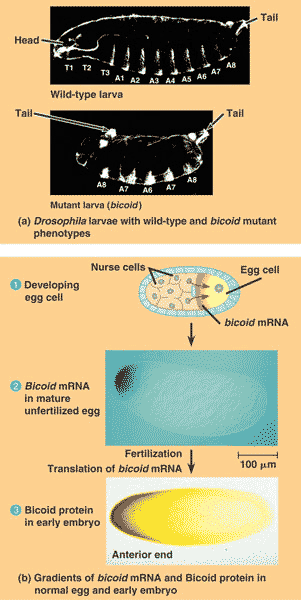 |
| Any of the master regulatory genes that control placement and spatial organization of body parts in animals, plants, and fungi by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells is called a(n) ______. | homeotic gene p371 ,G-17 |
| The products of _____ genes are cytoplasmic determinants. These include proteins and/or RNA that are produced by the mother and enter the egg but don't spread out evenly in the egg. The different concentration of these substances in the egg lead to the establishment of the axes in the developing embryo. | maternal effect genes (a.k.a. - egg polarity genes) p371 |
| The products of maternal effect genes are ______. These include proteins and/or RNA that are produced by the mother and enter the egg but don't spread out evenly in the egg. The different concentration of these substances in the egg lead to the establishment of the axes in the developing embryo. | cytoplasmic determinants p371 |