| A | B |
|---|
| What are the building blocks of all matter? | atoms p. 33 |
| The nucleus of an atom is made up of ____ and ____ | protons and neutrons p. 33 |
| Electrons have a ___ charge | negative p. 33 |
| Protons have a ___ charge | positive p. 33 |
| Neutrons have a ___ charge | neutral (no) charge p. 33 |
| Which type of sub-atomic particle orbits the nucleus? | electrons p. 33 |
| Positive charges are attracted to ____ charges | negative p. 33 |
| Positive charges are repelled by ____ charges. | positive p. 33 |
| Negative charges are repelled by ____ charges | negative p. 33 |
| An electron would be attracted to which type of sub-atomic particle? | proton p. 33 |
| The center region of an atom is called a(n) ____. | atomic nucleus p. 33 |
| All of the elements are listed in the ____. | periodic table p. 36 and appendix B |
| The ____ is equal to the number of protons in an atom. | atomic number p. 33 |
| The number of protons + the number of neutrons is equal to the ____ | mass number p. 33 |
| The mass number is equal to the | number of protons and neutrons p. 33 |
| The atomic number is equal to the number of ____ in an atom | protons p. 33 |
| The number below the chemical symbol on the periodic table that usually has a few decimal places is known as the ____. | average atomic mass p. 34 |
| If an element has a mass # of 23 and an atomic # of 11, how many protons will it have? Neutrons? | 11 protons and 12 neutrons p. 33 |
| Two or more different elements bond together to form ____. | compounds p. 31 |
| A compound held together by covalent bonds is called a(n) ___. | molecule p. 38 |
| Atoms or molecules that become charged because they gain or lose electrons are called ___. | ions p. 40 |
| A negatively charged ion would be ____ by another negatively charged ion. | repelled p. 40 |
| A positively charged ion would be ____ by another positively charged ion. | repelled p. 40 |
| A negatively charged ion would be ___ by a positively charged ion. | attracted p. 40 |
| Matter is _____. | Anything that takes up space and has mass. p. 31 |
| _____ is anything that takes up space and has mass. | Matter p. 31 |
| A(n) ______ is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions. | element p. 31 |
| A compound in which atoms are joined together by ionic bonds is called a(n) ___. | ionic compound p. 40 |
| A(n) ___ is the smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of an element. | atom p. G3 |
| The tiny bits of matter that make up an atom are called ___. | sub-atomic particles p. 33 |
| Isotopes of a certain element have the same number of ____ but differ in the number of _____. | protons, neutrons p. 34 |
| Elements that differ from each other because of the number neutrons, but not protons, are called ____. | isotopes p. 34 |
| _____ is defined as the capacity to cause change. | Energy p. 35 |
| In _____ bonds, pairs of electrons are shared between two or more atoms. | covalent p. 38 |
| Bonds in which electrons aren't shared at all (because one atom has a MUCH higher electronegativity than the other) are called ______. | ionic bonds p. 40 |
| A charged atom, (or molecule) is called a(n) ___. | ion p. 40 |
| Compounds formed by ionic bonds are called ____ . | ionic compounds p. 40 |
| The most important characteristic about a biological molecule is its ____. | shape p. 42 |
In the chemical reaction picture below, the molecules on the left side of arrow are called the ____ while the molecules on the right side of the arrow are called the ____., 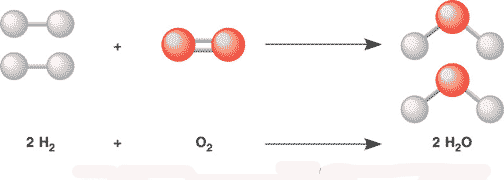 | reactants, products (notice how there are the same number of each type of atom on both sides of this balanced chemical reaction),  |
