| A | B |
|---|
| Evolution above the species level (ie - the kind that creates new species) is called _______. | macroevolution p507 |
| A(n) ______ is a structure that originally evolved for a different purpose than the one it has presently. | exaptation (ex: Feathers probably evolved for insulation and were later modified to help with flight) p530 |
| _____ is an evolutionary change in the rate or timing of developmental events and can have a significant impact on body shape. | Heterochrony (In the human evolutionary lineage, mutations that slowed the growth of the jaw relative to other parts of the skull produced an adult whose head resembles that of a chimpanzee infant) p525,  |
| In ______, the rate of reproductive development accelerates compared to somatic development, leading to sexually mature species that retain body features that were juvenile structures in an ancestral species. | paedomorphosis (This adult aquatic salamander that retains the gills common to all juvenile amphibians is a classic example) p526,  |
| ____ genes determine such basic features as where a pair of wings and a pair of legs will develop on a bird or how a flower’s parts are arranged. | Homeotic genes p526 |
| The products of one class of homeotic genes called ____ genes provide positional information in animal embryos. | Hox (Examples include the development of fins in fish and limbs in tetrapods) p526 |
| According to the ________________ model, trends may result when species with certain characteristics endure longer and speciate more often than those with other characteristics. | species selection model p530 |
| _____ is a method paleontologists use for determining the ages of rocks and fossils on a scale of absolute time, based on the half-life of radioactive isotopes. | Radiometric dating p512,  |
| The number of years it takes for 50% of an original sample of a radioactive isotope to decay is called the isotope's _____. | half-life p512,  |
| An RNA molecule that acts as a catalyst is called a(n) _____. | ribozyme (It is thought RNA may have been the first genetic material and RNA ribozymes may have been the first catalysts for self-replication of RNA molecules) p509 |
| Fossilized bacterial mats that formed as far back as 3.5 billion years ago are called _____. | stromatolites p514 |
| The supercontinent formed near the end of the Paleozoic era when plate movements brought all the landmasses of Earth together is called ______. | Pangaea p520, 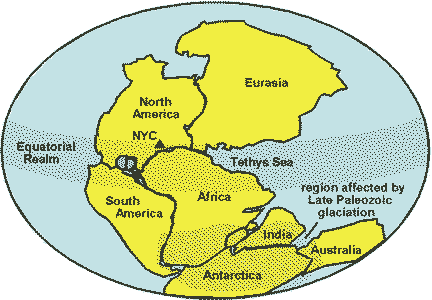 |
| The model of the origin of eukaryotes that proposes that mitochondria, chloroplasts, and perhaps other cellular structures were formerly small prokaryotes that lived symbiotically inside larger cells. | endosymbiont theory (aka - endosymbiotic theory) p516,  |
| The half-life of carbon-14 is 5700 years. If there was 10 grams of carbon-14 in a bone fragment 11,400 years ago, how much carbon-14 would still be left today? | 2.5 grams (After 5700 years, half of the 10 gram original sample would be left, so after 5700 years there would be 5 grams. In the next 5700 years, half of that 5 grams would be left, so after a total of 11,400 years ago, only 2.5 grams would be left) p512,  |
| Scientific data indicates that Earth formed about _____ years ago. | 4.6 billion p508 |
| The first genetic material was probably ____ due to its ability to catalyze reactions including its own self replication. | RNA p509 |
| ______ are similar fossils found in the same rock strata in different locations. They allow strata at one location to be correlated with strata at another location. | Index fossils (Not in this version of the textbook, but I want you to know this term),  |
| Each era is a distinct age in the history of Earth and its life, with boundaries marked by ________ seen in the fossil record. | mass extinctions p514 |
| The geologic record is divided into three _____. These are further subdivided into _____ which themselves are further subdivided into ____. | Eons, eras, periods p515, 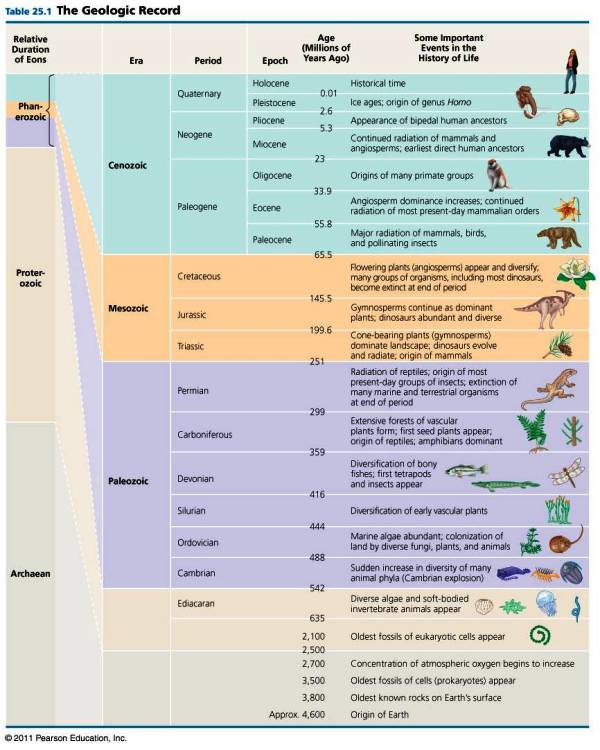 |
