| A | B |
|---|
Lewis and Clark,  | Explored the Louisana Purchase territory |
Louisiana Purchase, 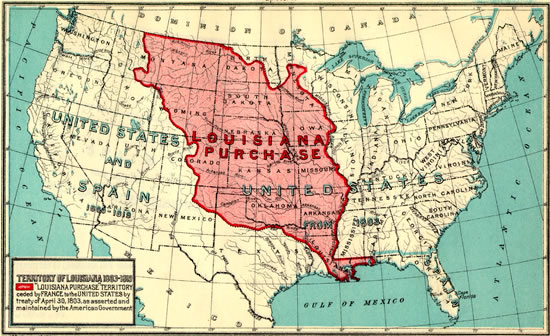 | Thomas Jefferson purchased this area from France doubling the size of the USA |
Sacagawea,  | Was a guide and translator for Lewis and clark |
The Trail of Tears,  | Thousands of Cherokee Indians died while being moved to Oklahoma |
Nullification Crisis,  | When South Carolina said said states could void the tariff of 1832 & acts of Congress |
The Monroe Doctrine, 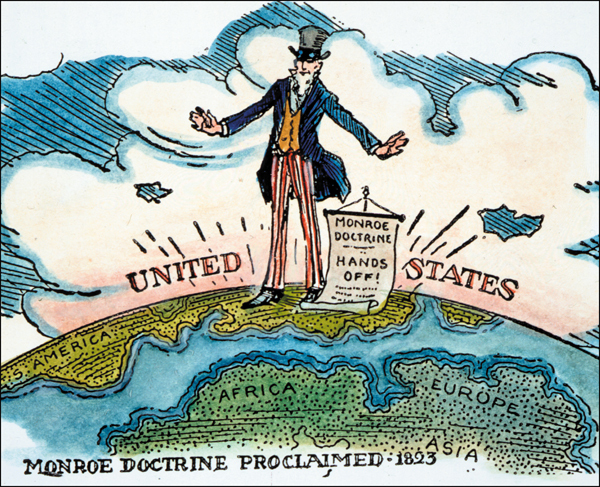 | Stated that the Americas were not open to European colonization. |
Missouri Compromise,  | east/west line in Louisiana territory that banned slavery north of line and allowed it south of it |