What type of molecule is this?, 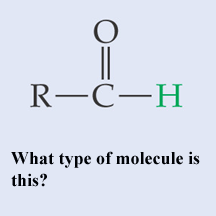 | A basic aldehyde pp64&65,  |
What type of molecule is this?,  | carboxylic-acid pp64&65,  |
What type of molecule is this?, -copy.gif) | aldehyde (hexanal) pp64&65, -copy.gif) |
What type of molecule is this?, .gif) | ketone (2-butanone) pp64&65, .gif) |
What type of molecule is this?, 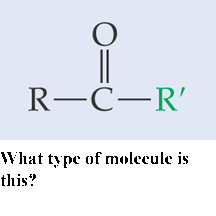 | Ketone pp64&65, 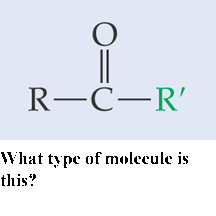 |
| What is the molecular formula and shape of benzene? | C6H6, ring p61 |
| One of several organic compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures, and therefore, different properties. | isomer p62 |
| A functional group present in organic acids consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. | carboxyl group pp64&65,  |
| A functional group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (--SH). | sulfhydryl group pp64&65,  |
| A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. It can act as a base in a solution, accepting a hydrogen ion and acquiring a charge of +1. | amino group pp64&65, 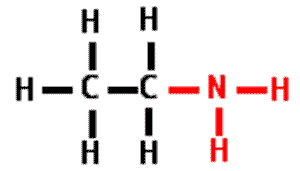 |
| An organic molecule consisting only of carbon and hydrogen is called a(n) _____. | hydrocarbon (the butane molecule below is a hydrocarbon because it has only hydrogens and carbons) p61, 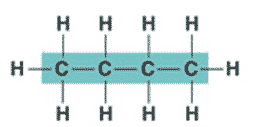 |
| An arrangement of two non-carbon atoms, each bound to one of the carbons in a carbon-carbon double bond,where the two non-carbon atoms are on the same side relative to the double bond. | cis p62, 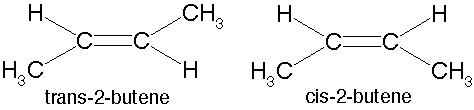 |
| An arrangement of two non-carbon atoms, each bound to one of the carbons in a carbon-carbon double bond,where the two non carbon atoms are opposite sides relative to the double bond. | trans p62, 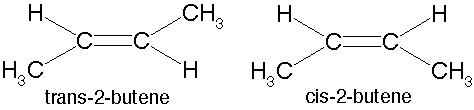 |
| A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeleton of organic molecules and usually involved in chemical reactions. | functional group (the carboxyl-group in red below is a functional group that makes the molecule acidic because it often loses the hydrogen as a hydrogen ion into the solution which lowers the pH of the solution) p63,  |
| A type of isomer in which carbons have covalent bonds to the same atoms, but these atoms differ in their spatial arrangements due to the inflexibility of carbon-carbon double bonds. | Cis-trans isomers (a.k.a. geometric isomer) p62, 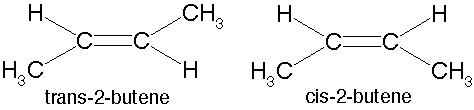 |
| A functional group that is important in energy transfer. | Phosphate group (think of ATP-->ADP + P + energy) p66, 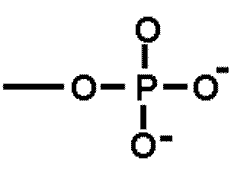 |
| One of several organic compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms. | structural isomer p62, 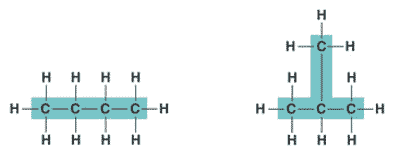 |
| A functional group present in aldehydes and ketones that consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom. | carbonyl group pp64&65, 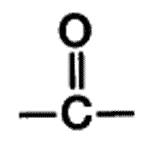 |
| A functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom joined to an oxygen atom by a polar covalent bond. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water and are called alcohols. | hydroxyl group pp64&65,  |
| One of two molecules that are mirror images of each other. | enantiomer (also called a stereo-isomer) p62, 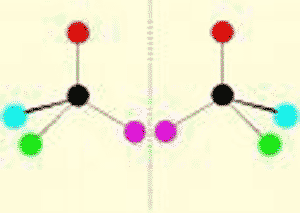 |
What type of molecule is this?,  | An aldehyde (It's an aldehyde because the carbonyl group is coming off a terminal carbon. If it wasn't, it would be a ketone. The name of this molecule is ethanal, since it has two carbons like ethane) pp64&65,  |
