| A | B |
|---|
| What are the four phases of the cell cycle? | G1, S, G2, and M p231,  |
| Chromosomes are only visible (with a light microscope) when ___. | the cell is dividing (After cell division in the G1 phase, the chromosomes are in the form of a single, long thin chromatin fiber. After DNA replication in the S phase, the chromatin fibers are attached forming two attached sister chromatids, and these start to condense by coiling more tightly, but are not visible with a light microscope until they have completely condensed into discreet visible chromosomes, still referred to as sister chromatids until they have separated into individual chromosomes at the start of anaphase) pp.229&232 |
| During which phase(s) of interphase is the cell growing by producing proteins and organelles? | G1, S, and G2 (The cell grows in all three phases of interphase, but only replicates the DNA during the S phase.) p231,  |
| When DNA is replicating, the cell is in the ___ phase of interphase. | S p231,  |
| Name the three major phases of interphase in the order that they occur. | G1, S, and G2 (Non-dividing cells, such as most nerve cells, spend their time in a phase of interphase called G0, "G-zero") p231,  |
| When the cell is undergoing cell division, it is in the ___ phase. | M (The mitotic (M) phase of the cell cycle includes mitosis and cytokinesis),  |
| In order, what are the five stages of mitosis? | Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (remember "I pinched pretty Martha's arm today" for interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Interphase is NOT a stage of mitosis, but it does come before mitosis) pp231-233,  |
| G1, S, and G2 all occur during ____. | interphase p231,  |
| Cell division ends when ___ is complete. | cytokinesis p230,  |
| The ____ is a series of events that a cell goes through from the time it is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two daughter cells. | cell cycle p228,  |
| The ___ is a region of a each sister chromatid in a duplicated chromosome containing specific DNA sequences where the chromatid is attached most closely to its sister chromatid. Proteins associated with this region give the condensed, duplicated chromosome a narrow waist. | centromere (The centromere is a region of a each sister chromatid in a duplicated chromosome containing specific DNA sequences where the chromatid is attached most closely to its sister chromatid. Proteins associated with this region give the condensed, duplicated chromosome a narrow waist) p229&230,  |
| The centromere is a region on a chromosome where ______ are held together most closely. | sister chromatids pp229&230,  |
| After chromosomes undergo DNA replication, they consist of two identical ____ that are attached to each other along their length by proteins called cohesins (most closely in a region called the centromere). | sister chromatids pp229&230,  |
| During which stages of mitosis are sister chromatids attached to each other? | prophase, prometaphase and metaphase p232,  |
| During which stage of mitosis do sister chromatids start to separate? | anaphase p233,  |
| During which stage of mitosis are sister chromatids lined up along the center of the cell? | metaphase (think metaphase = middle) p233,  |
| During which stage of mitosis do the chromosomes condense to become visible? | prophase p232,  |
| In animal cells, ________ are found in the centrosome, but don't seem to affect the ability of the cell to undergo mitosis. | centrioles p231,  , , 
|
| The division of the cytoplasm itself is called ___. | cytokinesis p230,  |
| During which stage of mitosis are the chromosomes divided into the two opposite ends of the cell with the nuclear membrane starting to reform? | telophase p233,  |