Nat Turner & Gabriel Prosser,  | Led slave rebellions in Virginia |
The Seneca Falls Declaration,  | Statement that women should have the same rights as men |
Republic of Texas, 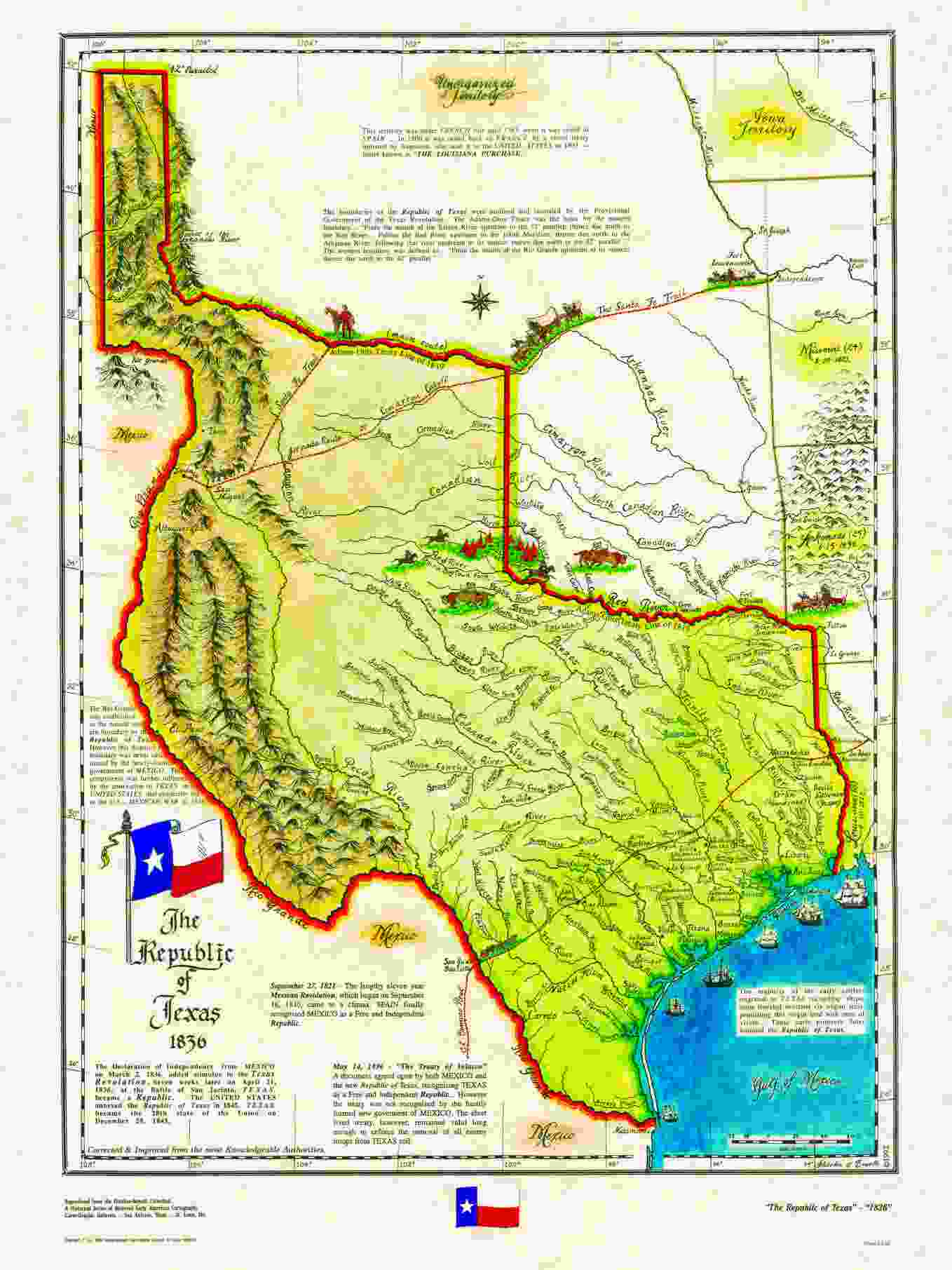 | Won independence from Mexico and joined the USA in 1845 |
The Alamo,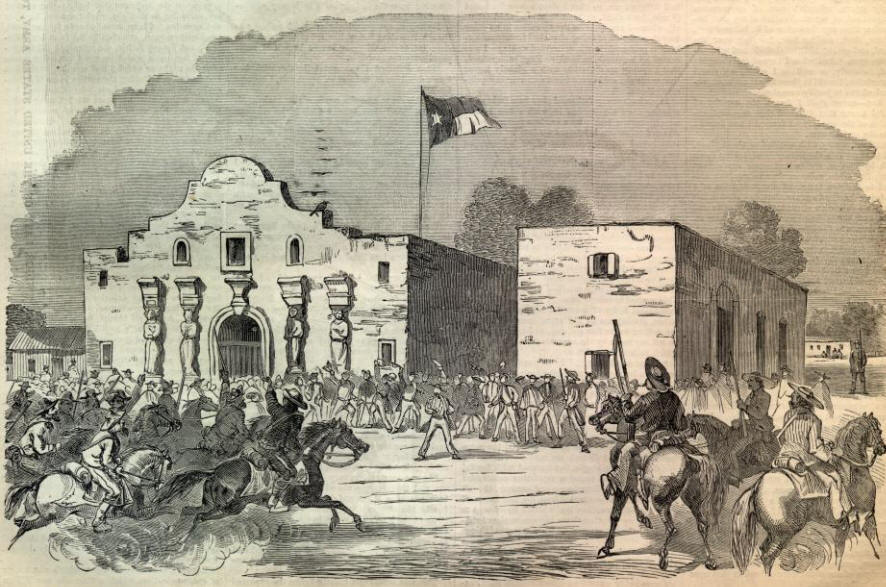  | 183 Texans fought to the last man here |
Oregon Territory, 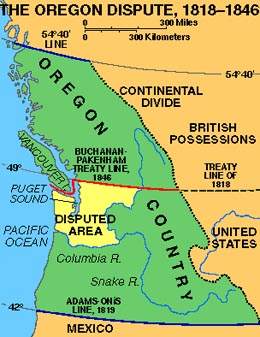 | The US acheived a land claim there after the War of 1812 |
Florida, 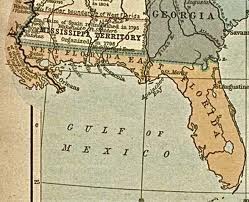 | The US puchased this territory from Spain after the War of 1812 |
Andrew Jackson,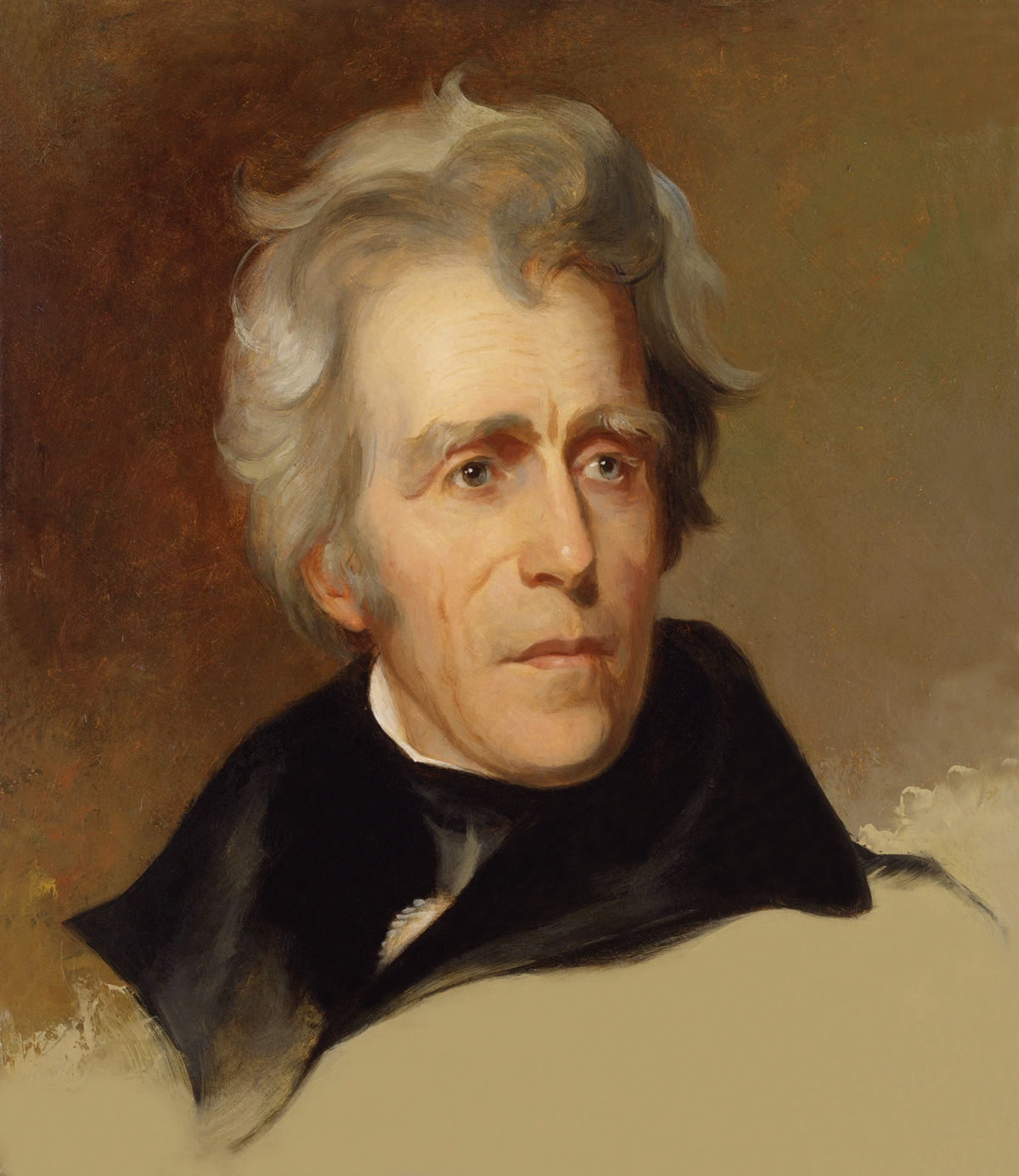  | President that personified the democratic spirit of the time and who challenged the eoncomic elite |