What is the name of the functional group in red?,  | amino group pp64&65,  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | carbonyl group pp64&65,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?, 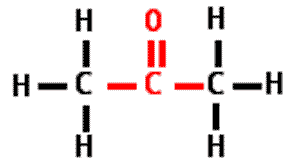 | ketone, carbonyl group (The specific name of the molecule pictured is propanone because it is a ketone with 3 carbons like propane) pp64&65,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?,  | Carboxylic acid, carboxyl group (This molecule is called ethanoic acid but is more commonly referred to as acetic acid which is the acid in vineger) pp64&65,  |
What is the name of this molecule?, 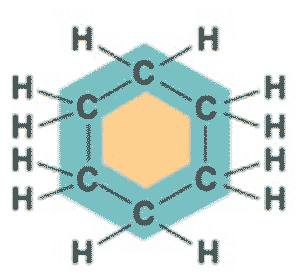 | cyclohexane p61,  |
What do we call these two molecules?,  | enantiomers (or stereoisomers; notice that they are mirror images of each other) p62,  |
What type of isomers are these?, 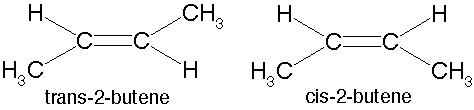 | cis-trans isomers (a.k.a. geometric isomers) p62, 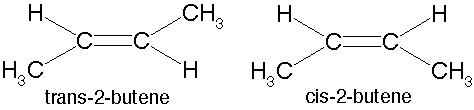 |
Which of these cis-trans isomers would be considered the "cis" isomer and which would be the "trans" isomer?,  | The one on the left is "cis" and the one on the right is "trans" (the prefix trans means across) p62,  |
What is the name of this type of molecule and what is the name of its functional group?,  | An alcohol, hydroxyl group (This is ethanol because it has two carbons like ethane. The common name is ethyl alcohol) p64&65,  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | phosphate group p64&65,  |
What type of isomers are these?,  | structural isomers p62,  |
What is the name of this functional group?,  | Sulfhydryl group p64&65,  |
| Carbon can form a wide variety of compounds because it forms ____ covalent bonds. | 4 (p60) |
Each line in a structural formula (like the one below) represents a _____., 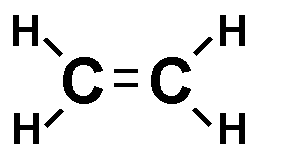 | pair of shared electrons, 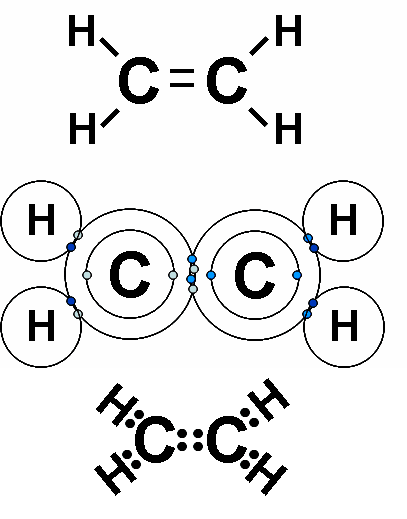 |
| ____ is the source of carbon for all of the organic molecules found in organisms. | carbon dioxide p58 |
| An important energy storing molecule that has 3 phosphate groups is called _____. | Adenosine tri-phosphate (ATP) p66, 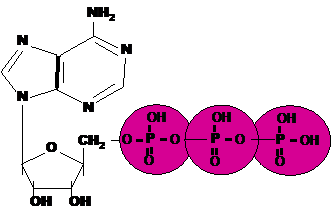 |
| Hydrocarbons can be either _____, _____, or _____ shaped. | straight, branched, or ring shaped p61 |
| Organic molecules consisting of only carbon and hydrogen are called ______. | hydrocarbons p61 |
| The repeating building blocks of larger molecules are known as ____. | monomers p68 |
| Many monomers linked together make up a ____. | polymer p68 |
| A polymer is a large molecule made up of many ____. | monomers p68 |
| The four categories of biological macromolecules are ___, ___, ___, and ___. | carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids (Although some people, including the authors of this textbook do not consider lipids to be macromolecules) p68, 
|
| The type of macromolecule that is used primarily as a source of quick energy is ___. | carbohydrates p70, 
|
| Bread, pasta, cereal and fruits are high in which type of macromolecule? | carbohydrates (from your notes), 
|
| The monomers of complex carbohydrates are ___. | simple sugars (a.k.a. monosaccharides) p69, 
|
| Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of ____. | simple sugars (or monosaccharides - note; these three are all hexose sugars meaning they have six carbons. There are also simple sugars that are pentose sugars with 5 carbons such as ribose and deoxyribose, found in nucleotides. Triose sugars such as glycerodehyde are important in respiration and photosynthesis) p70, 
