| A | B |
|---|
| Revolve (def) | To orbit something |
| Rotate (def) | To spin on an axis |
| Approximate age of the Solar System | 4.6 Billion years old |
| Cause of Earth's Shape | Earth's Rotation |
| Latitude (def) | Angular distance in degrees north or south of the equator |
| Latitude of the North Pole | 90 degrees N |
| Latitude of the South Pole | 90 degrees S |
| Latitude of the Equator | 0 degrees lat. |
| Latitude of the Tropic of Cancer | 23.5 degrees N |
| Latitude of the Tropic of Capricorn | 23.5 degrees S |
| Latitude of the Arctic Circle | 66.5 degrees N |
| Latitude of the Antarctic Circle | 66.5 degrees S |
| Longitude of the Prime Meridian | 0 degrees long. |
| Longitude of the International Date Line | 180 degrees long. |
| Ion (def) | An electrically charged atom; formed when an atom either loses or gains an electron |
| What causes winds to curve to their right in the northern hemisphere? | Coriolis Effect |
| 1st planet from sun | Mercury |
| 3rd planet from sun | Earth |
| A comet's tail always points | away from the sun |
| The same side of the Moon faces Earth because | Moon's rotation rate = the moon's revolution rate |
| The moon & sun rise in the east & set in the west because | Earth rotates west to east |
| 3 names given to a small rock in space, the rock burning in the atmosphere & the rock hitting Earth | Meteoroid, Meteor, Meteorite |
| Scientific explanation for the formation of the Universe | Big Bang Theory |
| Steps in the life cycle of our sun in order | Nebula, Protostar, Stable State, Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, White Dwarf, Black Dwarf |
| Advantage of Hubble telescope over ground based telescopes | Outside Earth's Atmosphere |
| Examples of Jovian planets | Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune |
| The name of our galaxy | Milky Way |
| Geocentric | Earth centered model of the solar system |
What letter represents Rigel, a blue super giant?, 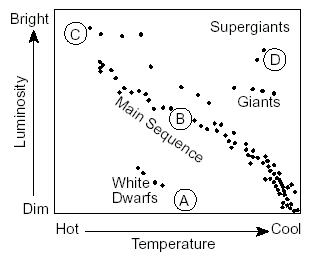 | C,  |
| Order of the moon phases from new to full | New, Waxing Crescent, 1st Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon |
| An object will move in a straight line unless | external forces change it direction |
| Constellation containing the pointer starts used to find Polaris | Ursa Major |
| Moon phases for Spring tides | New & Full |
| Next stage in the life cycle of our sun | Red Giant |
| 2 moon phases that can produce spring tides | New & Full |
| 2 moon phases that can produce neap tides | 1st & 3rd Quarter |
| List the terrestrial planets | Mercury, Venus, Earth & Mars |
| How much later does the moon rise & set each day? | 50 minutes |
| Which planet is the hottest? | Venus, because of its thick atmosphere |
What season is it in the Northern hemisphere?, 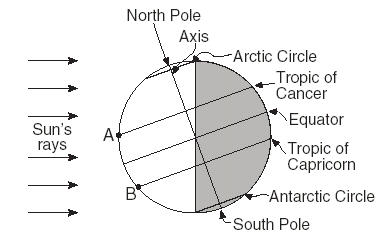 | Summer because the northern hemisphere is tilted toward the sun & above 66.5 degrees N has 24 hrs of daylight,  |
