| A | B |
|---|
Jamestown,  | the first permanent English settlement in the Americas |
Plymouth,  | founded by persecuted Puritans seeking religious freedom |
Rhode Island,  | founded by Roger Williams on the principle of separation of church and state |
Pennsylvania,  | founded by William Penn as a refuge for English Quakers |
Indentured Servants,  | worked several years in exhcange for relief from debt or passage to America |
Middle Passage, 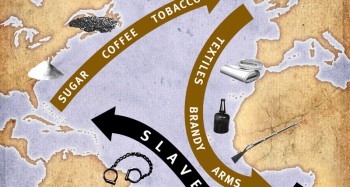 | the southern leg of the triangular trade route that brought slaves to the Americas |
House of Burgesses,  | the first democratically elected assembly in the New World |
Mayflower Compact,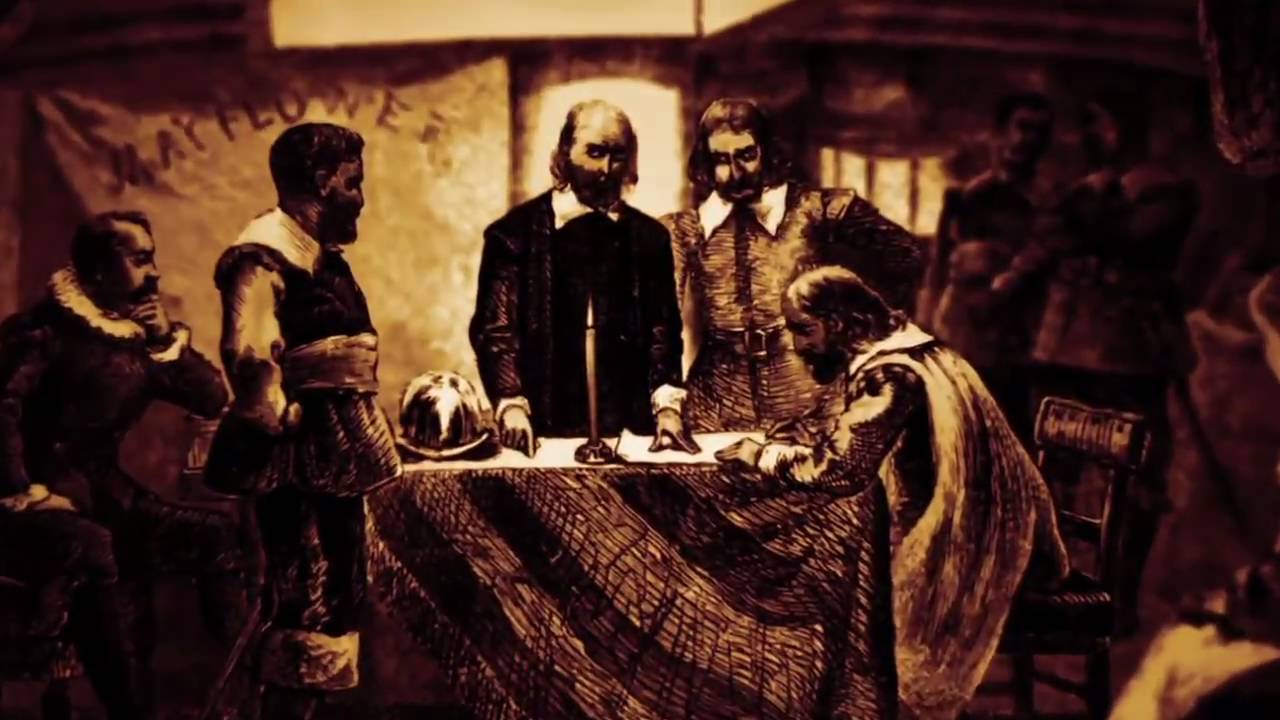  | the Puritans agreed to a covenant community based on democratic and Puritan principles |
Great Awakening,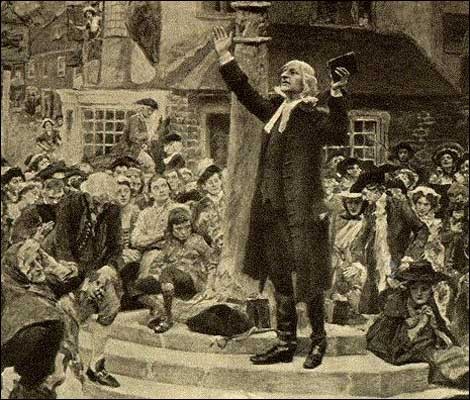  | religious revival challenges the established order & lays a foundation for American Revolution |
Cash Crops,  | rice, indigo and tobacco frequently exported to Europe in this period |
| social standing in South | status was based upon land ownership and family |
