| A | B |
|---|
Aeneas fled this city when it was overrun by the Greeks and eventually made his way to Italy,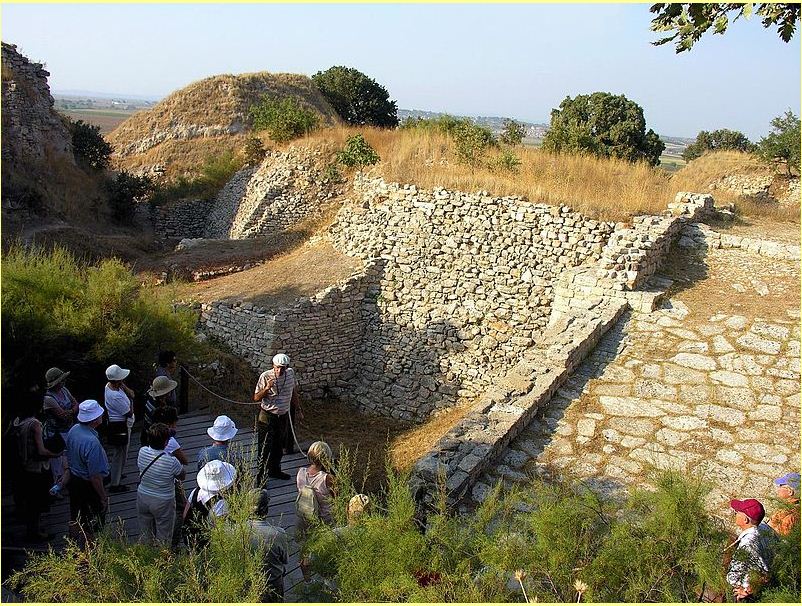  | Troy |
After 42 BCE, these mountains marked the northern border of Italy, ) | Alps |
A monument in this port city on Italy's 'heel' marked the end of the Via Appia,  | Brundisium |
When the city of Rome's needs outgrew this neighboring city's natural harbor, the Emperor Trajan built a new, hexagonal one, 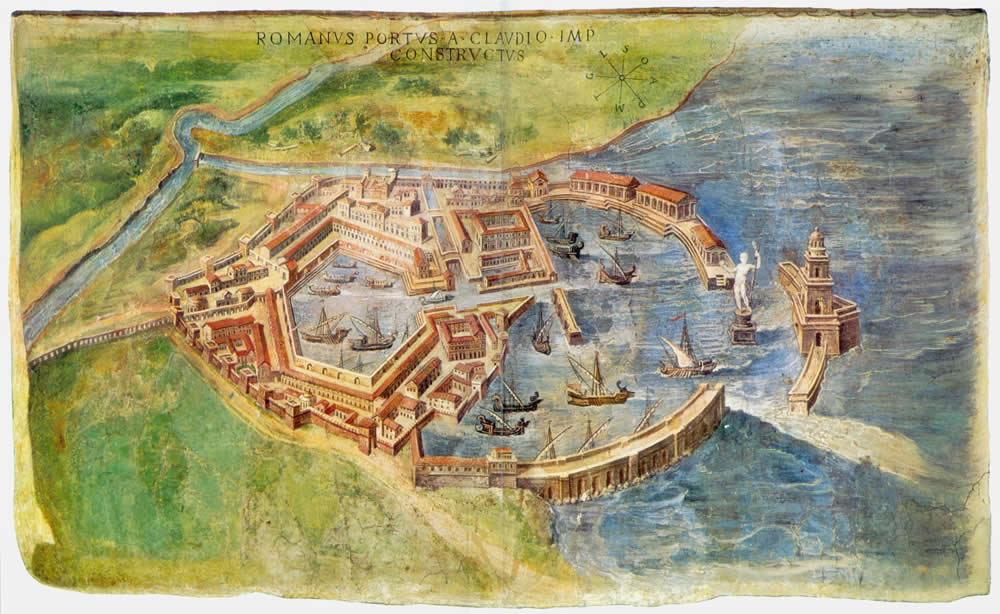 | Ostia |
This city was home to Plato, Socrates and the Parthenon,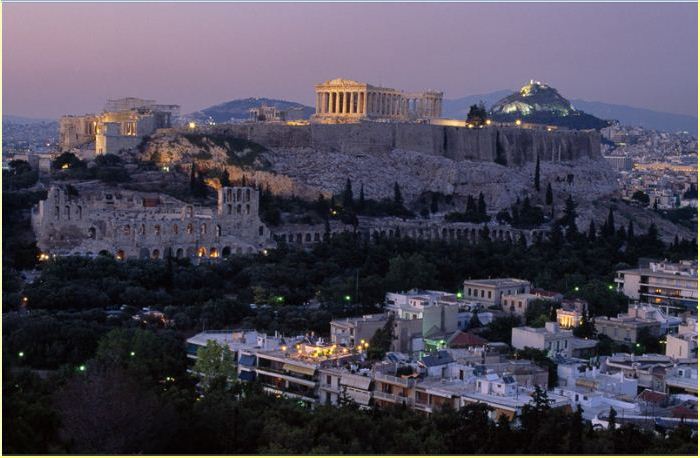  | Athens |