| The two main stages of cell division are ___. | mitosis and cytokinesis (Cell division is considered to be the mitotic (M) phase of the cell cycle. Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in-between cell division) p231,  , , 
|
| During normal cell division, a human cell with 46 chromosomes would produce two daughter cells with ___ chromosomes each. | 46 p230 |
The structures labeled A are,  | sister chromatids (This diagram shows sister chromatids joined only at the centromere, not by cohesin proteins all along the length of the chromatids. Evidently, some species do not have their sister chromatids joined at all points like humans do. See the description of prophase on page 232) p.231,  |
The structure labeled C is,  | a centromere (This diagram shows sister chromatids joined only at the centromere, not by cohesin proteins all along the length of the chromatids. Evidently, some species do not have their sister chromatids joined at all points like humans do. See the description of prophase on page 232) p.231,  |
| Cells that divide excessively and invade other tissues are referred to as ____ cells. | cancer p242 |
| When cells divide over and over again because of cancer, a lump of cells called a(n) ____ forms. | tumor p242 |
| All of the genetic information a cell possesses is called the cell's ______. | genome p229 |
| All body cells except reproductive cells are called ____ cells. | somatic p229 |
| Another word for reproductive, or sex cells is ________. | gametes p229 |
| How many molecules of DNA are contained in one chromosome? | one (It's very long. If stretched out, the DNA molecule in a typical human chromosome is about 4 cm long. All of the DNA in a typical human cell could stretch to about 2 meters) p229 |
| The type of cell division that produces sex cells (eggs and sperm) is called ______. | meiosis p229, 
|
| Prokaryotes reproduce by a type of cell division called ____. | binary fission (This term also applies to single-celled eukaryotic organisms like an amoeba, but binary fission in eukaryotic single-celled organisms involves mitosis while prokaryotic organisms to not use the steps of mitosis to divide their genetic material. The term binary fission simply means "division in half.") p236,  |
| Density-dependent inhibition is a phenomenon in which _____ cells stop dividing. | crowded (* Cancer cells don't seem to exhibit density-dependent inhibition) p241,  |
| Which type of cells do not seem to be affected by density-dependent inhibition or anchorage dependency? | cancer cells p242 |
| A tumor that stays at its original site of growth is called a(n) _____ tumor. | benign p242 |
| A tumor that is impacting other organs or tissues (is invasive) and is capable of spreading is called a(n) ______ tumor. | malignant (Individuals with malignant tumors are said to have cancer) p242 |
| The spread of cancer cells to locations distant from their original site of development is called _____. | metastasis,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | anaphase p233,  |
The process shown below is a special type of cell division called ______ that occurs in _______.,  | binary fission, prokaryotes (This term also applies to single-celled eukaryotic organisms like an amoeba, but binary fission in eukaryotic single-celled organisms involves mitosis while prokaryotic organisms to not use the steps of mitosis to divide their genetic material. The term binary fission simply means "division in half.") p237,  |
The picture below shows the formation of a _____ in a _____ cell.,  | cell plate, plant cell p235,  |
The red arrows are pointing to a(n) _____ in a(n) ____ cell.,  | cleavage furrow, animal cell p235,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | interphase p232,  |