|
| Sucrose is commonly called ____. | table sugar |
| Sucrose is a type of carbohydrate made of two simple sugar monomers (glucose bonded to fructose). Therefore, it is a ___. | disaccharide p70 |
| Another term for simple sugars is ___. | monosaccharides p69, 
|
| Many monosaccharides bonded together are called a ____. | polysaccharide p70, 
|
| Lactose is a type of disaccharide found in _____. | milk p70 |
Plants usually store their carbohydrates as the polysaccharide known as ____., 
| starch p71 |
Animals store carbohydrates in their liver and muscles as the polysaccharide known as ___., 
| glycogen p72, 
|
| The cell walls of plants are made of the polysaccharide known as ____. | cellulose p72,  , , 
|
| Sugars are classified as ___. | carbohydrates pp69&70, 
|
| The monomers of proteins are ____. | amino acids p78, 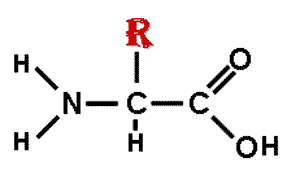 , , 
|
A long straight chain of amino acids is called a(n) ____., 
| polypeptide (It's not considered a protein until it folds into a specific 3-dimensional shape that allows it to do it's job) p77, 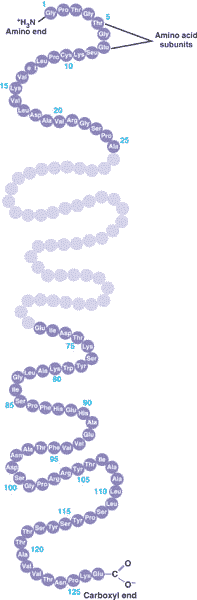 |
A polypeptide that folds into a 3-D structure that has a specific function is called a(n) ___., 
| protein (The picture below shows the different bonds that hold the protein in its folded shape) p77, 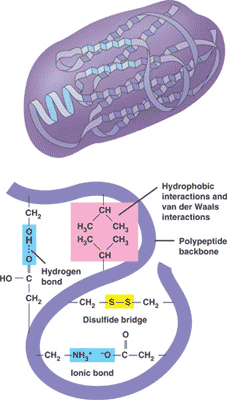 |
Lean meat is highest in the macromolecule group known as ____., 
| protein (from your notes) |
Organic catalysts (substances that speed up chemical reactions) are known as ___., 
| enzymes p68, 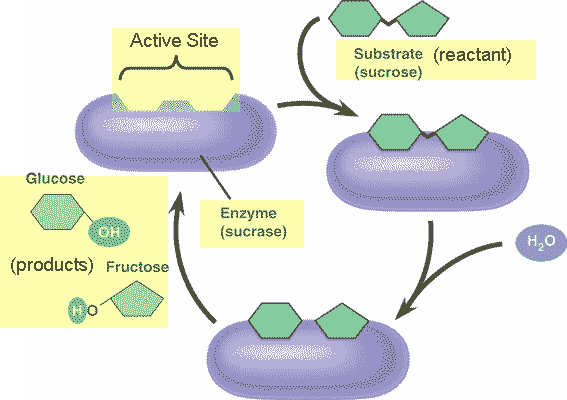 |
| An enzyme ____ a chemical reaction. | speeds up p68,  |
| DNA and RNA are types of ____. | nucleic acids p86, 
|
| The type of molecule that holds an organism's genetic information is called ___ and belongs in the class of macromolecules known as ____. | DNA, nucleic acids p86,  |
| The monomers of nucleic acids are ____. | nucleotides p86,  , , 
|
| DNA is made up of four different types of ____. | nucleotides (Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are the nucleotides in DNA. In RNA, uracil is substituted for thymine. The picture below shows the nitrogenous bases of each which give the nucleotides their names) p88, 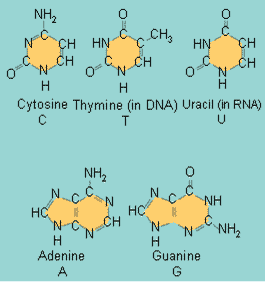 |
The order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule determines the order of ____ in a protein., 
| amino acids p88,  , , 
|
A type of nucleic acid that is usually single-stranded is ___., 
| RNA p88 |
A type of nucleic acid that is double stranded is ___., 
| DNA p88 |
| Fats, steroids and waxes are classified as ___. | lipids pp74-77 |
| The main function of fats in an animals body is to ____. | store energy for later use (other functions can include insulation of the body using fat that lies just under the skin "subcutaneous fat" and cushioning of the organs inside the body cavity) p76 |
| Red meats, dairy and fried foods are high in the category of macromolecules known as ___. | lipids (from your notes) |
| Phospholipids are major component of the ___. | cell membrane p76,  |
| A major component of cell membranes is a type of lipid called a(n) ___. | phospholipid p76, 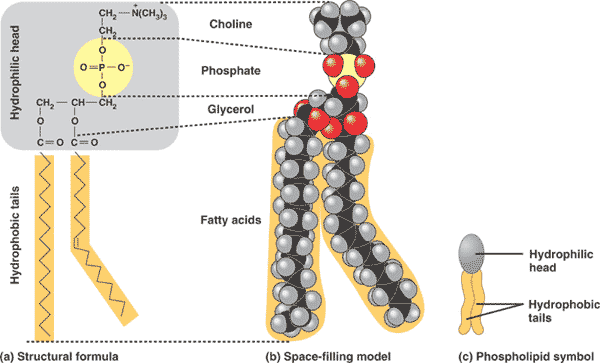 |
The picture below shows the basic structure of a(n) ______.,  | amino acid (notice that your book shows the amino acids in their ionized form as they would be when dissolved in water) p79,  |
The picture below is showing part of a molecule of _____ which has a ______ shape.,  | DNA, double helix,  |
