| A | B |
|---|
Daniel Shays,  | A former Continental Army captain who led farmers into a rebellion caused by banks taking farmers lands and farmers loosing business |
John Dickinson,  | Feared a strong central government and approved highly of the Articles of Confederation |
Appalachian Mountains,  | The point in which the West lay beyond and the area where states were fighting for the land |
Land Ordinance of 1785, 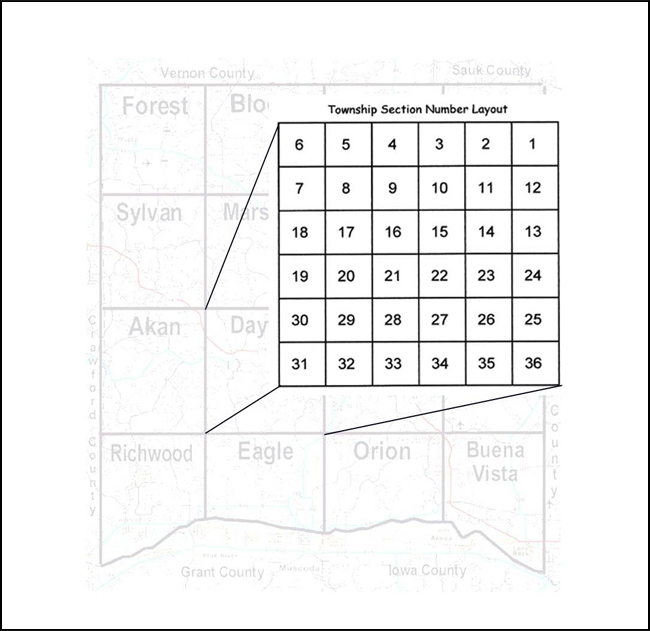 | The disputed land was divided up into townships of 6 square miles and each township was sectioned and auctioned off to people |
| Northwest Ordinance | A law that provided big populated territiories to eventually become a state with a proper constitution and a big population |
Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, and Wisconsin, 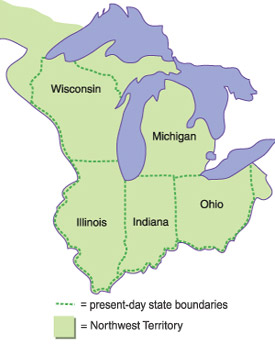 | States that were created because of the Northwest Ordinance |
Shays Rebellion,  | The rebellion that the farmers created that caused many people to realize that the central government was too weak |
| Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, and Thomas Paine | Three important and well-known delegates who were overseas at the time of the convention |
| Patrick Henry | An important politician who did not attend the convention because he feared that a strong central government would be created |
Benjamin Franklin,  | The convention's oldest delegate and an important figure throughout the entire creation of the United States and the constitution |
George Washington,  | The man chosen unanimously to preside over the convention |
James Madison,  | The man who called the meeting and who brought a completed draft of a new government |
Edmund Randolph,  | The presenter of Madison's proposal because he was a better speaker than Madison |
| Virginia Plan | Madison's proposal that called for a strong central government with three branches of government and favored larger states |
Legislative branch,  | Makes the laws and is split into two houses, where the states are represented in both houses based population |
Executive Branch,  | Carries out the laws |
Judicial Branch,  | Determines if the laws are fair |
William Paterson,  | Created a counter-plan that would favor the smaller states over the larger states |
| New Jersey Plan | Stated that there would be three branches of government but the legislative branch would only have one house where each state only had one representative |
| Great Compromise | The comittiees agreement between the Virginia Plan and the New Jersey Plan, a three branch government and it called for a two house congress: the Senate, two state representatives and the House of Representatives, population based |
| Three-Fifths Compromise | The delegates compromise on how slaves should be counted during a census, only three-fifths of all enslaved people in Southern states would be counted for representation and taxation |
| Iroquois League | The uniting of the mutiple Iroquois tribes for protection and defense of their tribe |
| Magna Carter | A bill in the English Parliament that limited the power of the ruler, something that the founders looked at for inspiration to create a better constitution |
John Locke,  | Wrote the Two Treatises on Government, believed that all people had natural rights to life, liberty, and property and that there should be a contract between the ruler and the ruled |
Baron de Montesquieu,  | Wrote The Spirit of Laws and believed that by seperating the governing bodies the power of each would be limited |
United States Congress,  | The legislative branch of the national government. Is the law-making branch of government but also has the power to declare war, form an army, collect taxes, and regulate trade |
Senate,  | Each state has two senators, who are voted for by the people |
House of Representatives,  | Each state is represented based on population, who are voted for by the people |
| Representatives | Members of the House, each representative serves a two-year term |
| Senators | Members of the Senate, each senator serves a six-year term |
President,  | The head of the Executive Branch, executes the laws made by Congress, the commander in chief of armed forces, and is resposible for relations with other countries |
| Vice President | The Presidents advisor and the next in line after the President |
| Federalists | People who favored the Constitution and the strong national government it created |
| Anti-federalists | People who did not want the Constitution to replace the Articles of Confederation |
| James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay | The best known federalists, who, with fake names, the wrote a series of essays defending the Constitution |
| John Hancock, Samuel Adams, and Patrick Henry | Were Anti-Federalists who attacked everything about the Constitution and complainedthat it failed to protect basic liberties and that the Comstitution could easily take these rights away |
Bill of Rights,  | The first ten amendments to the Constitution that outline basic rights of all American citizens |