| A | B |
|---|
| 3 most common forms of energy | Heat, light, and electricity |
| Hydrocarbons (def) | Organic fuels that contain carbon & hydrogen |
| Fossil Fuels (ex.) | Coal, Natural Gas, Oil |
| Fossil Fuels (def) | Organic fuel made from the remains of plants & animals |
| Location of Neutron in atom | Nucleus |
| Location of Proton in atom | Nucleus |
| Location of Electron in atom | Outside Nucleus |
| Charge of Neutron | Neutral |
| Charge of Proton | Positive |
| Charge of Electron | Negative |
| Peat (def) | First stage in the formation of coal |
| Petroleum (def) | Liquid Fossil fuels |
| Bioconversion (def) | The conversion or processing of organic materials into fuels |
| Bituminous coal (def) | 3rd step in coal formation, must be mined, most abundant form of coal in USA |
| Lignite (def) | 2nd step in the formation of coal; must be mined; burns smokey & does not release a lot of energy |
| Natural gas (def) | Cleanest burning fossil fuel, usually a mixture of methane, ethane, propane, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium |
| Biomass fuels (def) | A fuel formed from the products of recently living organisms |
| Biomass fuel ex. | Wood, methane, garbage, alcohol |
| Ion (def) | Charged atom; formed by gaining or losing electrons |
| Isotope (def) | Formed when there is a change in the number of neutrons in an atom |
| What happens if the # of protons are changed in an atom? | Atom forms a different element |
How many protons and neutrons does Aluminum have. Use the image, 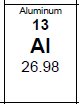 | 13 Protons & 14 Neutrons (Atomic # = protons & Mass # - Atomic # = neutrons |
| Type of radiation that is a form of electromagnetic energy | Gamma particles |
| A mixture of 90 percent gasoline to 10 percent ethanol | Gasohol |
| Type of radiation made up of two protons and two neutrons | Alpha particles |
| Simple formula for nuclear fusion | H +H = He + Energy |
| % of atmosphere that is Nitrogen | 78% |
| % of atmosphere that is Oxygen | 21% |
| albedo | % of energy that is reflected without being changed |
| Where most of the water on Earth is found | Oceans |
| Where most of the freshwater on Earth is found | Frozen in Glaciers & Icecaps |
| #1 Source of Useable Fresh Water | Groundwater |
| Water Cycle Synonym | Hydrologic Cycle |
| Water Cycle (def) | The movement of water from one part of the hydrosphere to another |
| Precipitation (def) | Any form of moisture falling from the sky |
| Condensation (def) | Process in which water going from the gas phase to the liquid |
| Precipitation Examples | Rain, Sleet, Snow, Hail, Freezing Rain |
| Evaporation (def) | Process in which liquid water changes to water vapor |
| Cause of Evaporation | Increase in Heat or Decrease in Pressure |
| Cause of Condensation | Decrease in Heat or Increase in Pressure |
| Evapotranspiration (def) | Process by which water is added to the atmosphere from bodies of water, land & plants |
