| A | B |
|---|
| What does "in vitro" mean? | in a test tube (Or other type of laboratory container. The opposite of in vitro is "in vivo" which means "in the living") p396 |
| DNA in which nucleotide sequences are combined from two different sources - often different species - is called _______. | recombinant DNA p396,  |
| The direct manipulation of genes for practical purposes is called _____. | genetic engineering p396,  |
| The manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products is called ______. | biotechnology p396,  |
| Making multiple copies of DNA fragments that code for a specific polypeptide is called _______. | gene cloning p397,  |
| What are two basic purposes that cloned genes are useful for? | 1) To make many copies of a particular gene. 2) To produce a protein product. p397,  |
| A common approach to cloning a gene involves splicing the gene of interest into a(n) ____ _____ , then reinserting it back into the ________ which will then reproduce, making many copies of the gene. | bacterial plasmid, bacterium p397,  |
| Enzymes that cut DNA molecules in a limited number of specific locations are called _______. | restriction enzymes p398,  |
| The sequence of nucleotides that can be recognized and cut by a particular restriction enzyme is called a(n) ________. | restriction site p398,  |
| Pieces of DNA that have been cut by a restriction enzyme are called _______. | restriction fragments p398,  |
| Restriction fragments (Segments of DNA that were produced using restriction enzymes) can be permanently sealed by an enzyme called _______ which catalyzes the formation of covalent bonds between the sugar at the end of one fragment and the phosphate group at the end of the other fragment. | DNA ligase p398,  |
| An agent used to transfer DNA in genetic engineering. Plasmids that move recombinant DNA and viral DNA that can be transfered along with recombinant DNA by infection are both examples. | cloning vector p398,  |
| The most commonly used vector is a(n) _______. | bacterial plasmid (Remember, a vector is a DNA molecule that can carry foreign DNA into a cell and replicate there) p398,  |
| A method of quickly producing a lot of DNA copies in vitro from a small amount of original DNA is called ______. | PCR (stands for polymerase chain reactions) p405, 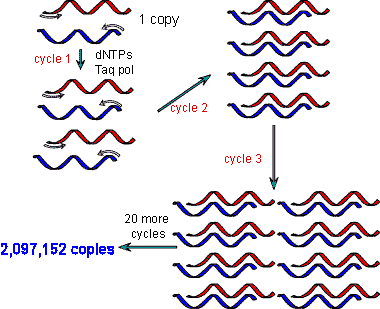 |
| A technique for separating DNA or protein based on size and charge is called _______. | gel electrophoresis p405,  |
| A technique that combines the techniques of gel electrophoresis with nucleic acid hybridization to separate and identify specific sequences of DNA is called _____. | Southern blotting p406, 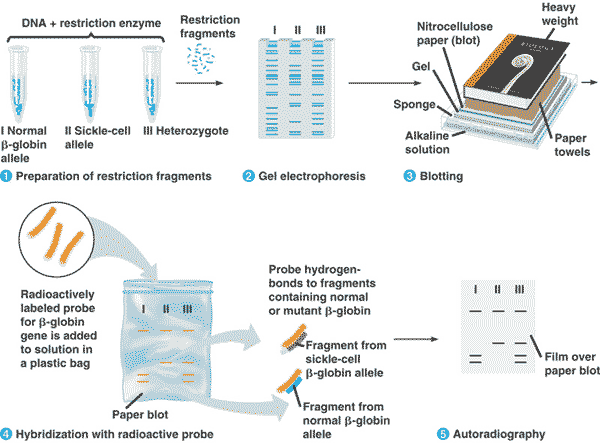 |
| Differences in DNA sequences on homologous chromosomes that can result in different patterns of restriction fragment lengths | RFLP's (restriction fragment length polymorphisms) p406, 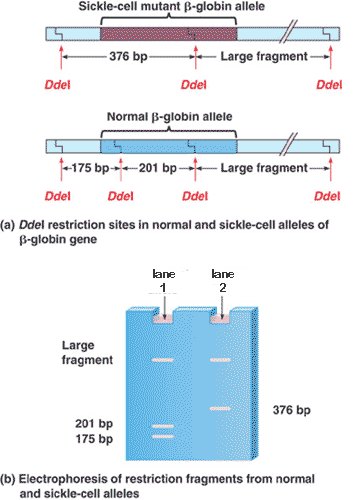 |
| Base pairing between a gene and a complementary sequence on another nucleic acid molecule that usually carries some type of marker is called _____. | nucleic acid hybridization (This technique is used to identify genes of interest in a genomic library. A nucleic acid probe is used. This is a short string of nucleotides known to be complementary to a portion of the gene of interest. It has a radioactive isotope, fluorescent marker, or some other type of tag so it can be easily identified and isolated) p401, 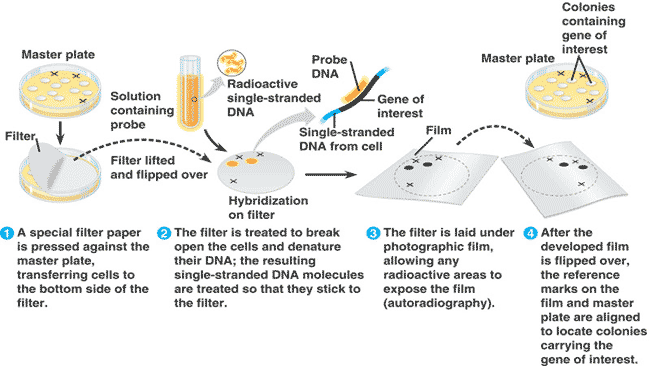 |
| An artificial version of a bacterial chromosome that can carry inserts of 100,000 to 300,000 base pairs is called a(n) ______. | BAC (Bacterial artificial chromosome. These are basically just synthetic huge plasmids, capable of storing many more genes in a genomic library compared to a normal plasmid. This minimizes the number of clones required to make up a genomic library.) p400 |