What is "G" pointing out?, 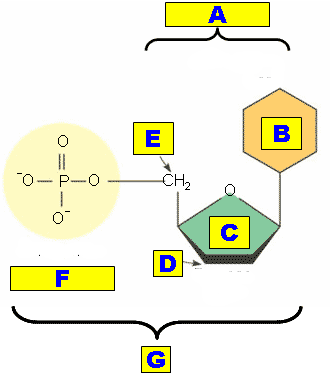 | An entire nucleotide p87,  |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein.,  | primary structure p82,  |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein., 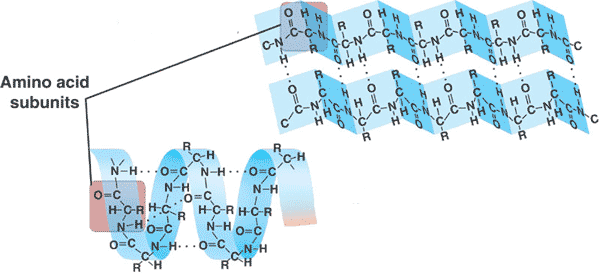 | secondary structure (The one up top is a beta-pleated sheet while the one below is an alpha helix. These are the two different types of secondary structure that proteins can have) p82,  |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein.,  | tertiary structure p83 |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein., 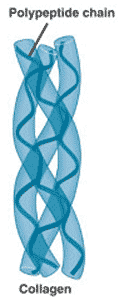 | quarternary structure (notice how the collagen protein, which is a major component of connective tissue, has 3 proteins that form a braid. The alpha-helix structure of the individual proteins give collagen its rubber band-like stretchy characteristics. Old people lose that elasticity in their collagen, leading to wrinkled skin) p83,  |
This picture shows the _____ structure of a protein., 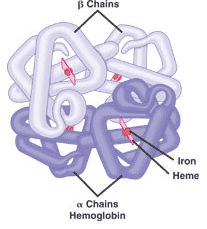 | quarternary structure (This hemoglobin protein is made up of four intertwining polypeptide chains. As the oxygen carrying molecule in red blood cells, hemoglobin also has 4 heme groups with iron at the center to bind directly to oxygen) p83 |
The picture below shows a molecule of _____ which is made of ____ bonded to _____.,  | fat (a.k.a. - a triglyceride), made of glycerol bonded to three fatty acids p75,  |
| Which macromolecule stores more than twice as much energy per gram compared to the other categories? | Lipids (They have about 9 kilocalories per gram compared with 4 for carbohydrates and proteins) ** see your notes |
| What is the molecular formula of a hexose sugar such as glucose? | C6H12O6 (fructose and galactose have the same molecular formula as glucose. Therefore, all three are isomers) p70 |
| What trait do all lipids share? | They are hydrophobic (don't mix well with water) p74 |
| Steroids are a type of _____ made of a carbon skeleton with a(n) ______ structure. | lipid, ring (Some steroids work as hormones which are chemical messengers that travel from one part of the body to another. Most hormones are actually proteins, not lipids like steroids are) p77,  |
| Any chemical agent that selectively speeds up chemical reactions is called a(n) _____. | catalyst (Some catalysts are inorganic, like manganese dioxide which can break down hydrogen peroxide, or the metals inside the catalytic converter that convert harmful exhaust from your car into less harmful gases) p77 |
| How many different amino acids do cells use in order to build their proteins? | 20 p78 |
What does "A" in this graph represent?,  | Energy of activation without an enzyme present p153,  |
What does "B" in this graph represent?,  | The lowered energy of activation due to an enzyme being present p153,  |
What does "C" in this graph represent?,  | The change in free energy (∆G) for this reaction, which would be negative, indicating an exergonic reaction p153,  |
What is the name of this molecule and which part of it does "A" represent?,  | "A" represents the three phosphate groups in ATP p149,  |
The graph below represents a(n) ____ reaction,  | endergonic (notice the positive ∆G) p147,  |
The graph below shows the change in free energy for a(n) _____ reaction.,  | endergonic p147,  |
The change in free energy is ____ for this reaction.,  | positive p147,  |
The letter "A" represents a(n) ____ for this enzyme.,  | active site p154,  |
The letter "B" represents a(n) ____.,  | enzyme p154,  |
The letter "C" represents a(n) ____.,  | substrate p154,  |
