| A | B |
|---|
| 3 most common forms of energy | Heat, light, and electricity |
| Hydrocarbons (def) | Organic fuels that contain carbon & hydrogen |
| Fossil Fuels (ex.) | Coal, Natural Gas, Oil |
| Fossil Fuels (def) | Organic fuel made from the remains of plants & animals |
| Location of Neutron in atom | Nucleus |
| Location of Proton in atom | Nucleus |
| Location of Electron in atom | Outside Nucleus |
| Charge of Neutron | Neutral |
| Charge of Proton | Positive |
| Charge of Electron | Negative |
| Peat (def) | First stage in the formation of coal |
| Petroleum (def) | Liquid Fossil fuels |
| Bioconversion (def) | The conversion or processing of organic materials into fuels |
| Bituminous coal (def) | 3rd step in coal formation, must be mined, most abundant form of coal in USA |
| Lignite (def) | 2nd step in the formation of coal; must be mined; burns smokey & does not release a lot of energy |
| Natural gas (def) | Cleanest burning fossil fuel, usually a mixture of methane, ethane, propane, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium |
| Biomass fuels (def) | A fuel formed from the products of recently living organisms |
| Biomass fuel ex. | Wood, methane, garbage, alcohol |
| Ion (def) | Charged atom; formed by gaining or losing electrons |
| Isotope (def) | Formed when there is a change in the number of neutrons in an atom |
| What happens if the # of protons are changed in an atom? | Atom forms a different element |
How many protons and neutrons does Uranium have. Use the image,  | 92 Protons & 146 Neutrons (Atomic # = protons & Mass # - Atomic # = neutrons |
| First scientist to use the word radioactivity to describe an element and won a Noble Prize for their work with these types of elements | Marie Curie |
| The biological activities that occur within the cells of organisms give rise to various __? | Chains of hydrocarbons |
| Type of radiation that is a form of electromagnetic energy | Gamma particles |
| A mixture of 90 percent gasoline to I0 percent ethanol | Gasohol |
| Type of radiation made up of two protons and two neutrons | Alpha particles |
| Location of an ocean thermal energy conversion system, or OTEC | Keyhole Pt. Hawaii |
| Renewable Resource (def) | resource replaced in nature as fast or faster than it is used |
| Nonrenewable Resource (def) | resource that exists in a fixed amount and is used up faster than it is replaced |
| Examples of Renewable Resources | Oxygen, Solar Energy, Carbon Dioxide |
| Examples of Nonrenewable Resources | All Metals, Sand, Gravel, Sulfur |
| Respiration (def) | Process by which oxygen is combined with food molecules to produce energy |
| Pollution (def) | Process that occurs when some part of the environment is changed in a way that makes it unfit for human, plant, or animal use |
| Pollutant (def) | Component or new chemical added to something to the point it causes harm |
| 7 Important Nonmetals | Sand, Gravel, Building Stone, Rock Salt, Talc, Graphite, Gypsum |
| The 4 R's of Conservation | Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Respond |
| Coal (def) | An organic Sedimentary rock; solid fossil fuel |
| 4 Steps in the formation series of Coal | Peat, Lignite, Bituminous Coal, Anthracite Coal |
| Type of Coal with the highest % of Carbon | Anthracite |
| Step of Coal formation that produces the most smoke | Peat |
| Does coal burn cleaner or with more smoke if there is a higher % of Carbon in the Coal | Cleaner |
| 4 Examples of Hydrocarbons | Gasoline, Diesel Fuel, Propane, Motor Oil |
| Oil Trap (def) | Impermeable layer of Shale above sandstone. The sandstone has petroleum in it. |
| Order of Oil, Water, & Natural Gas in an oil trap from bottom to top | Water, Oil, Natural Gas |
| 4 Alternative Energy Sources | Solar, Hydroelectric, Wind, Geothermal |
| Photo (def) | Light |
| Voltaic (def) | Electricity |
| Photon (def) | Light particle |
| Silicon (def) | The element that makes up the greatest % of a solar cell |
| Phosphorus (def) | Sprayed to create the negative side of a solar cell |
| Boron (def) | The element that causes part of a solar cell to have a positive charge |
| Static Electricity (def) | Involves electrons that are moved from one place to another usually by rubbing or brushing a nonconductor |
| Direct Current (def) | Current that directly flows through a conductor, such as a metal wire. |
| Alternating Current (def) | A back-and-forth movement of electrons in a wire, |
| Island in the Atlantic known for its use of Geothermal Energy | Iceland |
| Type of windmill that is slower & looks like an upside down egg beater | Darius |
| Drawbacks to to solar & geothermal power | Equipment is expensive, supply is not available all the time, everywhere |
| Albedo (def) | Reflectivity of a surface |
| Permeable (def) | allows water through it |
| Impermeable (def) | does not allow water through it |
The diagram represents the present number of decayed and undecayed atoms in a sample that was originally 100% radioactive material. If the half-life of the radioactive material is 1,000 years, what is the age of the sample represented by the diagram?, 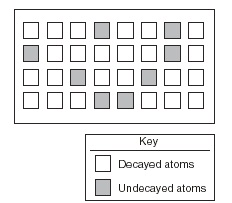 | 2,000 years (2 half lives),  |
| On the diagram, shade in the amount of stable decay element present after the second half-life period. | 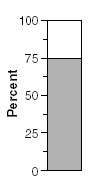 |