| A | B |
|---|
What type of evolution caused these unrelated animals to have the same general fusiform (tapered at both ends) body shape?,  | Convergent evolution p.853,  |
| The rate of exchange for nutrients, waste products, and gases is proportional to membrane _______ . | surface area p.853,  |
| The amount of material that must be exchanged across cell membranes to sustain life is proportional to cell _______. | volume p.853,  |
| What are three things that must be exchanged across membranes in order to sustain life? | Nutrients, waste products, gases p.853,  |
| Cells are organized into _____, groups of cells with similar appearance and common function. | tissues p.855 |
| Different types of tissues are organized into functional units called _____. | organs p.855 |
| Groups of organs that work together make up a(n) ______. | organ system p.855 |
| Which two organ systems does the pancreas belong to? | Digestive and endocrine (The pancreas produces digestive enzymes, and it produces the hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels) p.855,  |
| What are the four main types of animal tissues? | Epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is food processing? | Digestive system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is the internal distribution of materials? | Circulatory system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is gas exchange? | Respiratory system p.855,  |
| Which two systems' main function is to defend the body against pathogens? | Immune and lymphatic system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is to dispose of metabolic waste and regulate the osmotic balance of blood? | Excretory system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is to create offspring? | Reproductive system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is to coordinate body activities and maintain homeostasis by producing hormones? | Endocrine system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is to detect and respond to stimuli? | Nervous system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is to protect against mechanical injury, infection, dehydration, and to maintain thermoregulation? | Integumentary system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is to provide body support, protect internal organs, and facilitate movement? | Skeletal system p.855,  |
| Which system's main function is locomotion and other movement? | Muscular system p.855,  |
| __________ tissues cover the outside of the body and line the organs and cavities within the body? | Epithelial p.856,  |
| ________ tissue, consisting of a sparse population of cells scattered through an extracellular matrix, holds many tissues and organs together and in place. | Connective tissue p.857,  |
| Which type of connective tissue consists of collagen that becomes mineralized to form hardened structures? | Bone p.857,  |
| What is found within the central canals that run through bones? | blood vessels and nerves p.857,  |
| ________ connective tissue is a specialized type of loose connective tissue that stores fat in cells embedded in the matrix of the tissue. | Adipose connective tissue p.857,  |
| What type of cells are specialized for storing fat? | Adipose cells p.867,  |
| What are three different purposes of adipose tissue? | Padding, insulation, and energy storage p.857,  |
| Which type of connective tissue has cells suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma? | Blood p.857,  |
| Blood is a connective tissue that consists of cells, platelets, and dissolved substances suspended in a liquid matrix called _____. | plasma p.857,  |
| What are the three solid substances that are found in blood? | red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets p.857,  |
| Platelets are a component of blood made of cell fragments whose function is to _____________. | aid in blood clotting p.857 |
| Which type of connective tissue is found between the discs that separate vertebrae as well as the ends of many bones? | Cartilage p.857,  |
| All muscle cells consist of filaments containing the proteins ______ and _______. | actin and myosin p.858,  |
| The three types of muscle tissue in vertebrate bodies are ____, _____, and _____. | skeletal, smooth, and cardiac p.858,  |
| ______ connects muscle to bone. | tendons p.857 |
| ______ connects bone to bone. | ligaments p.857 |
| What type of muscle tissue is responsible for the voluntary movement of bones relative to each other? | skeletal muscle tissue (a.k.a. - striated muscle) p.858,  |
| What type of muscle tissue is responsible for involuntary movement such as the movement of food down the digestive tract or the constriction of blood vessels? | Smooth muscle tissue p.858,  |
| In adult mammals, building muscle increases the ____ but not the ____ of muscle fibers. | size (but not the) number p.858,  |
| What type of muscle tissue is responsible for the contraction (beating) of your heart? | cardiac muscle tissue p.858 |
| Which type of tissue is responsible for the receipt, processing, and transmission of information in the body? | Nervous tissue p.858, 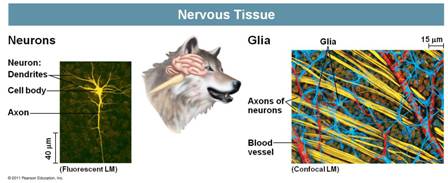 |