Town Meetings,  | a form of direct democracy practiced in New England |
Disease, 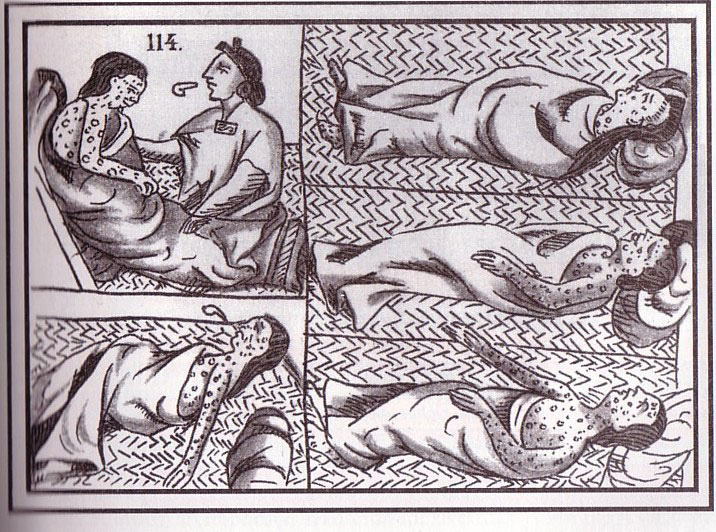 | ravaged Native-American communities as Europeans arrived |
| social standing in New England | status was based upon religious standing |
Church of England,  | had great influence in the Southern Colonies |
Cavaliers,  | English nobility that recieved large land grants in Virginia from the King |
Shenandoah Valley,  | poor English immigrants settled here rather than the 'lowlands' |
Plantations, 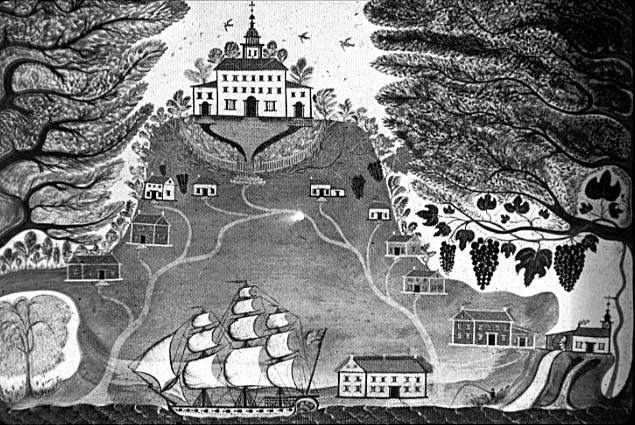 | large self-contained cash crop farms using indentured servants or slaves as labor |
New France, 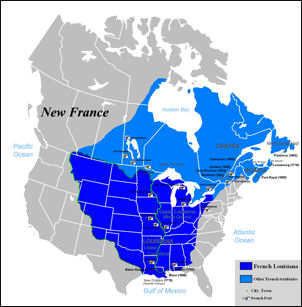 | No large scale immigration but more cooperative with Native Americans |
Spanish Colonies, 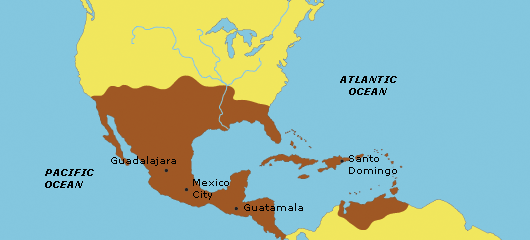 | formed in South and Central America as well as Florida and the Caribbean |
English Colonies, 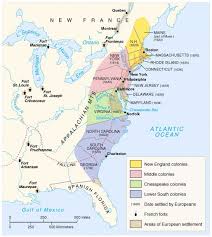 | formed on the Atlantic seaboard of North America |
Civil War,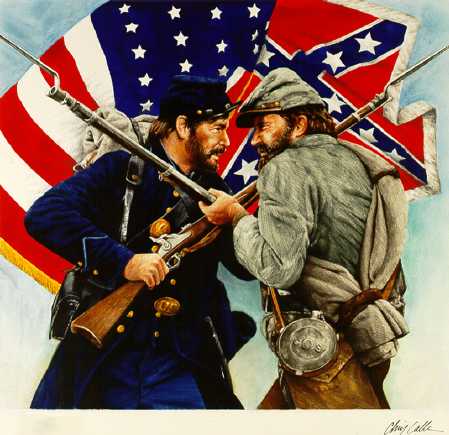  | resulted from the slave based plantation economy of the south |