| A(n) ______ library is gene library containing clones that carry complementary DNA (cDNA). The library contains only the genes that were transcribed in the cells whose mRNA was isolated to make cDNA through reverse transcription. | cDNA library (cDNA is made off of mRNA using reverse transcriptase) p401 & G-6 |
| An individual's unique collection of DNA restriction fragments, detected by electrophoresis and nucleic acid probes. | Genetic profile (Many people still refer to it as a "DNA fingerprint.") p420, 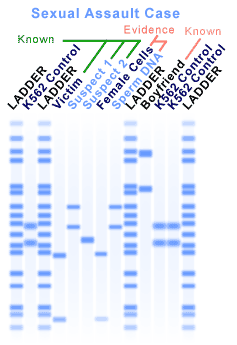 |
| An organism that has acquired one or more genes by artificial means can be called a(n) ______ or a(n) _______. | genetically modified (GM) organism or a transgenic organism. pp419&422 |
| The alteration of genes of a person afflicted with a genetic disease is called ______. | gene therapy p418,  |
| A one base-pair variation in the genome sequence is called a(n) _____. | SNP (Single nucleotide polymorphism.) p411 |
| A labeled single-strand nucleic acid molecule used to bond to and identify a specific nucleotide sequence in a nucleic acid sample. | nucleic acid probe p401 |
| A technique to discover the function of a gene by introducing specific changes into the sequence of a cloned gene, reinserting the mutated gene into a cell, and studying the phenotype of the mutant. | in vitro mutagenesis p410 |
| A single-strand end of a double-stranded DNA restriction fragment is called the ______. | sticky end p398,  |
| A method to detect and measure the expression of thousands of genes at one time. Tiny amounts of a large number of single-stranded DNA fragment representing different genes are fixed to a glass slide. These fragments, ideally representing all the genes of an organism, are tested for hybridization with various samples of cDNA molecules. | DNA microarray assay p410, 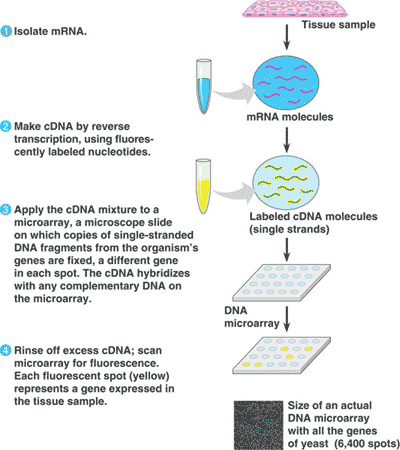 |
| A degradative enzyme that recognizes and cuts up DNA (including that of certain phages) that is foreign to a bacterium. | restriction enzyme p398,  |
| A lineage of genetically identical individuals or cells is called a(n) _____. | clone G-7 |
| A cloning vector that contains the requisite prokaryotic promoter just upstream of a restriction site where a eukaryotic gene can be inserted. | expression vector p402 |
| A technique to introduce recombinant DNA into cells by applying a brief electrical pulse to a solution containing cells. The electricity creates temporary holes in the cells' plasma membrane, through which DNA can enter. | electroporation p403 |
| A plasmid of a tumor-inducing bacterium that integrates a segment of its DNA into the host chromosome of a plant; frequently used as a carrier for genetic engineering in plants. | Ti plasmid pp421, 422 & G-35, 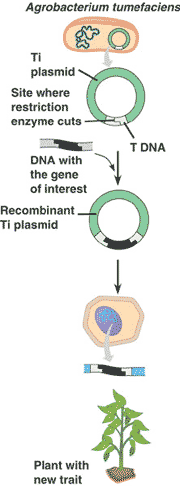 |
| In DNA, the separation of two strands of a double helix by heating them is called ______. | DNA denaturation p403 & G-9 |
| A technique to silence the expression of selected genes in order to determine what those genes do. The method uses synthetic double-stranded RNA molecules matching the sequence of a particular gene to trigger the breakdown of the gene's messenger RNA. By observing what happens when a gene has been silenced, scientists can determine what the normal gene does. | RNAi (RNA interference) p411 |
| A DNA molecule made in vitro using mRNA as a template and an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. | cDNA (complementary DNA) p401 |
| A set of cell clones containing all the DNA segments of a genome, each within a plasmid, BAC (bacterial artificial chromosome) or other cloning vector. | genomic library p400 & G-15, 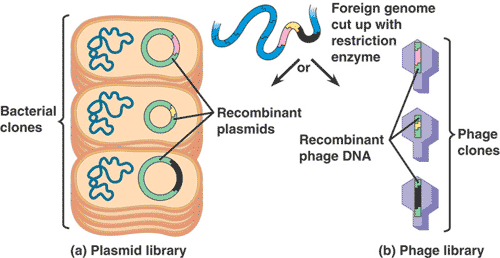 |
The picture below shows the _____ of the victim and several suspects in a sexual assault case. The banding patterns produced by using a restriction enzyme and comparing the RFLP's of each person can be used to solve the case.,  | genetic profiles (Many people still refer to it as "DNA fingerprints.") p420,  |