| Deficit (def) | When the need for water is greater than the rain fall & the soil water storage is gone |
| Deficit Synonym | Drought |
| Surplus (def) | When rain fall is greater than the need & soil water storage is filled |
| Surplus Synonym | Flooding |
| Recharge (def) | The filling of the ground water supply by precipitation |
| Runoff (def) | Water that flows over land because the soil storage is full & can not absorb anymore water |
| Respiration (def) | Process by which oxygen is combined with food molecules to produce energy |
| Photosynthesis (def) | Process by which plants use light to convert carbon dioxide & water into sugars & oxygen |
| Formula for Methane | CH4 |
| Formula for Nitrates | NO3- |
| Formula for Nitrites | NO2- |
| Formula for Carbon Dioxide | CO2 |
| Formula for Glucose | C6H12O6 |
| Products of Photosynthesis | O2 & Food (glucose) |
| Reactants of Photosynthesis | CO2, H2O & sunlight |
| Products of Respiration | CO2, H2O & energy |
| Reactants of Respiration | O2 & Food (glucose) |
| Building block of proteins | Amino acids |
| Organic building block of life | Carbon |
| Important elemental component of amino acids | Nitrogen |
| Lithification (def) | The hardening of sediments into rock |
| Biogeochemical Cycles | Flow of chemical elements & compounds between living organisms & the physical environment |
| 2 nutrients that cause Eutrophication | Nitrogen & Phosphorus |
| 4 processes that return Carbon Dioxide to the atmosphere | Respiration, Burning & Decay, Weathering & Erosion, Volcanism |
| Element being used to make food by chemosynthetic organisms that live by black smokers | Sulfur |
| Examples of impermeable rocks | Shale, Granite, & Basalt |
| Living thing that fixes nitrogen in the roots of legumes | Bacteria |
| Name 4 greenhouse gases | CO2, CH4, CFC's, H2O, NO2 |
| 2 compounds that contribute to acid rain | Nitrogen oxides NO2 & Sulfur Oxides SO2 |
| The process by which a body of water acquires a high concentration of nutrients | Eutrophication |
| Biogeochemical Cycle that does not cycle into the atmosphere | Phosphorus |
| Slowest biogeochemical cycle | Phosphorus |
| 3 ways humans alter the water cycle | Withdrawing large amounts of freshwater, clearing vegetation and eroding soils, polluting surface and underground water, & contributing to climate change |
| 3 things biogeochemical cycles do | Regulate nutrients, Influence climate stability, & Influence the purity of drinking water |
| Ways humans alter the Nitrogen cycle | Adding gases that contribute to acid rain, Contaminating ground water from nitrate ions in inorganic fertilizers, Adding nitrous oxide to the atmosphere through farming practices which can warm the atmosphere and deplete ozone, & Releasing nitrogen into the troposphere through deforestation |
| Effects of increased Nitrogen | Loss of soil nutrients, Acidification of rivers and lakes, & Increases nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere |
| Energy source that drives winds & waves | Sun |
| Energy sources that drives the water cycle | Sun |