The graph below represents a(n) ____ reaction,  | exergonic (notice the negative ∆G) p147,  |
The graph below shows the change in free energy for a(n) _____ reaction., 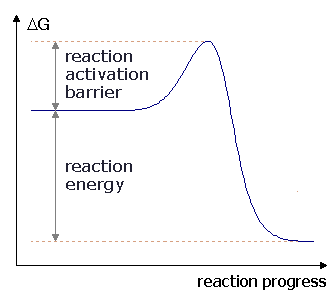 | exergonic p153,  |
The molecules labeled "A" are known as the _____.,  | reactants p152,  |
The molecules labeled "C" are known as the _____.,  | products p152,  |
The arrow labeled "D" shows the ______.,  | change in free energy (∆G) for the reaction (which is negative indicating an exergonic reaction) p152,  |
The difference in free energy between A and B is called the ____.,  | activation energy (a.k.a. energy of activation) p152,  |
| The reactant on which an enzyme works is called the _____. | substrate p153 |
| ______ energy is energy stored by matter as a result of location or spatial arrangement. | Potential energy p143 |
| A macromolecule serving as a catalyst is called a(n) ____. | enzyme (the type of macromolecule that acts as an enzyme is almost always a protein. Sometimes the nucleic acid RNA can act as an enzyme) p152 |
| Any substance, organic or inorganic, that speeds up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction is called a(n) _____. | catalyst p152 |
| The specific portion of an enzyme that attaches to the substrate by means of weak chemical bonds is called _____. | the active site p154 |
| The amount of energy that reactants must absorb before a chemical reaction will start. | activation energy (or energy of activation) p152 |
| A spontaneous chemical reaction, in which there is a net release of free energy. | exergonic reaction p147 |
| The energy of motion, which is exponentially related to the speed of that motion is called ____ energy. Moving matter does work by imparting motion to other matter. | kinetic energy p143 |
| A quantitative measure of disorder or randomness is called ____. | entropy (the greater the entropy, the greater the disorder) p145 |
| The principle of conservation of energy which states that energy can be transferred and transformed, but it can't be created or destroyed. | first law of thermodynamics p144 |
| The potential energy stored in molecules available for release in chemical reactions is called ____. | chemical energy p143 |
| The principle whereby every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe. Ordered forms of energy are at least partly converted to heat, and in spontaneous reactions, the free energy of the system also decreases. | second law of thermodynamics p145 |
| A non-spontaneous chemical reaction, in which free energy is absorbed from the surrounding. | endergonic reaction p148 |
| The average kinetic energy of a body of matter. | temperature (Temperature is related, but not the same as heat. As an example, a rock that has been "heated up" to lets say, 180C, would have more thermal energy, or heat, than the air in a container the same size as the rock, even if that air was much "hotter," like say, 150C. Heat is the "total" amount of kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. There are many more particles packed into the rock than in the gasses that make up the hot air in the container that has the same volume as the rock. If you wanted the temperature of a small cold room to increase, you would be better off bringing the rock into the room, than the small amount of really hot air, even though the molecules of air are moving at an overall faster average speed, and therefore have a higher average kinetic energy (a.k.a. - temperature) (G-34) |
| The sum of all of an organism's chemical reactions is called ______. | metabolism p142 |
