| A | B |
|---|
| A type of grouping that excludes some members that share a common ancestor with members that are included in the taxon. | Paraphyletic p543, 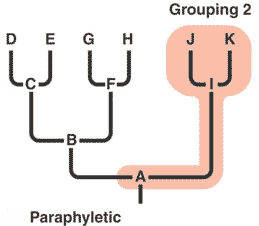 |
| In classification, the taxonomy category above class (less specific than class) is called ______. | phylum p537 |
| ____ is a discipline focused on classifying organisms and determining their evolutionary relationships. | systematics (Taxonomy is very similar to systematics. However, taxonomy doesn't concern itself with determining evolutionary relationships, only with naming organisms, maintaining collections, describing differences, and making sure that two groups of organisms are actually different species) p536 |
| In classification, the taxonomic category above genus (less specific than genus) is called _____. | family p537 |
| An evolutionary timing method based on the observation that at least some regions of the genome evolve at constant rates. | Molecular clock p549 |
| Homologous genes that are found in the same genome due to gene duplication are called _____. | paralogous genes p548,  |
| In classification, the taxonomic category above family (less specific than family) is called _____. | order p537 |
| A type of grouping in which taxa are grouped together without linking them to an ancestral form. | polyphyletic p543, 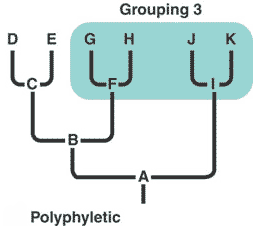 |
| A taxonomic category above the species level, designated by the first word of a species' binomial scientific Latin name. | genus p537 |
| The hypothesis that much of evolutionary change in genes and proteins has no effect on fitness and therefore is not influenced by Darwinian natural selection. | Neutral theory p550 |
| In classification, the taxonomic category above order (less specific than order) is called _____. | class p537 |
| A branching diagram that represents a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships is called a(n) _____. | phylogenetic tree p538 |
| An evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade is called a(n) _____. | shared derived character p543 |
| The taxonomic category above the kingdom level (less specific than kingdom) is called _____. | domain p537 |
| When writing a scientific name, what is capitalized and what font style is used? | Only the first letter of the genus name is capitalized. Italics are used for all letters.37 |
| The scientific name is composed of the organisms ______ name and _____ name. | genus and species name p537 |
| Felis catus and Felis concolour belong to the same ____. | They belong to the same genus, but not species. Since they belong to the same genus, they automatically belong to the same family, order, class, phylum, kingdom and domain also. p537 |
| Put the following terms in order from largest group to smallest as far as the number of species that belong to each: Class, Domain, Family, Genus, Kingdom, Order, Phylum, Species, | Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (Remember the phrase, "Did King Phillips court order fresh grilled salmon?") p537 |
| A genus is composed of a number of related ____. | species p537 |
| Cat is a(n) _______ name that is different from country to country or language to language but Felis catus is a _______ name that is used by all scientists throughout the world. | common, scientific p537 |
| What genus does Ursus maritimus belong in? | Ursus (the first part of a scientific name is always the name of the genus to which the organism belongs) p537 |
| Homo sapien belongs to which species? | sapien (the second name of the scientific name is always the species name to which the organism belongs) p537 |
| The animals Panthera leo (lion) and _____ tigris (tiger) belong to the same genus. | Panthera p537 |
| In biology, an evolutionary innovation is also referred to as a(n) ____. | derived characteristic (for example, feathers were an evolutionary innovation that set feathered dinosaurs, and later, birds, apart from all other reptiles. Therefore feathers are a type of derived characteristic that today would only be seen in birds and not other animals) p543 |
| ______ is the evolutionary history of a species or group of related species. | Phylogeny p536 |
| Similarity between two species that is due to convergent evolution rather than to descent from a common ancestor with the same trait is called _____. | analogy p540 |
| The principle of _____ states that when considering multiple explanations for an observation, one should first investigate the simplest explanation that is consistent with the facts. | maximum parsimony p544 |
| A type of grouping in which the taxon includes all species derived from a single ancestral species. | Monophyletic p543, 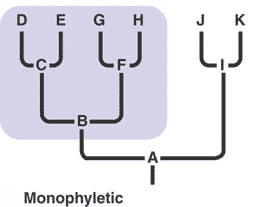 |
| Another word for an analogous structure is a(n) _______. | homoplasy p541 |