New England Colonies, 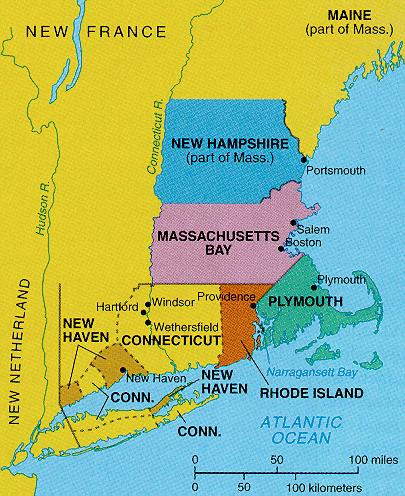 | Subsistance farming; shipbuilding; fishing; lumbering & later manufacturing |
Middle Colonies,  | small scale farming; trade; shipbuilding; entrepeneurs; artisans & flexible social structures |
Philadelphia/New York,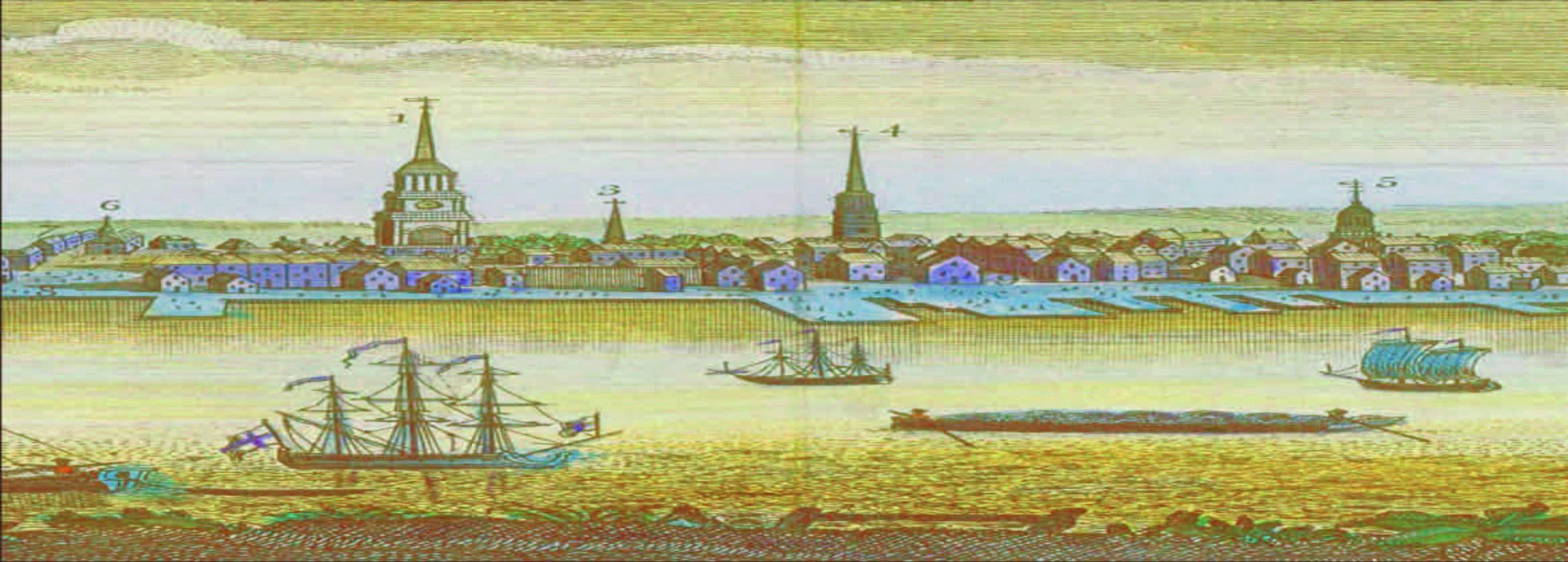  | Major seaports that became important trade and commerce centers in Middle Colonies |
the Puritan Ethic,  | hard work and thrift (saving your $) |
| free-enterprise & private property | characterized all of the English Colonies |
Baptist & Methodist,  | these evangelical churches grew as a result of the Great Awakening |
1619,  | The year in which the first slaves arrived in Jamestown |
Athens,  | New England town meetings are based on the practices of this ancient civilization |
New York (colony),  | Huguenots & Jews settled here |
New Jersey,  | Presbyterians settled here |
Appalachian foothills,  | settled by Scots-Irish/English; subsistance farms; Hunting; Trading |
Puritans,  | Intolerant of dissenters who challenged combining religion and government |