| True or False: Breaking bonds releases energy. | False (Breaking bonds always requires energy. The formation of bonds releases energy) p148 |
| It's a fact that the breakdown of sucrose (table sugar) is an exergonic reaction and is therefore spontaneous. Does that mean that sucrose breaks down into glucose and fructose monomers quickly? | No (A spontaneous reaction is not necessarily a quick reaction. A sugar solution, like Mountain Dew, would take years for the sugar to react and break down on it's own. Most exergonic reactions in your body require a catalyst for the reactions to occur quickly enough to be useful. It's a good thing that all of the possible exergonic spontaneous reactions in our body don't happen quickly on their own because otherwise, we would spontaneously combust) p152 |
| An organic catalyst is known as a(n) _____. | enzyme p152 |
| A liquid that has a uniform mixture of two or more substances is know as a(n) ___. | solution p.50 |
| In a glass of salt water, the ___ would be the solvent. | water p.50 |
| In a glass of salt water, the ___ would be the solute. | salt p.50 |
| In a solution of sugar and water, the sugar would be the ___. | solute p.50 |
| In a solution of sugar and water, the water would be the _____. | solvent p.50 |
| Acidic solutions have a pH that is ____ seven. | below pp.53&54 |
| Basic solutions have a pH that is ___ seven. | above pp.53&54 |
| Distilled water has a pH of ___. | seven pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 1 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 5. | more acidic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 6 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 2 | less acidic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 8 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 14. | less basic pp.53&54 |
| A liquid with a pH of 13 would be described as being ___ than a liquid with a pH of 7.8. | more basic pp.53&54 |
| As temperature ____, particles move faster and faster | increases p.48 |
| As temperature ____ particles move slower and slower. | decreases p.48 |
| Bonds in which the electrons between two atoms are shared about equally (because both atoms have similar electronegativities) are called _____. | nonpolar covalent bonds p.39 |
| Bonds in which the electrons between two atoms are not SHARED equally (because one atom has a significantly higher electronegativity) are called _____. | polar covalent bond p.46 |
| Bonds in which electrons aren't shared at all (because one atom has a MUCH higher electronegativity than the other) are called ______. | ionic bonds p. 40 |
| A weak attraction between hydrogen in one molecule and either an oxygen or nitrogen atom in another molecule is called a(n) _____. | hydrogen bond p.40 |
| Molecules in which the overall charge is unequally distributed, leading to parts of the molecule having a partial positive charge while other parts have a partial negative charge (like water) are called ______. | polar molecules p.46 |
| The fact that water molecules are attracted to each other is an example of ____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| The ability to pour water into a glass past the top of the glass, water forming drops that stick together, and waterbugs not falling through the surface of a pond can be explained by the phenomenon of _____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| The attraction of water molecules to the surfaces of some materials is called _____. | adhesion (Adhesion between water molecules and the glass in the graduated cylinder are responsible for the upward pull of water molecules along the sides, known as a meniscus. Specifically, the glass just above the water line is also attracting water molecules, so the water is pulled upward. This is also how capillary action works.) p.48,  |