The letter "A" in the picture below is pointing to _____.,  | two sister chromatids p234,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | metaphase p233,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | prophase p232,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | prometaphase p232,  |
The diagram below depicts a cell in ______.,  | telophase p233,  |
| How many chromosomes can be found in the typical human cell? | 46 p229 |
| How many PAIRS of chromosomes can be found in the typical human cell? | 23 pairs (One of each of the paired chromosomes comes from the person's father while the other comes from the mother) p229 |
| How many chromosomes can be found in the typical human reproductive cell? | 23 p229 |
| How many PAIRS of chromosomes can be found in the typical human reproductive cell? | zero (after going through meiosis, the newly formed gamete only has 1 of each pair of chromosomes, not both) p229 |
| The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the letter ___. | n p251 |
| A carrot has a diploid number of 18. What is it's haploid number? | 9 p251 |
| Gametes are normally produced by the process of ___. | meiosis pp251&252, 
|
| Another word for sex or reproductive cell is ___. | gamete p249 |
| What are the two main types of gametes? | sperm and egg p249 |
| During which stage of meiosis do chromosomes undergo synapsis to pair up and connect with each other? | prophase I (Below is a pair of homologous chromosomes, loosely attached to each other. Each chromosome is duplicated as a pair of sister chromatids. This formation is often times called a tetrad) p254, 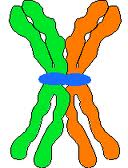 |
| During which stage of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell? | metaphase I p254 |
| During which stage of meiosis do sister chromatids separate from each other? | anaphase II p255 |
| What happens between meiosis I and meiosis II that reduces the number of chromosomes? | DNA replication does not occur but cytokinesis does. pp253-255 |
| When does DNA replication occur during meiosis? | Interphase I only (remember, there is no interphase II) p253 |
| What is the diploid number of chromosomes in humans? | 46 (also written as 2n=46) p251 |
| What is the haploid number for humans? | 23 (also written as n=23) p251 |
| The gametes of fruit flies have 4 chromosomes each. What is the diploid number of chromosomes for fruit flies? | 8 (remember the diploid number is always twice the haploid number) p251 |
| _________ chromosomes are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, but are not identical. | Homologous (They are not identical because one came from the mother and the other from the father) p250, 
|
| _________ are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, and are identical. | Sister chromatids p253 |
| A(n) _____ is a segment of DNA that has the instructions for making one protein. | gene p249 |
| An organism's gametes have ___ the number of chromosomes as are found in the organism's body cells. | half p251 |
| During which stage of meiosis might crossing over occur? | prophase I pp254&258 |
| When homologous chromosomes are lined up next to each other during meiosis, they might swap pieces of DNA. This phenomenon is called ___. | crossing over pp254&258 |
| Crossing over during meiosis is important because it increases ___. | genetic variation (= the number of different chromosomes, and therefore different combinations of traits, that offspring can inherit) p258 |
Which diagram is mitosis and which is meiosis?,  | Mitosis is on the left and meiosis is on the right. p256,  |