According to the DNA analysis of the crime scene shown below, who committed the crime?,  | Suspect #1 (notice how suspect #1's RFLP's match the sperm sample taken from the crime scene.) p420,  |
Which laboratory technique is shown below?,  | gel electrophoresis p405,  |
What is the name of the process shown below?,  | gene therapy p418,  |
What is "A" in the picture below?,  | restriction site p398,  |
What is "B" in the picture below?,  | restriction enzyme p398,  |
What is "C" in the picture below?,  | DNA ligase p398,  |
Which laboratory technique is shown below?,  | nucleic acid hybridization (Colonies of bacteria containing the gene of interest have their DNA denatured so they can base pair (hybridize) with a nucleic acid probe that has a complementary base-pair sequence to the gene of interest. The probe is labeled with a radioactive isotope or fluorescent tag for identification purposes.) p401&402,  |
Which laboratory technique is shown below?,  | Southern blot p406,  |
| Small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the main bacterial chromosome are called _____. | plasmids p397,  |
| A common way to insert foreign DNA into a bacterial cell is to mix the bacterial cells into a solution containing the foreign DNA fragments (or foreign DNA spliced into a plasmid). Under suitable experimental conditions, the foreign DNA will pass through the cell wall and cell membrane to enter the cytosol of the the bacterium. This process is called _____. | transformation p400 |
| What are the two genes that are often added to plasmids that will be used as a vector in order to allow researchers later identify which bacterial cells took up the plasmids to become recombinant bacteria with the gene of interest? | AmpR and lacZ (AmpR is a gene that gives bacterial cells resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin. Researchers grow the transformed bacteria on agar plates with ampicillin. Only bacteria that were transformed by taking in the plasmid vector with the ampR gene are able to grow. LacZ is a gene that codes for an enzyme that hydrolyzes lactose and can also hydrolyze a similar synthetic molecule called X-gal to form a blue product. Researchers will use a plasmid vector with lacZ and use a restriction enzyme that cuts the plasmid within the lacZ gene, thereby making it nonfunctional if the gene of interest is able to insert itself into the lacZ gene area. Bacteria that are transformed with a non-recombinant plasmid will have a functional lacZ gene and grow colonies that turn blue with the X-gal, while colonies that have been transformed with recombinant plasmids won't be able to hydrolyze X-gal because their lacZ gene has been destroyed by the gene of interest. These colonies will appear white. p399, 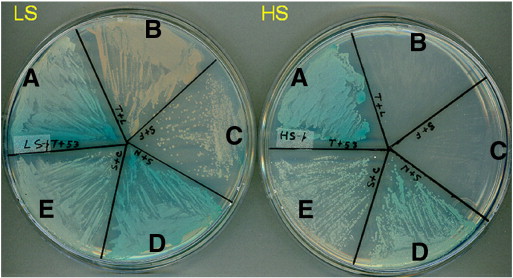 |
| Getting a bacterial cell to express cloned eukaryotic genes can be difficult because of the introns in eukaryotic genes. Bacteria can't remove the introns so that the gene can be expressed correctly. One way of getting around this it to use ____ which has no introns. | cDNA (remember, cDNA is DNA that was made off of an m-RNA transcript. The m-RNA transcript doesn't have the introns, so neither does the cDNA) p403 |
| Why might a cloned eukaryotic gene product not work properly when made by a prokaryotic host (even when the protein is put together correctly by translation on the ribosome of the bacterium)? | Many eukaryotic proteins will not function properly until they are modified after translation. Bacteria can't carry out these modifications. p403 |
| A type of analysis using banding patterns produced by gel electrophoresis to detect differences in DNA sequences. | Restriction fragment analysis (This type of analysis is the basis for comparing DNA fingerprints of crime scene samples. The picture below shows how a sickle-cell allele can be identified by comparing its RFLP's to that of a normal allele) p406,  |
