| A | B |
|---|
The cell below is a(n) _____ cell.,  | animal p.100,  |
The cell below is a(n) _____ cell.,  | plant p.101,  |
| The ____ is the simplest collection of matter that can be alive. | cell p94 |
| The first microscopes, as well as the microscopes that we use in lab, are called ____. | light microscopes (LM) p.95 |
| ______ in microscopy is the ratio of an object's image size to its real size. | Magnification p.95 |
| _____ is a measure of the clarity of an image under a microscope and is defined as the minimum distance that ______ can be separated and still be distinguished as _____. | Resolution, two points, two points p95 |
| _________ microscopes focus a beam of electrons through the specimen or onto its surface. | Electron microscopes p95 |
| The type of electron microscope that produces 3-D images of the surface of a specimen is called a ____. | scanning electron microscope (SEM) p95, 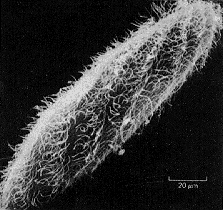 |
| The type of electron microscope that produces a two dimensional picture of a thinly sliced cross section of a specimen is called a ______. | transmission electron microscope (TEM) p95 |
| The study of cells is called _____. | cytology p97 |
| The semifluid, jellylike substance in which organelles are found is called _____. | cytosol p.98 |
| The entire region between the nucleus and the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells is called the ____. | cytoplasm (which includes the cytoplasm and the organelles, other than the nucleus) p.98, 
|
| The major reason that cells can't get too big is that as they get bigger, their _____ grows faster than their ____. | volume grows faster than their surface area (A cells requirement for nutrients and production of waste is proportional to its volume, but its ability to get nutrients in and waste out through the plasma membrane is proportional to the surface area of the plasma membrane) p.99 |
| The ________ directs protein synthesis by synthesizing m-RNA according to instructions provided by ______. | nucleus, DNA p.102 |
| The nucleus is enclosed by a double membrane called the ______ which has holes called _____ to allow materials to go back and forth between the cytoplasm and the interior of the nucleus. | nuclear membrane, nuclear pores p.102-103 |
| The dark structure inside the nucleus is called the _____. It's job is to make the large and small subunits of ______. | nucleolus, ribosomes p.102, 
|
| ________ are particles that carry out protein synthesis when _____ attaches to them to deliver the instructions. | Ribosomes, m-RNA p.102 |
| Where would find free ribosomes ____________. | suspended in the cytosol p.102 |
| Bound ribosomes would be found attached to the outside of the _____ or the _____. | endoplasmic reticulum or nuclear envelope p.102 |
The "B" is pointing to ____ in the picture below.,  | the stroma of a chloroplast (like the cytosol of the chloroplast) p.111,  |
The "C" is pointing to ____ in the picture below.,  | the inner and outer membranes of the chloroplast p.111,  |
The "D" is pointing to ____ in the picture below.,  | a granum in a chloroplast (singular of grana) - a granum is a stack of thylakoids. p.111,  |
The "E" is pointing to ____ in the picture below.,  | a single thylakoid in a chloroplast p.111,  |
What is "A" in the picture below?,  | A mitochondrion p.110,  |
What is "B" in the picture below?,  | the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion p.110,  |
What is "C" in the picture below?,  | the outer membrane of the mitochondrion p.110,  |
What is "D" in the picture below?,  | The inner membrane of the mitochondrion p.110,  |
What is "E" in the picture below?,  | Cristae of the mitochondrion (folds of inner membrane) p.110,  |
What is "F" in the picture below?,  | the matrix of the mitochondrion (the inner compartment) p.110,  |