Which process from meiosis is shown below and during which stage would it occur?, 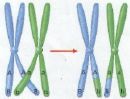 | The picture shows "crossing over" and it usually happens during prophase I. pp258&259,  |
| The transmission of traits from one generation to the next is called _______ or ________. | inheritance or heredity p248 |
| The scientific study of heredity is called ______. | genetics p248 |
| The fusion of sperm and egg is called _____. | fertilization pp248&251 |
| Segments of DNA that act as hereditary units are called ____. | genes p249 |
| Reproductive cells are called _____. | gametes (they are also called sex cells or reproductive cells and include the egg and sperm) p249 |
| The DNA of eukaryotes is subdivided into _____ within the nucleus of the cell. | chromosomes p249 |
| Most human cells have ____ chromosomes. | 46 p249 |
| How many DNA molecules make up a chromosome? | 1 p.249 |
| One chromosome includes several hundred to a few thousand _____, each of which is a specific sequence of nucleotides within the DNA molecule. | genes p249 |
| Single-celled eukaryotic organisms can reproduce asexually by _____ cell division. | mitotic p249 |
| In ______ reproduction, a single individual is the sole parent and passes identical copies of all its genes to its offspring. | asexual p249 |
| A(n) _____ cell is any cell other than a gamete. | somatic p249 |
| A picture of all the chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell, arranged side-by-side in homologous pairs is called a(n) _____. | karyotype p250,  |
| The X and Y chromosomes are referred to as the _______. | sex chromosomes p250 |
| When considering a homologous pair of chromosomes, one came from the ____ and the other came from the ____. | father, mother p250 |
| Diploid cells are cells that have ____________. | both pairs of homologous chromosomes p251 |
| Haploid cells are cells that have _____________. | a single chromosome set (not both pairs of a homologous set) p251 |
| A fertilized egg is called a(n) _____. | zygote p251 |
| The type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in half is called _____. | meiosis p252, 
|
| During _______ of meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate. | Anaphase I p254,  |
| During ____ of meiosis, sister chromatids line up in a straight line. | Metaphase II p255,  |
The picture below is called a(n) ______ .,  | karyotype (These are the chromosomes of a male. You can tell because there is one X and one Y chromosome) p250,  |
| In humans, what type of sex chromosomes do males have? | an X and a Y p250 |
| In humans, what type of sex chromosomes do females have? | two X chromosomes p250 |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | prophase I p254,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 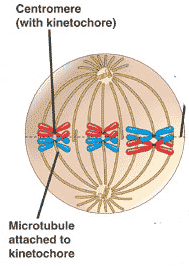 | metaphase I (Homologous chromosomes are lining up to get separated. In metaphase II, sister chromatids are lining up to get separated) p254,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | anaphase I (Notice that homologous chromosomes are separating, but not the attached sister chromatids) p.254,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 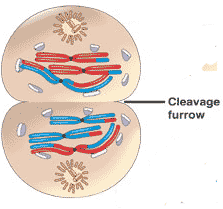 | telophase I p254,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 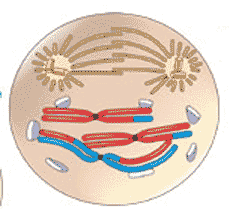 | prophase II p255,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | metaphase II (If it was metaphase I, you would see homologous pairs of duplicated chromosomes, a.k.a., tetrads, lined up) p255,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?,  | anaphase II (If it was anaphase I, you would see homologous chromosomes pulling apart with sister chromatids still stuck together) p255,  |