| The earliest known fossils date back about _____ years ago. | 3.5 billion pp507&514 |
| Prokaryotes were the only life forms from at least _____ to ______ years ago. | 3.5 billion to 2.1 billion p514 |
| Oxygen releasing photosynthetic bacteria are called ____. | cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green bacteria) p516 |
| Earth's early atmosphere was much different than today's atmosphere in that it lacked _____. | oxygen p516 |
| The oldest fossils of eukaryotic organisms date back about _____ years ago. | 2.1 billion p516 |
| Multicellular eukaryotic organisms first appeared somewhere between ____ and ____ years ago. | 1.5 to 1.2 billion (The oldest fossils are about 1.2 billion years old, but DNA evidence suggests that they may have existed as far back as 1.5 billion years ago) p517, 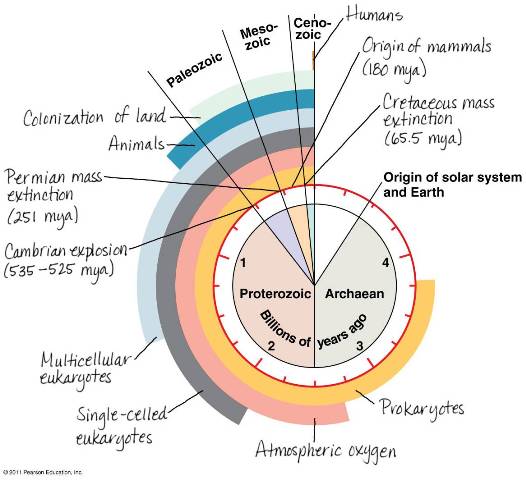 |
| The precursors to the first living cells, called ______ or _____, were droplets with membranes that maintained an internal chemistry different from that of their surrounding. | protocells, vesicles p508 |
| What may have acted as an early catalyst that concentrated organic molecules and increased the rate of vesicle formation? | mineral clays p509 |
| In 1953, ______, created laboratory conditions similar to those hypothesized for early Earth and found that amino acids along with other organic compounds were able to form spontaneously. | Stanley Miller p509,  |
| What type of rocks are most fossils in? | sedimentary p510 |
| The different layers in sedimentary rock are called ____. | strata p510 |
| The early, gradual rise in atmospheric oxygen levels was probably brought about by ancient ______. | cyanobacteria p516 |
| What feature do eukaryotic cells (but not prokaryotic) have that allows them to change shape and, in some cases, engulf other cells? | A cytoskeleton p516 |
| What does the hypothesis of serial endosymbiosis suggest? | Mitochondria evolved before plastids (Since all eukaryotic organisms have mitochondria, but not all have chloroplasts, it makes sense that mitochondria evolved first) p516,  |
| Although multicellular eukaryotes were probably around as far back as 1.5 billion years ago, larger, more complex multicellular organisms didn't appear in the fossil record until about _____ years ago. | 575 million p517 |
| The _____ refers to a relatively brief period of time in geologic history when many present-day phyla of animals first appeared in the fossil record. This burst of evolutionary change occurred about 535 to 525 million years ago and saw the emergence of the first large, hard-bodied animals. | Cambrian Explosion p518 and G-5 |
| The Cambrian explosion refers to a relatively brief period of time in geologic history when many present-day phyla of animals first appeared in the fossil record. This burst of evolutionary change occurred about _____ to ______ years ago and saw the emergence of the first large, hard-bodied animals. | 535 to 525 million years ago p518 and G-5 |
| What caused the major mass extinctions at the end of each era? | DUH!!! (Actually, some scientists, now dead, believed that the extinctions were caused by disruptive global environmental changes, but Chuck took issue with this) p521,  |
| According to the theory of __________, the continents essentially float on the hot underlying portion of the mantle. The continents can move relative to each other in a process called "continental ____." | Plate tectonics, continental drift p519 |
| Periods of evolutionary change in which groups of organisms form many new species whose adaptations allow them to fill vacant ecological niches in their community. | Adaptive radiation (This happened after the extinction of dinosaurs when mammals started filling the vacant predatory roles of dinosaurs) p524 |
| How long ago did dinosaurs go extinct? | 65 million years ago p524 |