Which organelle is shown in this micrograph?,  | a mitochondrion p.110,  |
| The ______ ER does not have ribosomes attached to its outer surface. | smooth p.105 |
| The ______ ER has ribosomes attached to its outer surface. | rough p.105 |
| The smooth ER does not have ________ attached to its outer surface. | ribosomes p.105 |
| The rough ER has ________ attached to its outer surface. | ribosomes p.105 |
| The _____ can be thought of as a center for warehousing, sorting, and shipping, and even some manufacturing. | golgi apparatus p.105 |
| A(n) _____ is a membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that an animal cell uses to digest all kinds of macromolecules. | lysosome p.106 |
| Mature plant cells contain a large _________ enclosed by a membrane called a tonoplast. | central vacuole p.108 |
| The ____ and _____ are organelles that convert energy into more useable forms for eukaryotic cells. | mitochondria and chloroplasts p.109 |
| Which two organelles have their own ribosomes and DNA that are different from the rest of the cell's DNA and ribosomes? | mitochondria and chloroplasts p.109 |
| Which organelle is involved with cellular respiration? | mitochondria p.109 |
| The mitochondria is involved with the process of _____. | cellular respiration p.109 |
| The chloroplast is involved with the process of _____. | photosynthesis p.109 |
| Which organelle is involved with photosynthesis? | chloroplast p.109 |
| The space between the inner and outer membranes of the mitochondria is called the _____. | intermembrane space p.109,  |
| The space inside of the inner membrane of the mitochondria is called the ____. | mitochondrial matrix p.110,  |
| The flattened interconnecting sacs inside chloroplasts are called ____. | thylakoids ("E" in the picture below) p.111,  |
| A stack of thylakoids is called a ______. | granum ("D" in the picture below) p.111,  |
| The space between the thylakoids and the inner membrane of the chlorplast is called the ____. | stroma p.111 |
| The green photosynthetic pigment in _____ is called _____. | chloroplasts, chlorophyll p.110 |
| _____, especially prominant in the liver, help detoxify alcohol and other poisons by transferring hydrogen from the poisons to oxygen, producing hydrogen peroxide. | Peroxisomes p.111 |
| Hydrogen peroxide produced in peroxisomes during oxidative reactions is quickly broken down by ____, also produced by peroxisomes. | catalase (This info is not in the chapter, but it is the enzyme we are doing a major research project on, so you should know it) |
| The _______ is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities of the cell. | cytoskeleton p.112, 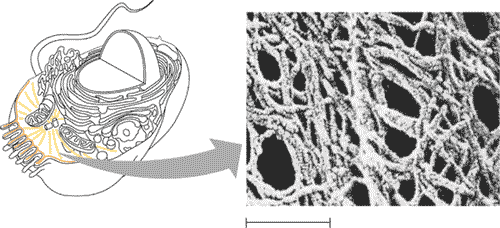 |
| Within the centrosome of animal cells are a pair of ______ that seem to help with separation of chromosomes during mitosis. | centrioles p.114 |
| Many single-cell organism have either _____ or ______, both with the same "9 + 2" arrangement of microtubules, to help propel them through the water. The ____ are the longer of the two. | cilia, flagella, flagella are longer (The picture below is a photosynthetic protist called Euglena that uses its flagellum to move through water) p.114,  |
| Microfilaments (actin filaments) often work in conjunction with a protein called _____ to cause contraction in such things as muscle cells, pinching of the cleavage furrow during cytokinesis, or movement of pseudopods in amoebae. | myosin p.117, 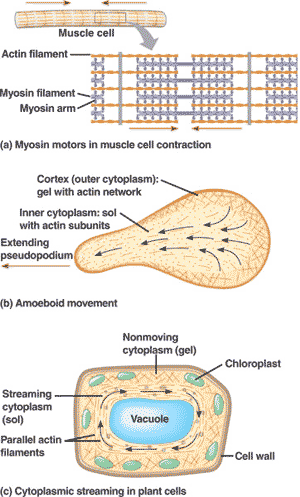 |
| The cell wall of plants is made mostly of ______. | cellulose p.118 |
| In eukaryotic cells, where is the DNA located? | In the nucleus (although some organelles, like chloroplasts and mitochondria, contain small amounts of their own DNA) p.98 |