Mexican-American War, 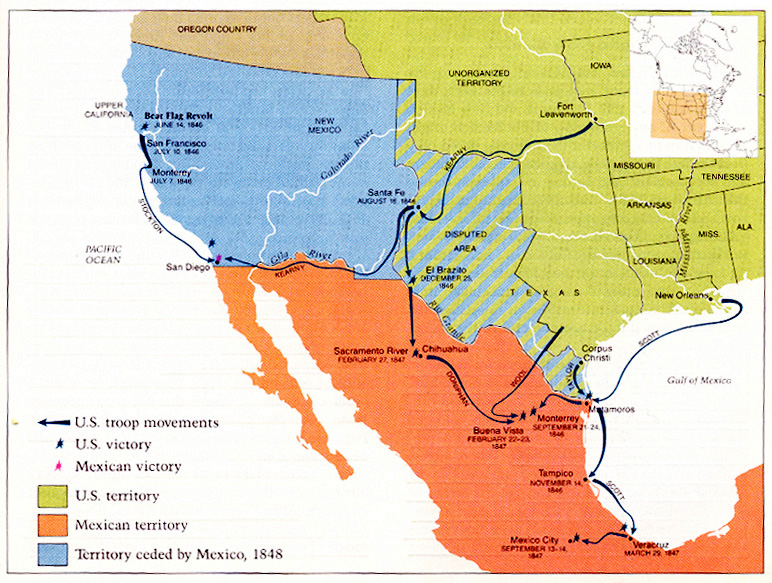 | Resulted in California, Utah, Nevada, Arizona, Colorado and NM coming into the USA |
the spoils system,  | the process of rewarding political supports with jobs after an election win |
cotton,  | the main cash crop of the South |
the Election of 1800, 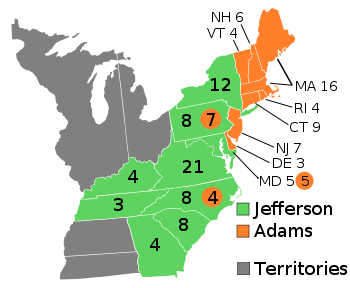 | First peaceful transfer of political power between parties in the US |
War of 1812,  | British interference with US trade and migration caused it. |
McCulloch v. Maryland,  | The Supreme Court affirmed that Congress had Implied Powers |
Marbury v. Madison,  | Judicial Review for the Supreme Court |