Which stage of meiosis is shown below?, 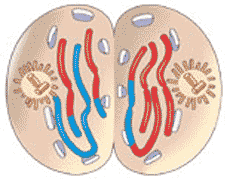 | telophase II (If it was telophase I, you would still see sister chromatids stuck together) p255,  |
| Meiosis results in ___ non-identical daughter cells (looking for a number here) | four p256 |
| Different forms of the same gene are called _____. | alleles p265 |
| Dominant alleles are represented by a _______ letter. | capital (ex:T= tall in pea plants) p266 |
| Recessive alleles are represented by a _______ letter. | lowercase (ex: t = short in pea plant; notice that the letter is the first letter of the dominant trait.) p266 |
| The types of alleles that an organism inherits is known as the ______. | genotype (example = Bb) |
| The physical expression of two alleles is known as the organism's _____. | phenotype p266 |
| Bb would be called the organism's _____ while "brown eyes" would be the organisms _____. | genotype, phenotype p266 |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is BB? | Brown eyes pp266&267 |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is Bb? | Brown eyes (remember that B is dominant) pp266&267 |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is bb? | blue eyes pp266&267 |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organisms genotype be if the organism was heterozygous? | Bb (remember that 'hetero' means 'different') pp266&267 |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organisms genotype be if the organism is homozygous dominant? | BB (remember that 'homo' means 'same' or 'alike') pp266&267 |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organisms genotype be if the organism is homozygous recessive? | bb (remember that 'homo' means 'same') pp266&267 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 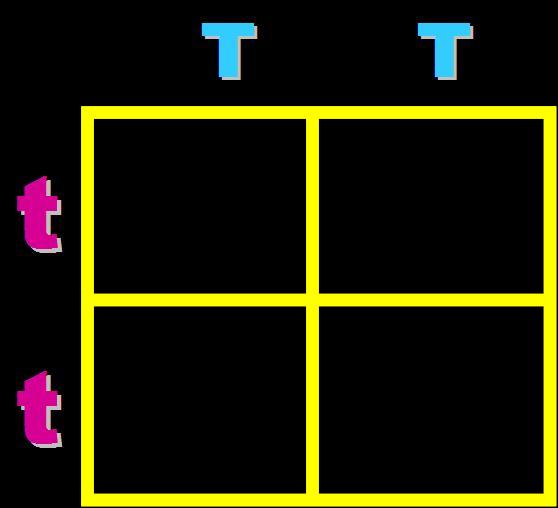 | Genotype = 100% Heterozygous (Tt) Phenotype = 100% tall pp266&267, 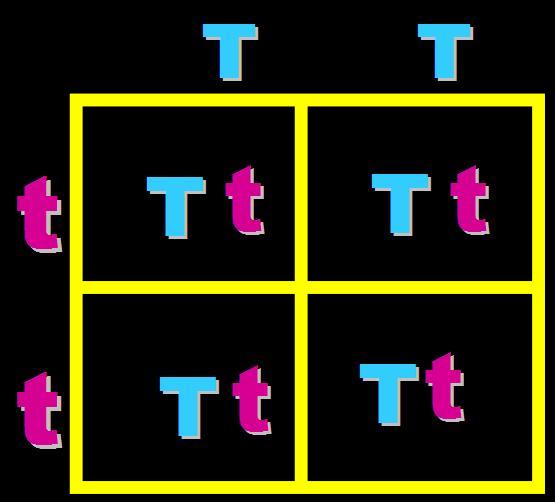 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 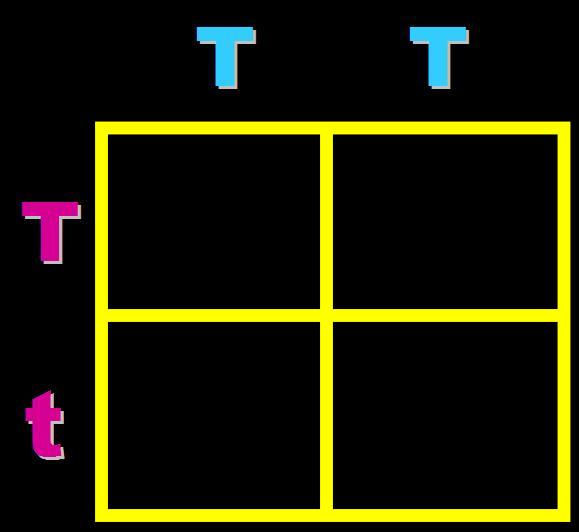 | Genotype = 50% homozygous dominant (TT) and 50% heterozygous (Tt) Phenotype = 100% Tall pp266&267, 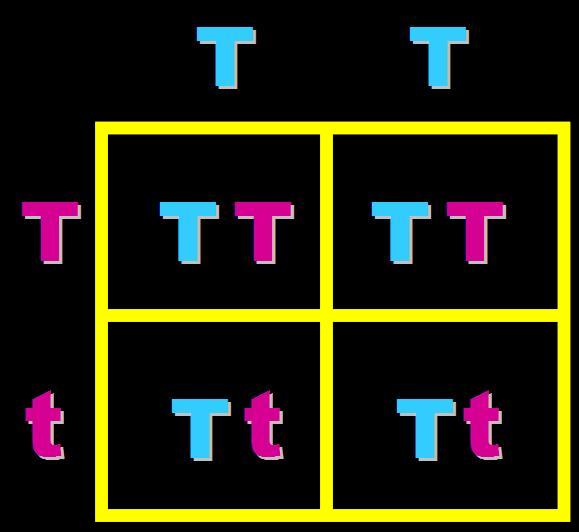 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 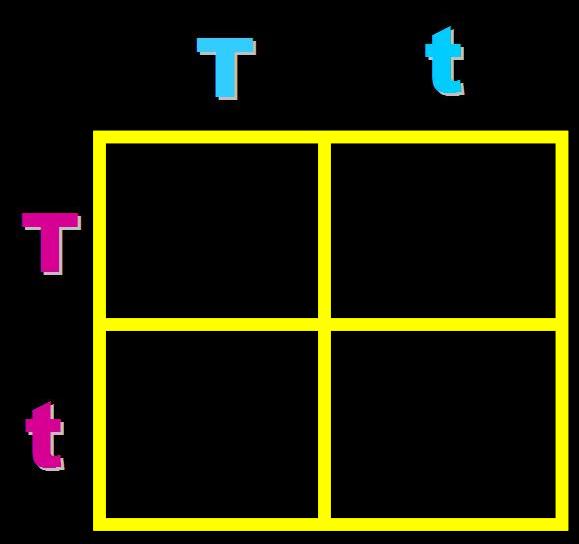 | Genotype = 25% Homozygous dominant (TT), 50% heterozygous (Tt) and 25% homozygous recessive (tt) Phenotype = 75% Tall and 25% short pp266&267,  |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages.,  | Genotype = 50% heterozygous (Tt) and 50% homozygous recessive (tt) Phenotype = 50%Tall and 50% short pp266&267, 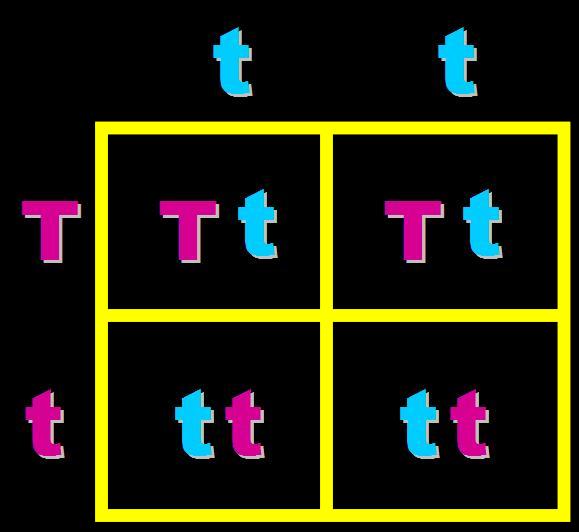 |
| How would you set up a Punnett Square for a cross between a short male pea plant and a heterozygous tall female? | pp266&267,  |
| Gregor Mendel used ____ to study the inheritance of traits. | pea plants p262 |
| The person considered to be the father of genetics is ___. | Gregor Mendel p262 |
| True-breeding pea plants that produced constricted pods were crossed with true-breeding plants that produced inflated pods. The resulting offspring all had inflated pods. It can be concluded that the ____ pod allele is dominant. | inflated pp266&267 |
| The type of inheritance where neither allele is dominant and they tend to produce a mix of the two traits such as blue + white = light blue would be _____. | incomplete dominance p271 |
| The type of inheritance where both alleles are dominant (such as red fur + white fur = red and white fur hairs in roan cattle) is known as ____. | codominance p272 |
| The type of inheritance where there is more than two alleles for a single character, such as A, B, and O alleles for blood type, is known as ____. | multiple alleles p272 |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,IA, what is your blood type? | type A p273 |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,i, what is your blood type? | Type A p273 |