| The major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is that prokaryotic cells do not store their DNA inside a(n) ____ and they lack other ____ organelles as well. | nucleus, membrane-bound organelles (Ribosomes, which are found in both types of cells, are not membrane-bound. Instead, they can best be described as solid structures with no interior region) p. 98 |
| ______ produce their organic molecules from carbon dioxide and other organic raw materials obtained from the environment. | Autotrophs p184 |
| _______ are autotrophs that use light as a source of energy to synthesize organic substances. | Photoautotrophs p184 |
| What are three types of organisms that are photoautotrophs? | All plants, some Protists and some Prokaryotes p184 |
| Photosynthesis converts _____ energy to the ______ energy of food. | light, chemical p184 |
| _____ are the major sites of photosynthesis in most plants. | Leaves p186 |
What is "B" referring to?, 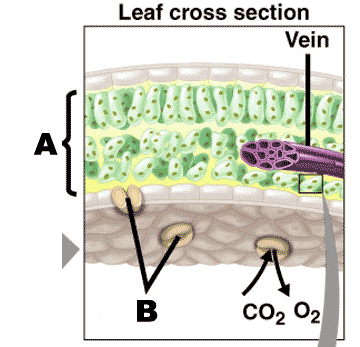 | stomata p186,  |
What is #1 pointing to?,  | a thylakoid p186,  |
What is #2 pointing to?,  | A granum (a stack of thylakoids) p186,  |
What is #3 pointing to?,  | The stroma p186,  |
| What is the net chemical equation for photosynthesis? | The equation below shows the net usage and production of molecules in photosynthesis. In reality, 12 water molecules are used as reactants and 6 water molecules are produced. p187,  |
| Energy from the sun is used to produce the high energy molecules NADPH and ATP during the ______ reactions of photosynthesis. | light p188,  |
| Energy from the sun is used to produce the high energy molecules ______ and ______ during the light reaction of photosynthesis. | NADPH and ATP p188,  |
| Electrons are stripped from water, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen molecules during the ______ reaction of photosynthesis. | light p188,  |
| Electrons are stripped from _____, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen molecules during the light reaction of photosynthesis. | water p188 |
| _______ are stripped from water, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen molecules during the light reaction of photosynthesis. | electrons p188,  |
| Electrons are stripped from water, producing _________ and ________ molecules during the light reaction of photosynthesis. | hydrogen ions and oxygen molecules p188,  |
| The _____ reaction of photosynthesis takes place on the thylakoid membrane. | light p189,  |
| The light reaction of photosynthesis takes place on the _________. | thylakoid p189,  |
| The _______ cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. | Calvin p189 |
| The Calvin Cycle takes place in the ______ of the chloroplast. | stroma p189 |
Which molecule belongs in the "A" spot?,  | water p188, 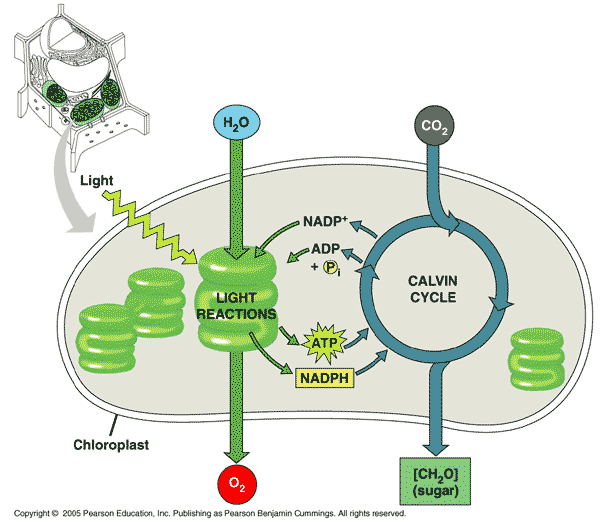 |
Which molecule belongs in the "B" spot?,  | oxygen p188,  |
Which molecule belongs in the "C" spot?,  | carbon dioxide p188,  |
Which molecule belongs in the "D" spot?,  | [CH2O] This is the generic formula for a carbohydrate. The actual carb that exits the Calvin cycle is a triose sugar called Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P). This molecule can be linked to form glucose, sucrose, or starch. Or it can be used as raw material to make amino acids and lipids. p188,  |
Which molecules belongs in the "E" spot?,  | NADP+ and ADP and P p188,  |
Which molecule belongs in the "F" spot?,  | NADPH and ATP p188,  |
What is "A" pointing to?,  | photosystem I (a.k.a. P700) p197,  |
What is "C" pointing to?,  | NADP+ (NADPH) p197,  |