Gibbons v. Ogden,  | Broad national view of the economy through the commerce clause |
Hartford Convention,  | Federalists threaten to secede over War of 1812 |
Manifest Destiny,  | Belief that USA should stretch from Atlantic to Pacific |
Elizabeth C. Stanton,  | Involved in the women's suffrage movement before the Civil War |
Jay Treaty,  | US trade and territorial agreement with England opposed by Democrat Republicans |
France,  | Naval battles with this country were opposed by Democrat Republicans |
Bank of the USA,  | Powerful financial institution opposed by Democrat Republicans |
Know Nothing Party,  | new political party that was anti-immigrant |
Whig Party,  | New political party that opposed Andrew Jackson |
Reservations, 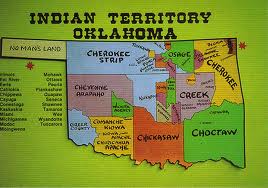 | Many Native-Americans were forced to live on these |
Democrat-Republican Party,  | Suported in the South by farmers, artisans and frontier settlers |
Federalist Party,  | Had support in the Northeast among bankers and business interests |
Thomas Jefferson,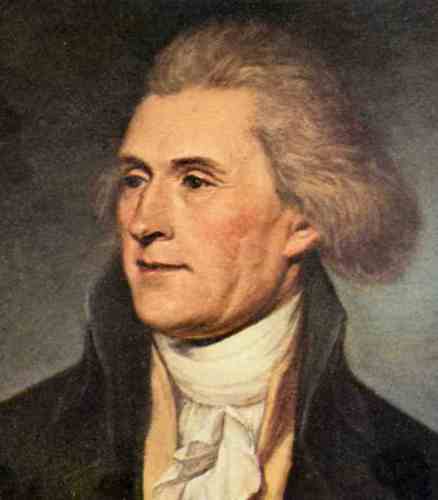  | Founder of the Democrat-Republican Party and won the election of 1800 |
John Adams,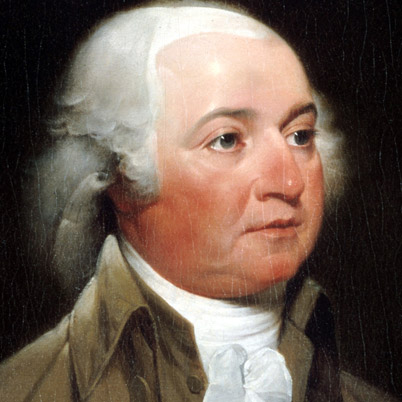  | Federalist and became President after George Washington left office |
Alexander Hamilton,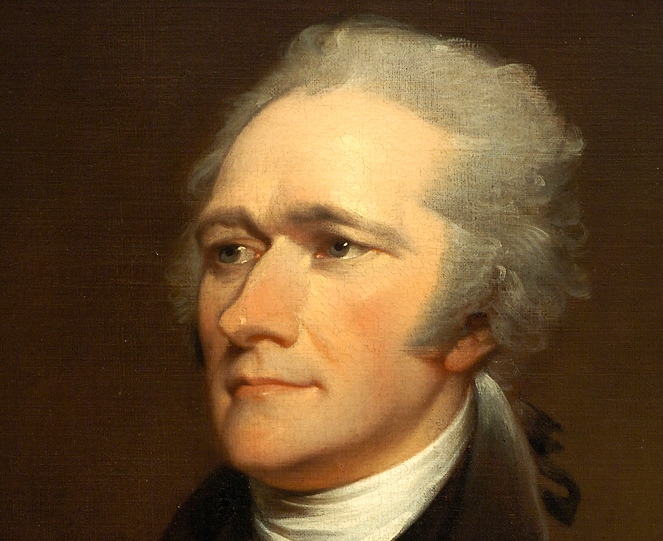  | Federalist and creator of the National Bank of the USA |
James Madison,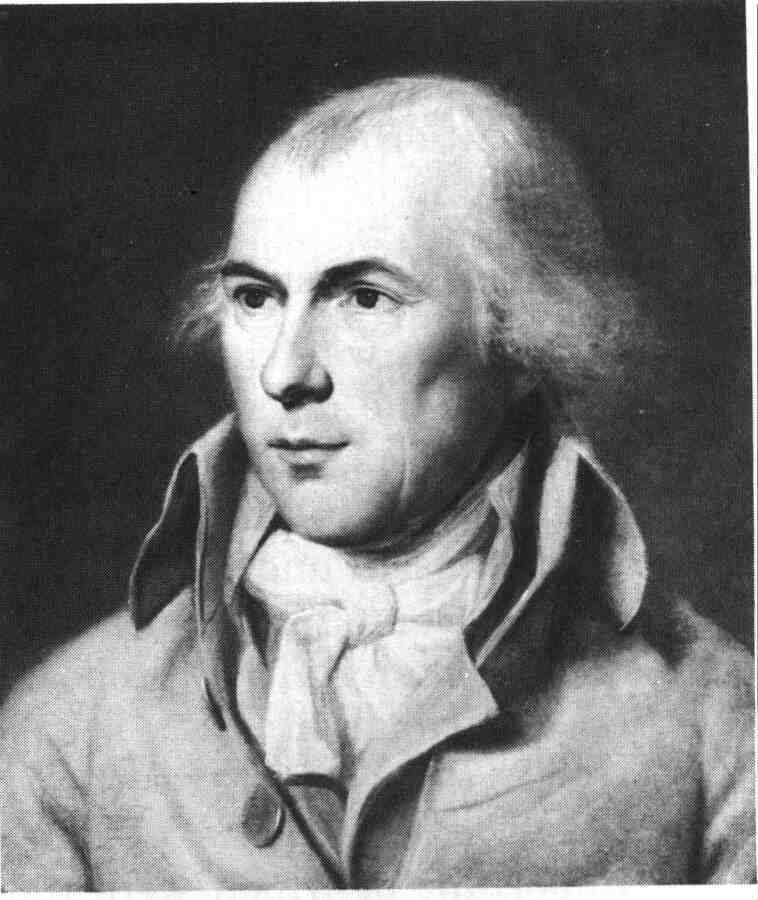  | Democrat-Repbublican leader and President during the War of 1812 |