| Energy source that drives weathering | Sun |
| Energy source that drives Earth's plates | Geothermal |
| Energy source that powers volcanoes, earthquakes, & the rock cycle | Geothermal |
| Energy source that slows Earth's rotation | Tidal energy |
| Year the Clean Water Act was signed into law. | 1972 |
| Frac Act (def) | Act that would repeal the exemption of hydraulic fracturing in the Safe Water Drinking Act |
| True or False: A well can be fracked multiple times | True |
| 3 Health consequences people of Garfield County have suffered after fracking occurred in their area | Faintness, Loss of smell & Brain Lesions |
| Carbon Sink (def) | a reservoir that accumulates and stores some carbon-containing chemical compound for an indefinite period Ex. Ocean |
| Pollution (def) | Process that occurs when some part of the environment is changed in a way that makes it unfit for human, plant, or animal use |
| Coal (def) | An organic Sedimentary rock; solid fossil fuel |
Oil Trap (def), 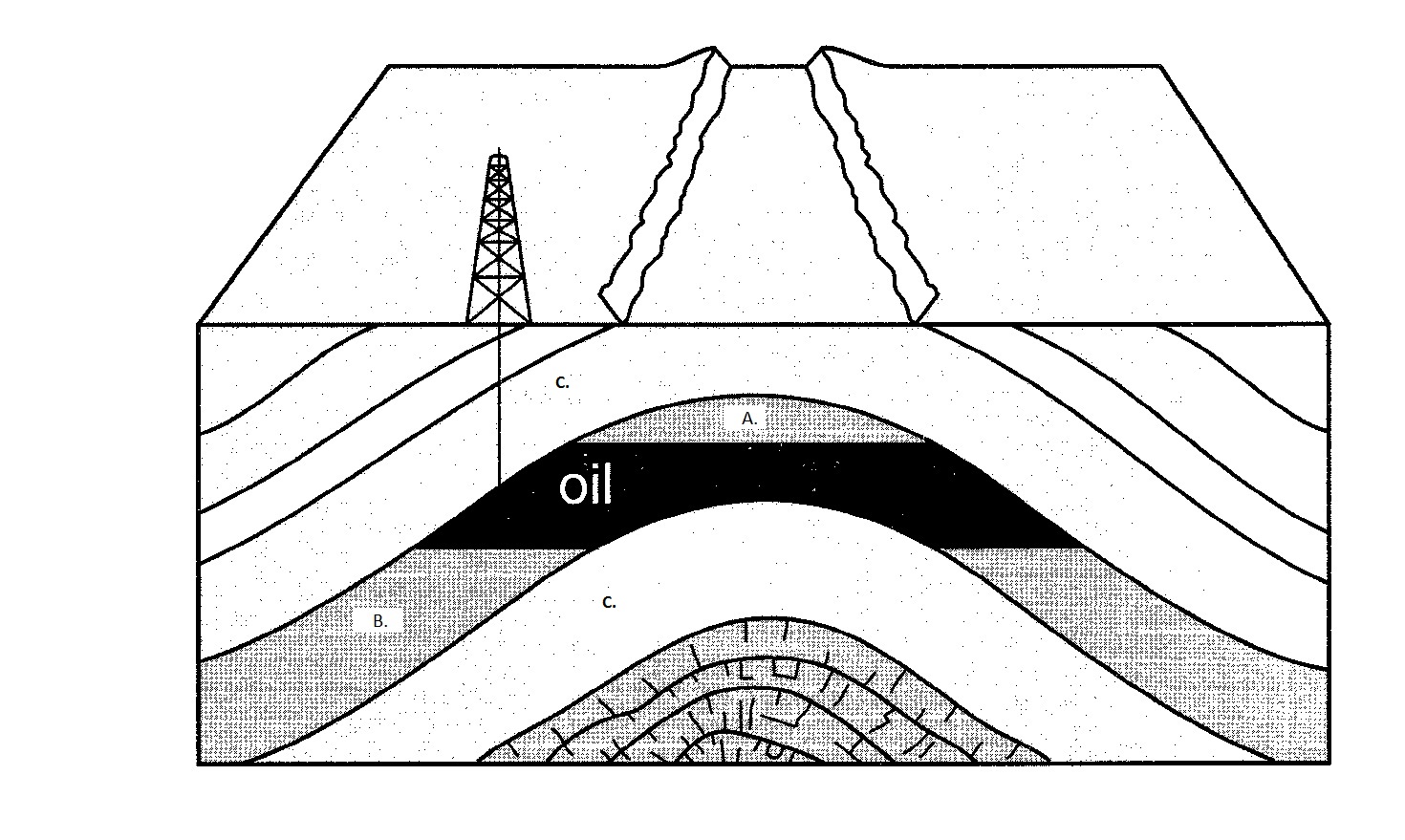 | Both letter C's are the impermeable layers of Shale above & below the sandstone. The sandstone is permeable & has Natural Gas (A), petroleum (oil) & Water (B) in it. |
| Order of Oil, Water, & Natural Gas in an oil trap from bottom to top | Water, Oil, Natural Gas |
| Photo voltaic cell (def) | Solar cell that creates electricity from sunlight (Ex. Active Solar) |
| Type of windmill that is slower & looks like an upside down egg beater | Darius |
| Drawbacks to to solar & geothermal power | Equipment is expensive, supply is not available all the time, everywhere |
| Permeable (def) | allows water through it |
| Impermeable (def) | does not allow water through it |
The diagram represents the present number of decayed and undecayed atoms in a sample that was originally 100% radioactive material. If the half-life of the radioactive material is 1,000 years, what is the age of the sample represented by the diagram?, 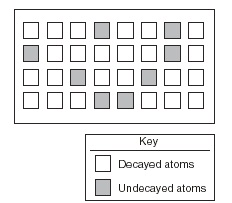 | 2,000 years (2 half lives) |
| On the diagram, shade in the amount of stable decay element present after the second half-life period. | 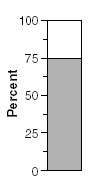 |
| Two processes that remove Carbon Dioxide from the atmosphere | Photosynthesis & Absorption by the oceans |
| What issue occurs with storing toxic chemicals in metal drums for long periods of time? | The metal drums corrode |
| Name 3 plants that contain nitrogen fixing bacteria | Clover, Beans, Legumes |
| EPA stands for: | Environmental Protection Agency |
| What fuel is very abundant & the fuel of Nuclear Fusion | Hydrogen |
| List 3 environmental impacts of windmills | Increased evaporation of soil moisture under windmills, impact on bird migration, changes in air pressure that effects bats. |
| Thermal pollution (def) | Decrease in water quality due to a change in water temperture (Nuclear Power plants contrubute to this) |
| Greenhouse gas that contributes the most to global warming | CO2 |