| What is the final electron receptor in the light reaction of photosynthesis? | NADP+ (In cellular respiration, it is oxygen. However, whereas the electrons at the end of the electron transport chain of cellular respiration contain very little potential energy, the electrons that end up in NADP+ to form NADPH still contain a significant amount of potential energy, so NADPH, unlike water, is an energy carrier and will be used in the next phase, the Calvin Cycle, to drive endergonic reactions that build up carbohydrates) p195 |
| What supplies electrons to the electron transport chain of photosynthesis? | Water (when it is split) p194 |
| Where do hydrogen ions end up when they are moved by active transport during the light reaction of photosynthesis? | inside the thylakoid space p196,  |
| In which direction do protons (aka - hydrogen ions) flow through ATP synthase in the light reaction of photosynthesis? | From the thylakoid space out to the stroma of the chloroplast. p196,  |
What is "D" pointing to?,  | Photosystem II (a.k.a. P680) p197,  |
What is "E" pointing to?,  | Electron transport chain of photosynthesis p197,  |
What is "G" pointing to?,  | thylakoid membrane p197,  |
What is "H" pointing to?,  | ATP synthase p197,  |
What is "I" pointing to?,  | stroma of the chloroplast p197,  |
What type of electromagnetic radiation is in the "D" spot?,  | visible light p189,  |
Violet light has ____ energy, _____ wavelength and ______ frequency compared to red light.,  | violet light has greater energy, shorter wavelength and higher frequency compared to red light p189,  |
| The frequency of electromagnetic radiation is inversely proportional to ______ but directly proportional to _____. | frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength but directly proportional to the energy of the ray. p189 |
| Where do the ATP and NADPH that are produced during the light reaction head next? | the Calvin Cycle pp198&199 |
| The light reactions convert light energy to the chemical energy of ____ and _____. | ATP and NADPH p188 |
| When electromagnetic energy hits matter, it can either be _____, _____, or _____ depending on the wavelength of energy and type of matter. | absorbed, reflected, or transmitted p190 |
| When electromagnetic energy hits matter, it can either be absorbed, reflected, or transmitted depending on the _______ and _____. | wavelength of energy and the type of matter p190 |
The red arrow signifies ______., 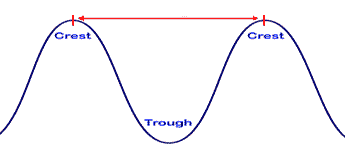 | The wavelength of this wave p189,  |
| The Calvin Cycle uses _____ and _____ to convert ______ to sugar. | ATP, NADPH, carbon dioxide p198 |
| The Calvin cycle for most plants occurs during the ____. | day p189 |
| Which enzyme helps fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in the Calvin cycle? | Rubisco pp.198&199 |
| When the ________ are open to take in carbon dioxide during the day, the plant becomes vulnerable to water loss through _________. | stomata, transpiration p199 |
| Which alternate method of carbon fixation reduces photorespiration by separating carbon fixation from the Calvin cycle spatially? | C4 (Carbon fixation takes place in the outer mesophyll cells and is then funneled into the inner bundle-sheath cells where the Calvin Cycle takes place. This keeps the carbon dioxide concentrations high for rubisco) p200, 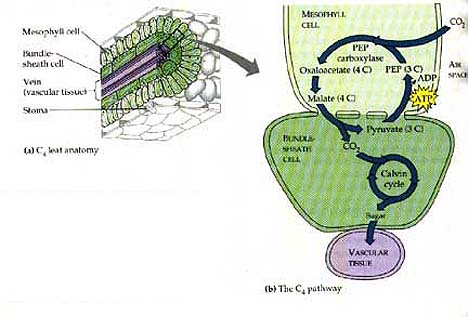 |
| Which alternate method of carbon fixation reduces photorespiration by separating carbon fixation from the Calvin cycle temporally? | CAM (CAM plants fix carbon dioxide at night and store the carbon in organic acids until daytime when the carbon is funneled into the Calvin Cycle. Separating something temporally means separating something by time, in this case, day versus night ) pp201&202, 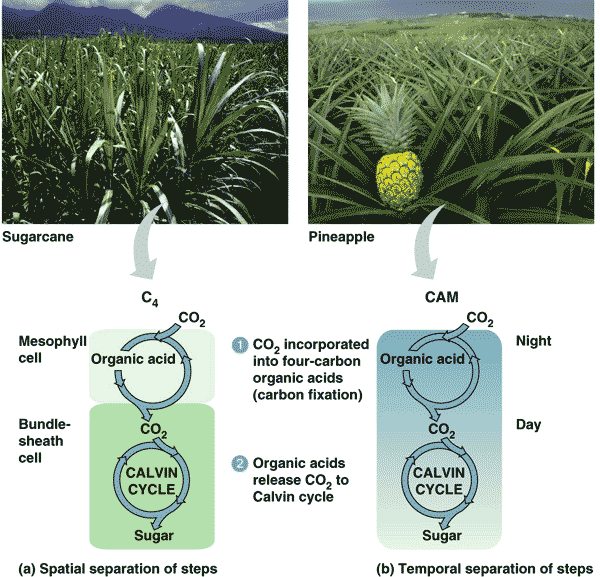 |
| Pineapples and most cacti are _____ plants (named for their mode of carbon fixation) | CAM p201,  |