the North, 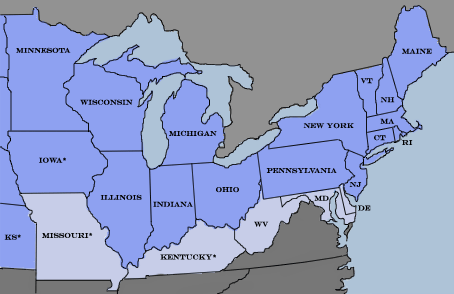 | favored high tariffs to protect norhern manufactured goods from foriegn competition |
the South, 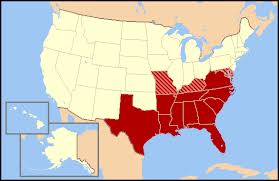 | favored low tariffs because they made imported goods more expensive |
Missouri, 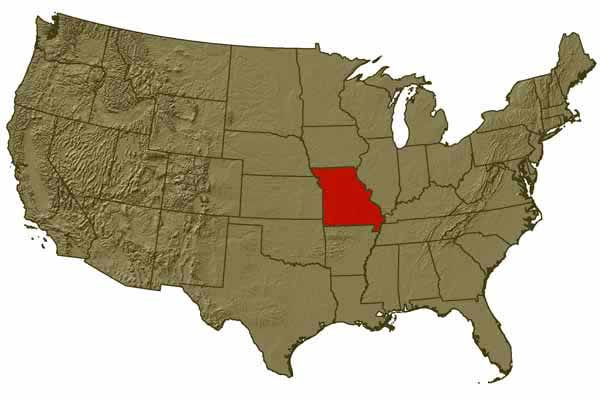 | this state became a slave state under the Missouri compromise |
Railroads & Canals,  | helped settlers move west & supported the new industrial economy |
Age of Common Man,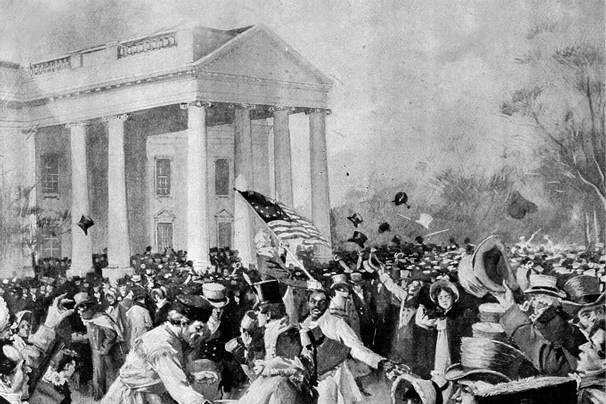  | More voter participation; new campaigning syle; more equality in political process |
Sectionalism,  | a period in which regional self-interests caused a number of national crises |