The meniscus observed in a graduated cylinder full of water is caused by the ____ of water to the molecules that make up the glass in the cylinder.,  | adhesion p.48,  |
| Pure water freezes at ___ Celsius and boils at ___ Celsius. | 0, 100 p.48 |
| The transformation from a liquid to a gas is called ____ or ____. | evaporation or vaporization (boiling is the temperature at which the average molecule has enough energy to overcome the attractions that hold molecules together as a liquid. Therefore, the molecules vaporize quite quickly once the boiling point has been reached) p.49 |
| The _____ of water from humans and other organisms helps keep them cool. | evaporation (or vaporization) p.49 |
| Water reaches its greatest density at ___ degrees Celsius. | 4 pp.49&50,  |
| If ice didn't float, lakes and oceans would ______. | eventually freeze solid because ice would sink, exposing liquid water to cold winter temperatures instead of insulating it from the cold temperatures. p.50 |
| 1 mole of a substance is equal to ____ particles of that substance | 6.02 X 10 ^23 (6.02 times ten to the twenty third power) pp.51&52 |
Which type of bond is represented by the dotted line? By the straight line inside the water molecule?,  | Dotted lines = hydrogen bonds, straight lines = covalent bonds p.47,  |
The picture below shows water dissociating into ___ and ___ ions., 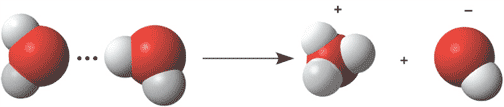 | hydronium and hydroxide ions p.53,  |
| If the concentration of hydrogen (hydronium) ions in a solution is higher than the concentration of hydroxide ions, the solution will be ____. | acidic p.53 |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydrogen ion, drop in pH (to become more acidic) p.53,  |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydronium ion, drop in pH (to become more acidic) p.53,  |
The substance shown below is a(n) ____ and an increase in its concentration will cause a(n) ___ in pH.,  | hydroxide ion, increase in pH (to become more basic) p.53 |
.,  | strong acids p.53,  |
.,  | strong bases p.53 |
.,  | weak acids p.53,  |
.,  | weak bases p.53,  |
| The pH scale is kind of like the richter scale (for earthquakes) in that a change of one (such as going from pH 4 to pH 3) represents a ___-fold change. | 10-fold change (for example, pH 3 is 10 times more acidic than pH 4) pp.53&54 |
| _____ are substances that minimize (or dampen) changes in pH. | Buffers p.54 |
| The binding together of like molecules, often by hydrogen bonds, is called ____. | cohesion p.47,  |
| A common measure of solute concentration, referring to the number of moles of solute per liter of solution is called ___. | molarity p.52 |
| A substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution is called a(n) ___. | base p.53 |
| The attraction between DIFFERENT kinds of substances is called ____. | adhesion (Adhesion between water molecules and the glass in the graduated cylinder are responsible for the upward pull of water molecules along the sides, known as a meniscus. Specifically, the glass just above the water line is also attracting water molecules, so the water is pulled upward. This is also how capillary action works.) p.48,  |
| A measure of how difficult it is to break or stretch the surface of a liquid is called ___. | surface tension (This is responsible for the ability of the water strider in the picture below to stay on the surface of the water) p.48,  |