| The more technical name for nerve cells is ______. | neurons p.858,  |
| The part of the neuron that receives information from other neurons is the ____ and _____. | cell body, dendrites p.858,  |
| The part of the neuron that transmits impulses to other neurons, muscle cells, endocrine cells and exocrine cells is the _____. | axon p.858,  |
| Which two systems facilitate communication between various parts of the body? | Nervous and endocrine systems p.859, 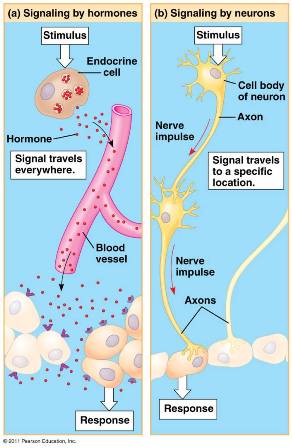 |
| The signaling molecules used for communication in the endocrine system are called ____. | hormones p.859,  |
| Which system produces signals for communication that are relatively slow acting but long-lasting and far-reaching? | Endocrine system p.859,  |
| Which system produces signals for communication that are relatively fast acting but do not endure for long? | Nervous system p.859,  |
| The _____ system is well suited for coordinating gradual changes that affect the entire body, such as growth and development, reproduction, metabolic processes, and digestion. | endocrine p.859,  |
| The _____ system is well suited for directing immediate and rapid responses to the environment, especially in controlling fast locomotion and behavior. | nervous p.859 |
Which animal in the diagram below is a regulator?, 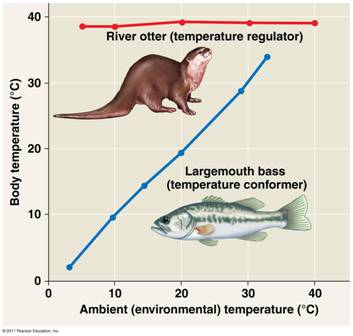 | The otter p.860,  |
Which animal in the diagram below is a conformer?,  | The bass p.860,  |
| The steady-state physiological condition of the body. | Homeostasis p.860 & G17 |
| Human bodies try to maintain homeostasis around a body temperature of _____ degrees Celsius and a blood pH of _____ | 37, 7.4 p.860 |
| What is the set point for human body temperature? | 37C p.860 |
| What is the set point for human blood pH? | 7.4 p.860 |
| Homeostasis in animals relies largely on ____ feedback. | negative p.861 |
| ______ feedback is a control mechanism amplifies rather than reduces a stimulus. | Positive p.861 |
| ______ feedback loops in animals DO NOT play a major role in homeostasis, but instead help drive processes to completion. | Positive p.861 |
| During childbirth, the pressure of the baby's head against receptors near the opening of the mother's uterus stimulates the uterus to contract. These contractions result in greater pressure against the opening of the uterus, heightening the contractions and thereby causing even greater pressure, until the baby is born. This is an example of a(n) ______ feedback loop. | positive p.861 |
| A physiological cycle of about 24 hours that persists even in the absence of external cues is called a(n) ______ rhythm. | circadian p.861 & G7, 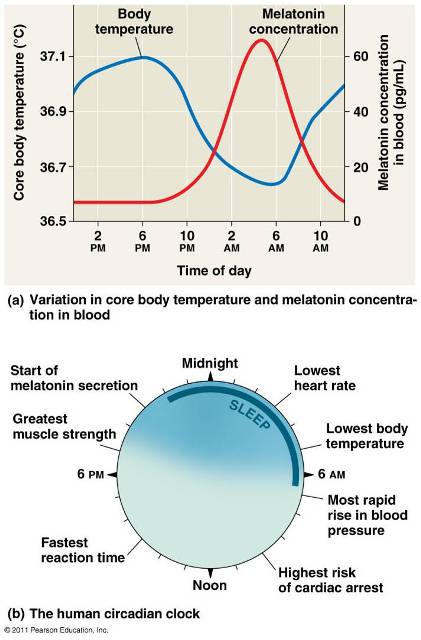 |
| What are the two sources of heat for thermoregulation? | internal metabolism and the external environment p.863 |
| Animals that are warmed mainly by heat generated by metabolism are said to be ______. | endotherms p.863 |
| Animals that are warmed mainly by heat generated by external sources are said to be ______. | ectotherms p.863 |
| Why does a bird (an endotherm) need to consume more food than a lizard (an ectotherm) of the same size? | The bird needs to use a lot of its energy to generate metabolic heat. p.863 |
| An animal whose body temperature varies with its environment is called a(n) _____. | poikilotherm (Most ectotherms are poikilotherms, but not all. For example, many ectothermic marine fishes and invertebrates inhabit waters with such stable temperatures that their body temperature varies less than that of humans and other mammals) p.863 |
| An animal whose body temperature remains relatively constant is a(n) _____. | homeotherm (Most endotherms are homeotherms, but not all. For instance, the bats and hummingbirds may periodically enter an inactive state in which they maintain a lower body temperature) p.863 |
| What are the four physical processes that any organism (and any object for that matter) uses to exchange heat? | Radiation, evaporation, convection, conduction p.864, 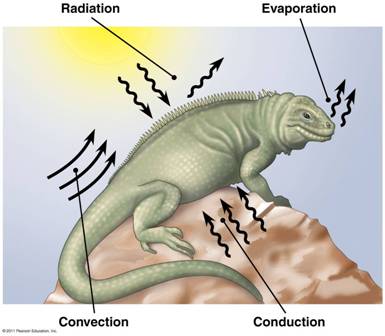 |
| _________ is the transfer of heat by the movement of air or liquid past a surface. | Convection (Technically, the movement of heat from the body's core to the extremities via blood flow is considered convection) p.864,  |
| The type of heat transfer that occurs when organisms absorb heat from the sun and lose heat to the environment in the form of electromagnetic waves. | Radiation p.864,  |
| ______ is the removal fo heat from the surface of a liquid that is losing some of its molecules with the highest kinetic energy as a gas. | Evaporation p.864,  |
| _____ is the direct transfer of thermal motion (heat) between molecules of objects in contact with each other. | Conduction p.864,  |
| Briefly explain how evaporation leads to cooling. | Water absorbs considerable heat when it evaporates. This heat is carried away from the body surface with the water vapor. p.865 |
| What is the main way that endotherms adjust metabolic heat production? | shivering (The increased muscle activity required to shiver generates heat) p.866 |
| Long-term torpor that is an adaptation to winter cold and food scarcity. | Hibernation p.872 |