This North African city was home to Republican Rome's fiercest enemy, Hannibal,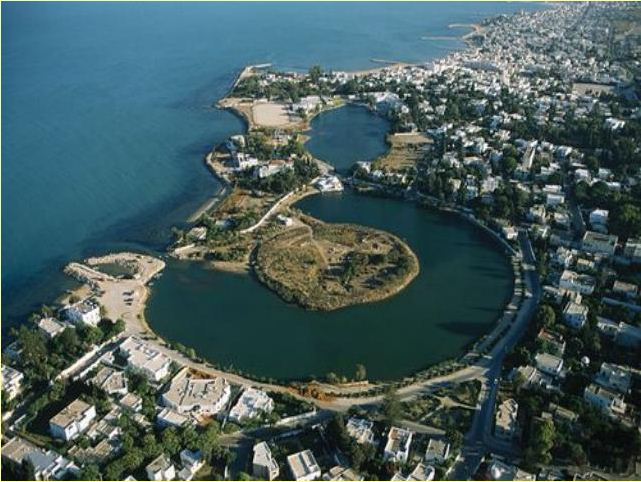  | Carthage |
The Romans believed this volcano on the island of Sicily lay over Vulcan's workshop,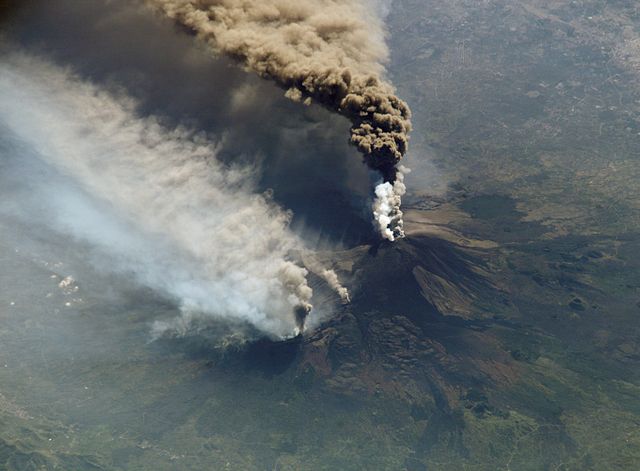  | Mount Etna |
The Romans used this Latin phrase to call the Mediterranean 'our sea',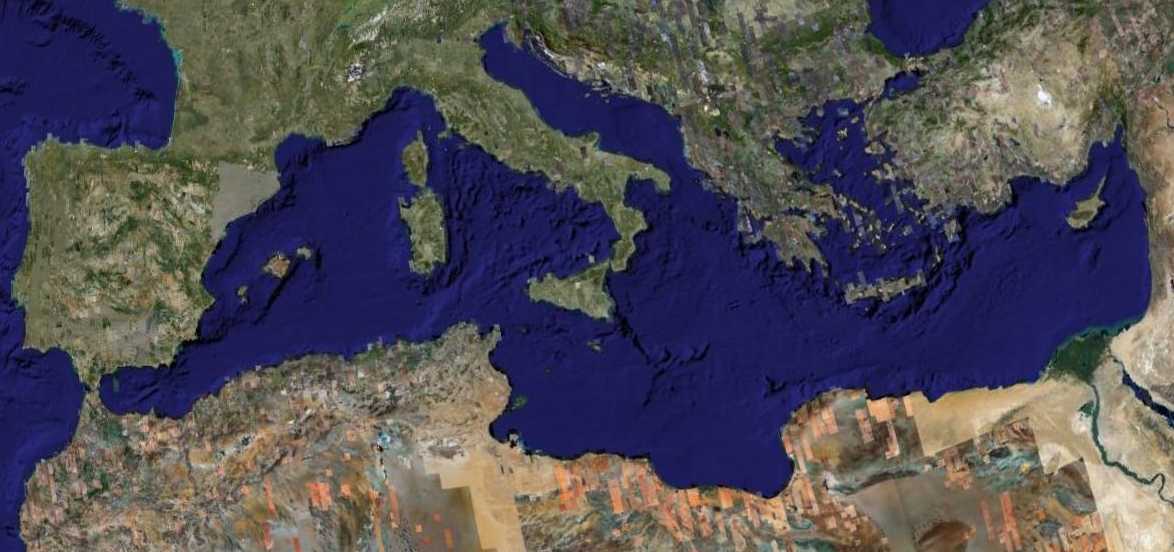  | Mare Nostrum |
The Greeks and Romans believed this mountain in Greece was home to the gods,  | Olympus |
These mountains run the length of the Italian peninsula,  | Apennines |
This volcano buried the cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum and Stabiae in 79 CE,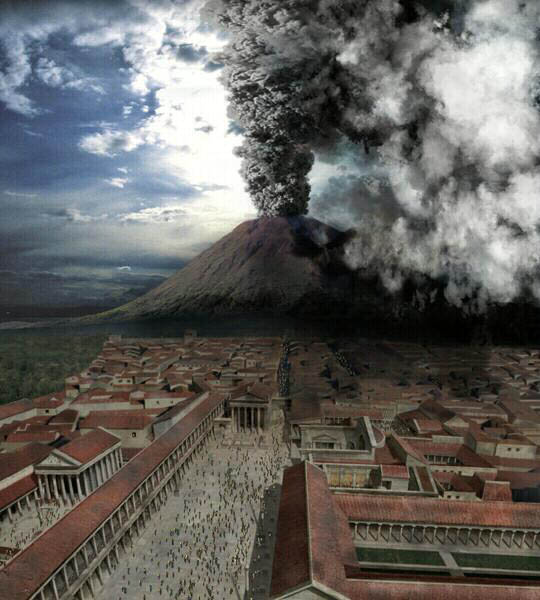  | Vesuvius |