| Most plants, including rice, wheat, and soybeans are ____ plants (named for their mode of carbon fixation). | C3 (They are called C3 plants because the first product after carbon fixation is the 3 carbon molecule 3-phosphoglycerate) p200 |
| Which method of carbon fixation keeps stomata closed during the hot daytime hours and opens them up at night to fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules that will be broken down during the day to provide carbon dioxide to the Calvin Cycle? | CAM pp201&202,  |
| The signals received by cells, whether originating from other cells or from changes in the physical environment, take various forms, including light and touch. However, cells most often communicate with each other by _____ signals. | chemical p206 |
| The process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted into a specific cellular response is a series of steps called a(n) ______________. | signal transduction pathway p207,  |
| Local signaling involves the secretion of signaling molecules that act on ______ cells. | nearby p208, 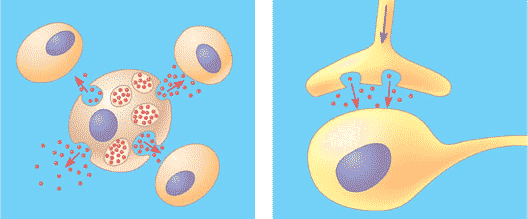 |
| The narrow space between a nerve cell and its target cell is called the _____. | synapse p208, 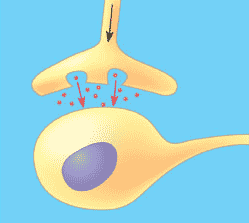 |
| ________ signaling occurs in an animals nervous system when molecules secreted by one nerve cell diffuse across the narrow space that separates it from the target cell (often another nerve cell). | synaptic signaling p208,  |
| Signaling molecules that communicate with distantly located cells by entering and travelling through the circulatory (in animals) system until their target is reached are called _____. | hormones (plants have hormones also) p209, 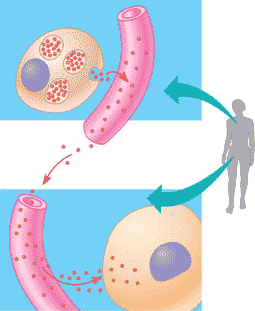 |
| Another word for endocrine signaling is ______. | hormonal signaling p209,  |
| The transmission of a signal from one end of a long neuron to the other end is accomplished by transmitting a(n) ______ signal down the neuron. | electrical signal (This can be considered a form of long distance signaling due to the long length of most nerve cells) p209 |
| The process going on at the receiving end of a cellular conversation can be broken down into three steps; ______, ______, and _______. | reception, transduction, and response p209,  |
| A chemical signal is "detected" when it binds to a _____ protein located at the cell's surface or inside the cell. | receptor protein p209 |
| A(n) ______ is a molecule that specifically binds to another, usually larger molecule. Often times, the larger molecule is a receptor protein. | ligand p210 |
| Genes can be activated by chemical signals that activate ______________ (special proteins that activate the transcription of DNA into messenger-RNA molecules) | transcription factors pp214&219 |
| ____________ factors control which genes are turned on and transcribed into m-RNA. | Transcription factors p214 |
| Where are most signal receptor proteins found? | Embedded in the plasma membrane (The other type are intracellular receptors. These require the signaling molecule to be able to cross the plasma membrane because the receptor proteins to which they attach are located in the cytosol or inside the nucleus. Steroid hormones, like testosterone, are classic examples of signaling molecules that bind intracellular receptors. But keep in mind, most signaling molecules molecules bind to receptors at the cell surface and never enter the cell) p210 |
| The addition of phosphate groups often changes a relay protein in a transduction pathway from a(n) __________ form to an _________ form | inactive to an active form (In some pathways, the opposite can occur, with where phosphorylation of the protein decreases the activity of the protein, but most often, phosphorylation activates proteins) p216,  |
| At the end of a signal transduction pathway, where in the cell are the two places that the response might occur? | cytoplasm, nucleus p219 |