| Any relatively unspecialized cell that can produce, during a single division, one identical daughter cell and one more specialized daughter cell that can undergo further differentiation. | stem cell p415 & G-33 |
| A stem cell with the ability to differentiate into any type of cell that makes up an organism is said to be ______. | totipotent p412 |
| A stem cell with the ability to differentiate into many, but not all of the types of cells that makes up an organism, is said to be ______. | pluripotent p416 |
| Cloning of animals often times involves a procedure called ______ in which the nucleus of a(n) ____ cell is removed and replaced with the nucleus of an adult cell from the animal that you want to clone. | nuclear transplantation, egg cell p413, 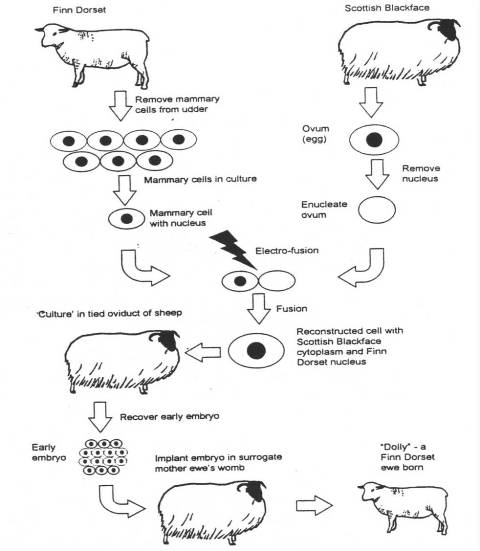 |
| Cloning of animals or animal cells falls into two categories depending on the goal of the cloning. If the goal is to reproduce new individuals (like Dolly, the sheep), it is called _____ cloning. If the goal is to produce new stem cells to treat disease, it is called ____ cloning | reproductive cloning, therapeutic cloning pp 414 & 416 |
Human embryonic stem cells are harvested from human embryos during a stage of embryonic development called the ____ stage., 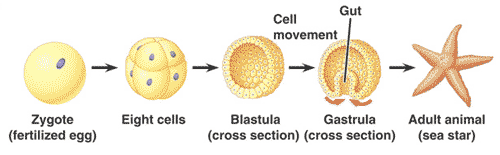 | blastocyst (The blastocyst is called the blastula in other animals. The picture on the front of this card shows the early developmental stages of a seastar, which is extremely similar to the stages that humans go through. In fact, the echinoderm phylum, which the seastar belongs to, is the phylum that is thought to be most closely related to our phylum, the chordate phylum) p415,  |
| What is an iPS cell? | Induced pluripotent stem cell (These are basically differentiated cells that have been induced to de-differentiate into becoming embryonic stem cells (ES cells) in the laboratory. The hope is that researchers will eventually be able to use them in place of embryonic stem cells, thereby sidestepping the controversial technique of harvesting embryonic stem cells from embryos, which kills the embryo. It should be noted that the embryos that are used come from fertility clinics and are unused, destined to be destroyed anyway.) p416 |
| Another name for pluripotent stem cells is ___ stem cells. The only kind of stem cells that are totipotent (able to differentiate into becoming any kind of cell) are ____ stem cells (although major advances have recently been made in reprogramming already differentiated cells to becoming totipotent). | adult stem cells, embryonic stem cells (a.k.a. ES cells) p416 |
| The deliberate effort to control the genetic makeup of the human population is called ___. | eugenics (This practice is currently considered to be immoral. A classic example of someone who tried to apply eugenics to the human population is Adolph Hitler. With the new genetic technologies becoming available, the practice of eugenics is theoretically becoming more easy to carry out, but is still considered to be immoral) p419 |
| Transgenic "pharm" mammals, such as goats, can be engineered to produce human proteins in their ___. | milk (Human proteins produced in transgenic "pharm" animals for use in humans may differ in some ways from the naturally produced human proteins, possibly because of subtle differences in protein modification. Therefore, such proteins must be tested very carefully to ensure that they (or contaminants from the "pharm" animals) will not cause allergic reactions or other adverse effects in patients who receive them) pp419&420 |
| Simple sequence DNA containing multiple tandemly repeated units of two to five nucleotides. These repeating regions of human chromosomes are highly variable and can act as genetic markers used to prepare genetic profiles (DNA fingerprints). | Short tandem repeats (STRs) p420 & G-32 |