This structure was built in the 2nd c. CE to mark the northern border of the province of Britannia,  | Hadrian's Wall |
Thousands of inhabitants of this southern Italian city were killed in the eruption of Mt. Vesuvius in 79 CE.,  | Pompeii |
This island off the 'toe' of Italy was the focal point of the first war between Rome and Carthage.,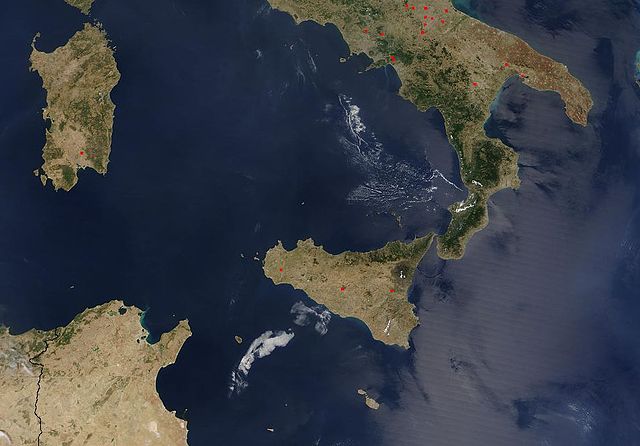  | Sicily |
This river flows from the Apennines Mountains through Rome and its port city, Ostia, to the sea.,  | Tiber |
The western end of the Mediterranean, which the Greeks and Romans believed was westward extent of Hercules's travels,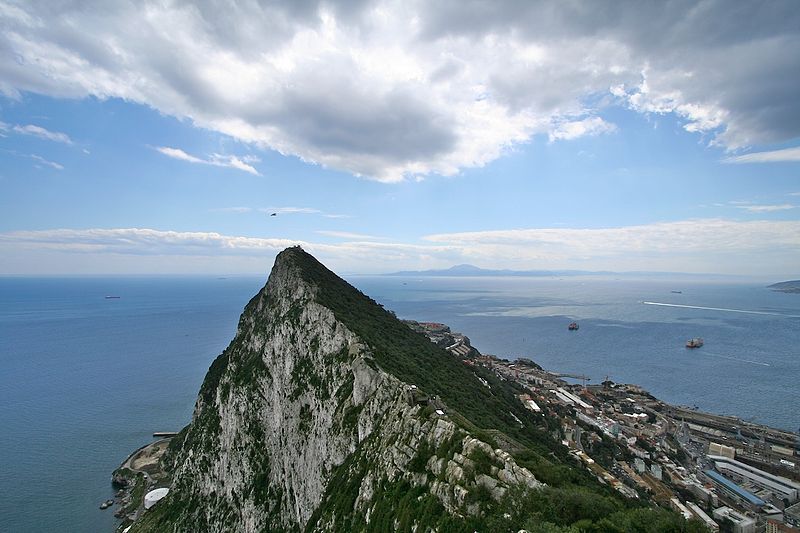  | Strait of Gibraltar |