Which type of long-distance signaling is being shown in the picture below,  | hormonal (or endocrine) signaling p208,  |
Which type of signaling is being shown in the picture below?,  | local signaling p208,  |
Which type of signaling is being shown in the picture below?, 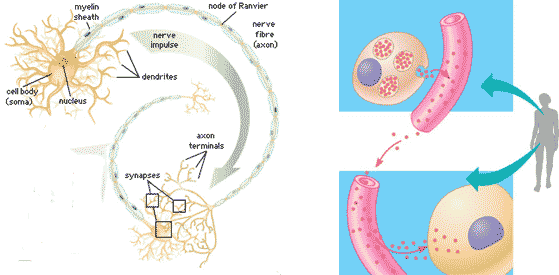 | long-distance signaling pp.208&209,  |
Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #1?,  | reception p209,  |
Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #2?,  | transduction p209,  |
Which of the three stages of a signal transduction pathway is shown under the #3?,  | response p209,  |
Which type of signaling is shown in the picture below?,  | synaptic p208,  |
The space between the two cells in the picture below is called the ______.,  | synapse p208,  |
| Sometimes a signaling transduction pathway leads to a response in the nucleus where a type of molecule called a(n) __________ is activated. This molecule can then turn genes (or in somecases, off), so that the process of making a specific __________ is either activated or deactivated. | transcription factor, protein p.219, 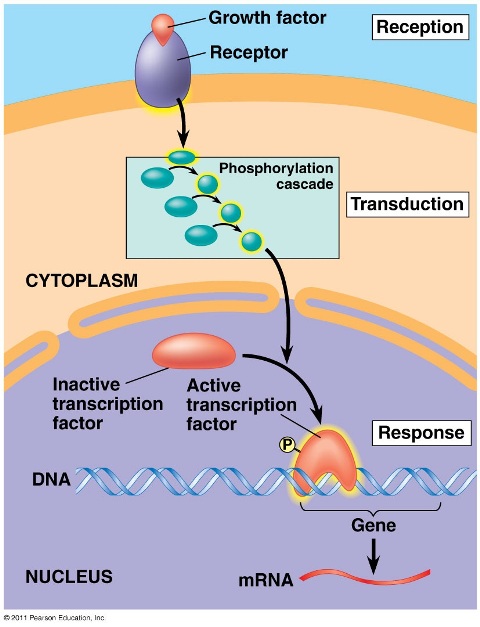 |
What is the name of the type of molecule shown below that is labeled A and then being transformed into the activated form of that molecule (labeled B) as a response to a signal transduction pathway?,  | transcription factor p219,  |
| Cells that are infected, damaged, or have reached the end of their functional life span often undergo "programmed cell death," a process called _____________. | apoptosis (Apoptosis is also a normal part of early development, such as the formation of the paws in mice as shown below) pp. 223-225,  |
| The movement of water molecules across a cell membrane is called ___. | osmosis p.133 |
| In a salt water solution, the salt is known as the ___. | solute p.50 |
| If a cell membrane allows glucose to pass through it, then the cell membrane is said to be ____ to glucose. | permeable p.131, 
|
| In a salt water solution, the water is known as the ____. | solvent p.50 |
| The movement of particles across a cell membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration is known as ____. | diffusion (The definition of diffusion can also be applied to particles just spreading out evenly in space if there is no membrane involved) p.132,  |
| The cell membrane is said to be _______ permeable to substances because it lets some pass through but not others. | selectively p.125 |
| The type of substances that can most easily diffuse across a cell membrane are ____ substances. | small non-polar substances p.131 |
| Cells will shrink if placed into a _____ solution. | hypertonic pp.133&134 |
| When energy is needed to force molecules across a cell membrane, _______ is taking place. | active transport p.135,  |
| Cells will grow bigger if placed in a ____ solution. | hypotonic p.135 |
| If a solution is 6% solutes, it will be ____ % water. | 94 (see your notes) |
| If a solution is 90% water, it will have ___ % solutes. | 10 (see your notes) |
| A solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the interior of a cell is known to be ____. | isotonic p.133 |
| Active transport requires _____. | energy p.135 |
| If a substance is diffusing across a cell membrane, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ___ concentration. | high, low p.132 |
The process pictured below is called ____., 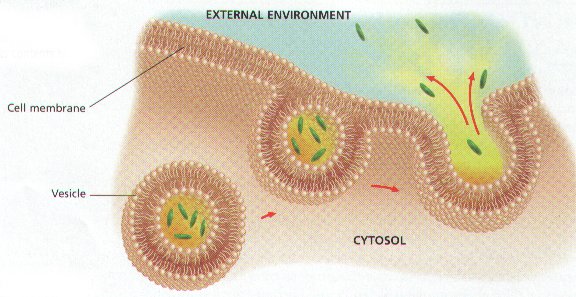 | exocytosis p.138,  , , 
|
The process pictured below is called ____., 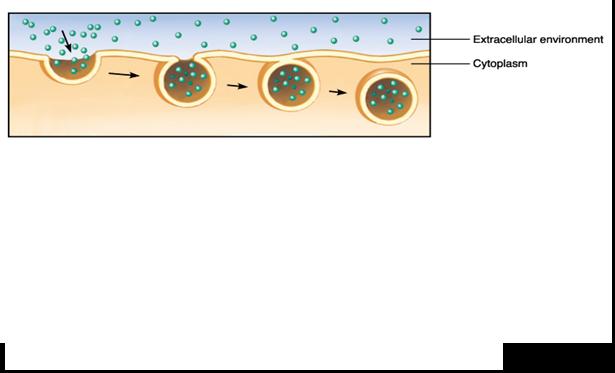 | endocytosis pp.138&139,  , , 
|
| The type of endocytosis that takes in solid particles (usually food) is called ____. | phagocytosis pp.138&139 |