| Another word for a homoplasy is a(n) ______. | analogous structure p541 |
| A group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants is called a(n) _____. | clade p542 |
| Similarity in characteristics resulting from a shared ancestry is called ____. | homology (Homologies can be broken into both molecular and morphological homologies) p540 |
| Homologous genes that are passed in a straight line from one generation to the next, but have ended up in different gene pools because of speciation are called ______. | orthologous genes p548,  |
| The comparison of nucleic acids or other molecules in different species to infer relatedness. | molecular systematics p542 |
| The branch of biology concerned with naming and classifying the diverse forms of life is called _____. | taxonomy p537 |
| The second broadest taxonomic category after domain is called _____. | kingdom p537 |
| The principle of _______ states that when considering multiple phylogenetic hypotheses, one should take into account the one that reflects the most likely sequence of evolutionary events, given certain rules about how DNA changes over time. | maximum likelihood p545 |
| Groups of organisms that share an immediate common ancestor (and are therefore each other's closest relatives, are considered to be in _____ taxa. | sisters p538, 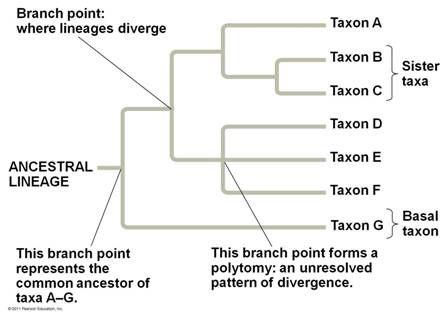 |
| The points where lineages diverge in a phylogenetic tree are called ____ points. | branch p538,  |
| _____ refers to a lineage that diverges early in the history of a group, and hence, lies on a branch that originates near the common ancestor of the entire group. | Basal taxon p539,  |
| A(n) _____ is a branch point in a phylogenetic tree in which more than two descendant groups emerge, signifying that evolutionary relationships among the taxa are not yet clear. | polytomy p539,  |
| Similarities in structure due to similar natural selection pressures instead of common ancestry are called analogies and are due to ______ evolution. | convergent p540,  |
| Homologies (phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared ancestry) may look quite different from each other due to ____ evolution. | divergent p540 |
| An approach to systematics in which organisms are placed into groups called clades based primarily on common descent. | cladistics G-7, p542 |
| A character, shared by members of a particular clade, that originated in an ancestor that is NOT a member of that clade. | shared ancestral character (For example, a backbone is a shared ancestral character of all mammals, but is not a shared derived character because it is found in lineages that predate the divergence of mammals, like fish) p543 |
| A species or group of species from an evolutionary lineage that is known to have diverged before the lineage that contains the group of species being studied. This group is selected so that its members are closely related to the group of species being studied, but not as closely related as any study group members are to each other. | outgroup p543, G-25 |
| A species or group of species whose evolutionary relationships we seek to determine. | ingroup p543, G-18 |
| Different genes evolve at different rates. DNA that changes slowly, like ______, is useful for investigating relationships between taxa that diverged hundreds of million of years ago, like the relationship of animals and fungi. In contrast, _____ evolves rapidly, and can be used to explore recent evolutionary events, like the relationships between different races of humans. | The DNA that codes for ribosomal RNA (rRNA), mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) p548 |
| Name the three domains and label each as being either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. | Archaea (prokaryotic), Bacteria (prokaryotic), Eukarya (eukaryotic) pp551&552 |
| Which prokaryotic domain seems to be most closely related to the Eukarya based on molecular studies? | Archaea (Analysis of other genes however suggest that the domain bacteria might be more closely related to Eukarya. For example, genes that influence metabolism in yeast are more similar to those in the domain Bacteria. To further complicate matters, horizontal gene transfer between domains early on make it difficult to know where genes originated from) p552 |
| From which domain are chloroplasts and mitochondria thought to have originated from? | Bacteria p552 |
| _____ is the process by which genes are transferred from one genome to another through mechanisms such as viral infection, exchange of transposable elements or plasmids, and perhaps even the fusion of organisms. | Horizontal gene transfer (It appears that there may have been horizontal gene transfer between bacteria and early eukaryotic organisms) p553 |