Which letter represents the position of our soloar system in the Milky Way Galaxy, 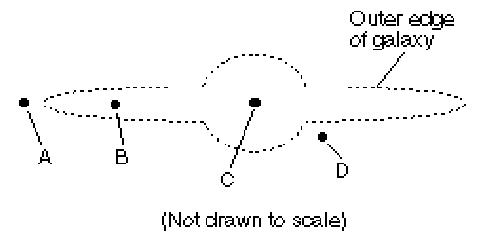 | B, we are in the outer arm of our spiral galaxy,  |
Which image best represents the size comparison of Earth & Venus, 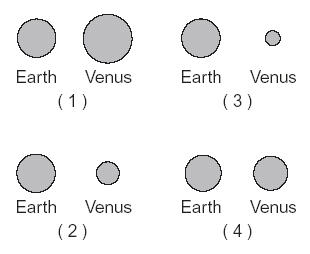 | 4, Venus is considered Earth's twin,  |
Which letter represents our sun?,  | B,  |
| 3 Reasons for seasons | Angle at which the Sun's rays strike the Earth's surface due to Earth’s tilt, parallelism of the Earth's axis aimed to Polaris, & Earth's Revolution around the sun |
| Doppler Effect (def) | An increase (or decrease) in the frequency of sound, light, or other waves as the source and observer move toward (or away from) each other. Ex Red Shift & Blue Shift |
| Red Shift (def) | Spectral lines move toward the Red end of the spectrum as an obj moves away from the observer, described by the doppler effect |
| The astroid belt is located between: | Mars & Jupiter |
| Why is there little to no weathering on the moon? | The moon lacks an atmophere |
Which # represents a waxing crescent moon?, 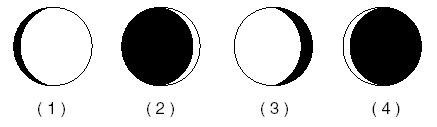 | 2 because a sliver is lit on the right,  |
Which number is the correct postion for a full moon?,  | 5,  |
Which numbers are the correct postions of the moon for neap tides to occur on Earth?,  | 3 & 7; Quarter moon phases,  |
Which number is the correct postion for a waning gibbous moon?,  | 6,  |
Which # is the correct alignment for a solar eclipse?,  | 1,  |
The top spectrum is for a star seen from Earth. Which # represents the change to the spectrum if the star is moving away from Earth?, 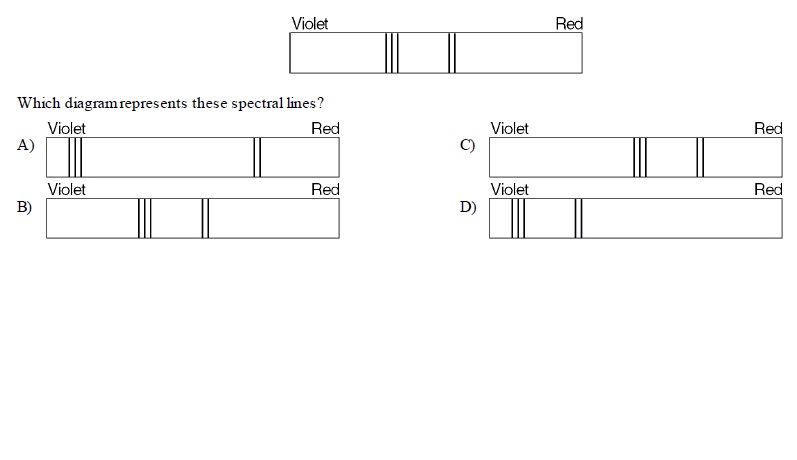 | C; the spectrum shifted toward the red end of the spectrum; redshift |
The top spectrum is for a star seen from Earth. Which # represents the change to the spectrum if the star is moving toward the Earth?,  | D, the spectrum shifted toward the violet/blue end of the spectrum.,  |
| What is the shape of our galaxy? | Spiral |
| Only planet that has water as a solid, liquid & gas | Earth |
| What is the eccentricity of an orbit having a major axis length of 90 million miles and a focal length of 60 million miles? | .67 Eccentricity = focal distance divided by major axis distance (orbit). |
| Approximate scientific estimate of the age or our universe | 13.7 billion years |
| The Foucault pendulum is evidence of Earth's _______? | Rotation |
| How are gravity & distance related? | Inversely; if distance increase between to objects then the gravitational force between them decreases. |
| How are gravity & mass related? | Directly; An increase in the mass of one of object causes the gravitation attraction between them to increase. |
| Person who found the 4 largest moons of Jupiter & was the 1st to use a telescope. | Galileo |
| Person who made long term sky observations with the naked eye. | Tycho Brahe |
| Person who stated the orbits of the planets are elliptical. | Kepler |
| Person who credited the moon's gravity for affecting tides. | Newton |
| Person credited with the heliocentric model of the solar sytem | Copernicus |