| The type of endocytosis that takes in water and anything dissolved in it is called ___. | pinocytosis pp.138&139 |
| ______ is the cellular uptake of macromolecules and particulate substances by localized regions of the plasma membrane that surround the substance and pinch off to form intracellular vesicles. | endocytosis pp.138&139,  |
| In comparing two solutions, the one with the greater solute concentration is called the _____ solution. | hypertonic p.133 |
| _______ transport involves the diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane. | Passive transport p.133 |
| Passive transport involves the ______ of a substance across a biological membrane. | diffusion p.133 |
| The cellular secretion of macromolecules by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane. | exocytosis pp.138&139,  |
| _______ involves the movement of a substance across a biological membrane against its concentration or electrochemical gradient with the help of energy input and specific transport proteins. | Active transport p.135,  |
| In comparing two solutions, the one with the lower solute concentration is called the _____ solution. | hypotonic p.134 |
| _______ diffusion is the spontaneous passage of molecules and ions, bound to specific carrier proteins, across a biological membrane down their concentration gradients. | Facilitated diffusion p.134,  |
The picture below is showing _____ transport.,  | active transport p.135,  |
Which process is shown below?,  | Simple diffusion p.132,  |
Which process is shown below?,  | facilitated diffusion (It's diffusion because the particles are travelling down the concentration gradient. It's facilitated because a channel protein is helping) p.134,  |
Which type of transport protein is pictured below?, 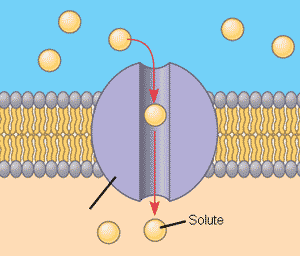 | channel protein p.131, 134&135,  |
What type of solution was the cell on the left exposed to?,  | hypotonic p.134,  |
What type of solution was the cell on the middle exposed to?,  | isotonic pp.133&134,  |
What type of solution was the cell on the right exposed to?,  | hypertonic pp.133&134,  |
| The most abundant lipids in most membranes are ______. | phospholipids p.125 |
| ______ is simply the diffusion of water molecules from one side of a cell membrane to the other. | Osmosis p.133 |
| Osmosis is simply the _____ of water molecules from one side of a cell membrane to the other. | diffusion p.133 |
| Where does the process of glycolysis take place? | Cytosol |
| Where does the Kreb's Cycle take place? | Inside the matrix of the mitochondria. |
| What is the main purpose of the electron transport chain? | The main purpose of the electron transport chain is to build up a surplus of hydrogen ions (protons) in the intermembrane space so that there will be a concentration gradient compared to the matrix of the mitochondria. |
| What are the two main reactants of cellular respiration? | ., 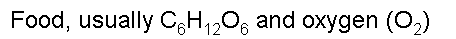 |
| What are the two main products of cellular respiration? | .,  |
| During which stage is oxygen, from the air we breath, used? What is it used for? | Oxygen is only needed at the very end of the electron transport chain. It accepts the "spent" electrons so that more electrons can travel through the chain. |
| What is the total possible net gain of ATP from one molecule of glucose that goes through aerobic cellular respiration? | 38 ATP |
| How many ATP have to be used to get glycolysis started? | 2 ATP need to be broken down to get glycolyis started. Later in glycolysis, 4 ATP are generated to produce a net gain of 2 ATP. |
| How many ATP can be generated from one molecule of glucose under anaerobic conditions? | 2 ATP per molecule of glucose can be generated under anaerobic conditions. |
| If an electron carrier molecule like NAD+ accepts two high energy electrons (and a hydrogen) from another molecule (as happens many times during respiration), it is said that the NAD+ is being __________ to NADH while the other molecule is being _______. | reduced (because the NAD+ is accepting electrons), oxidized (because the other molecule is losing electrons). Remember LEO says GER? |
| Where do the NADH's, generated during glycolysis, the transition phase and Kreb's Cycle, dump off their high energy electrons and hydrogen ions? | The NADH's dump off their high energy electrons to the system I proton pump of the electron transport chain. However, if the electron transport chain is backed up due to lack of oxygen, pyruvic acid from glycolysis will accept the electrons and hydrogen to form lactic acid. This way, NAD+ can be regenerated and used to keep glycolysis running. |
Which stage of cellular respiration is being depicted by this picture?,  | Glycolysis |
What is the name of the stage of cellular respiration that involves the parts bracketed by the letter A?, 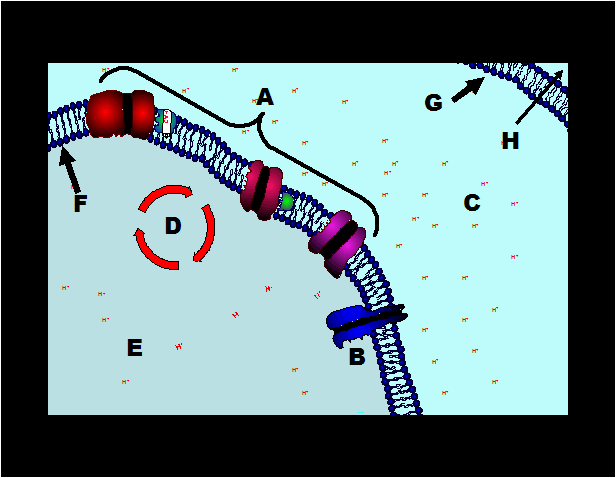 | electron transport system,  |
Through which set of proteins would protons flow freely using only passive transport? (Choose from A or B),  | B,  |
What is the name of the protein complex labeled B?,  | ATP synthase,  |
Through which set of proteins would protons travel through by active transport? (Choose from A or B),  | A,  |
Which set of proteins is involved with chemiosmosis? (Choose from A or B),  | B,  |
Which process does the letter D refer to?,  | Kreb's Cycle,  |
In which direction would protons flow by facilitated diffusion (C to E or E to C) and why?,  | C to E because the proton concentration is less in the area labeled E (the matrix),  |
In which direction would protons have to be pumped using active transport (C to E or E to C) and why?,  | E to C because there is already a higher concentration of protons in the intermembrane space (C), so you have to use energy to force more protons to go there.,  |
What is the name of this organelle?,  | mitochondria,  |
What is the area labeled D called?,  | The matrix,  |
Where would the proteins involved with the electron transport chain be located?,  | B,  |
Where would the Kreb's Cycle take place?,  | D,  |
Where would glycolysis take place?,  | F,  |
Where would protons (hydrogen ions) be building up during the electron transport chain?,  | C,  |
Where would protons (hydrogen ions) be headed during chemiosmosis?,  | D,  |
Where would ATP synthase be located?,  | B,  |
| Acetyl-CoA is a __ -carbon molecule that enters the Kreb's Cycle by bonding to oxaloacetic acid, a ___-carbon molecule to form citric acid, a __-carbon molecule. | 2,4,6 |
| During which stage of aerobic respiration is most of the ATP formed? | Chemiosmosis (34 ATP) |
| What do yeast and bacteria produce as the products of fermentation? | Ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide |
| What do humans produce if they are not getting enough oxygen to process their food aerobically? | Lactic acid |
| What is the purpose of converting pyruvate to lactic acid? | The purpose is to regenerate NAD+ so that glycolysis can continue to produce a small amount of ATP. The pyruvate accepts the hydrogen and high energy electrons from NADH because, without oxygen, the NADH can't dump off the hydrogen and high energy electrons to the ETS. NAD+ is needed to keep glycolysis going. |
| During which stages of cellular respiration are ATP produced? | Glycolysis, Kreb's Cycle, and Chemiosmosis |
| Which stage requires ATP to be broken down into ADP? | Glycolysis |
., 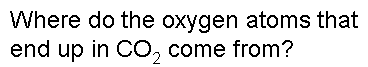 | ., 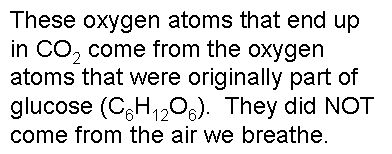 |
| Which two stages of aerobic respiration are collectively referred to as oxidative phosphorylation? | electron transport and chemiosmosis |