| If your genotype for blood type is IB,IB, what is your blood type? | Type B p273 |
| If your genotype for blood type is IB,i, what is your blood type? | type B p273 |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,IB, what is your blood type? | Type AB p273 |
| If your genotype for blood type is ii, what is your blood type? | Type O p273 |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring of this cross? (The A stands for IA and the O stands for i),  | 25% type AB blood, 25% type A blood, 25% type B blood, 25% type O blood p273,  |
| How would you set up a Punnett Square for a cross between a heterozygous blood type A male and a heterozygous blood type B female? | (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's) p273,  |
| How would you set up a cross between a male with type AB blood and a female with type O blood? (The A stands for IA, the B's stand for IB and the O stands for i) | (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's) p273, 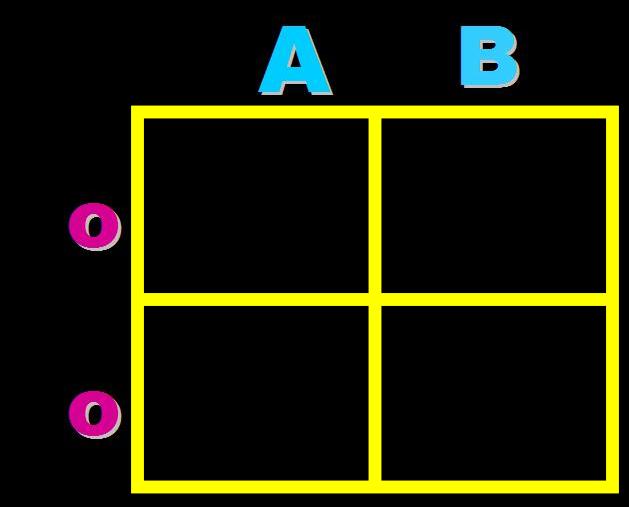 |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring and what are the odds of each?,  | 50% of the offspring are expected to have type A blood and 50% are expected to have type B blood. All offspring will be heterozygous (Remember that the O allele is recessive) p273,  |
| A trait, like human skin color, that involves several different genes is called a(n) _____. | polygenic trait (remember, "poly" means many and "genic" refers to genes) p274 |
| Mendel made sure he started his experiments with plants that were ______. This type of plant always produces offspring of the same variety when it self-pollinates. | true-breeding p264 |
| Which law states that the two alleles for a heritable character separate during gamete formation and end up in separate gametes? | The Law of Segregation p265 |
| A dihybrid cross between 2 individuals that are heterozygous for two independently assorting characterisitics (such as seed color and seed shape), produces the classic ________ ratio. | 9:3:3:1 ratio p268,  |
| Which law states that each pair of alleles segregate independently of other pairs during gamete formation? When is this law not true? | Law of independent assortment. This law does not hold true if the alleles for two different characteristics are located on the same chromosome. p269 |
| The type of inheritance that is shown when a trait is controlled by two or more genes is _______. | polygenic inheritance p274 |
| Human skin color is controlled by ________ inheritance. | polygenic (meaning that more than one gene affects skin color) |
| Can include physical appearance, internal anatomy, physiology and behavior. | Phenotype p266 |
| A(n) ________ is a family tree that describes the interrelationships of parents and children across generations. | pedigree p275,  |
A chart like the one below is called a _____.,  | pedigree p275,  |
| ________ disease is a genetic disease that causes red blood cells to become malformed but also gives carriers increased resistance against the _____ parasite. | sickle-cell disease, malaria parasite p277 |
| A cross in which you are following only 1 character and using a 2 X 2 Punnett square is called a(n) _______ cross. | monohybrid p267 |
| A cross in which you are following only 2 characters (like flower color and pod shape in pea plants) and using a 4 X 4 Punnett square is called a(n) _______ cross. | dihybrid p268 |
| An aberration in chromosome structure resulting from reattachment in a reverse orientation of a chromosome fragment to the chromosome from which the fragment originated. | inversion p298 |
| _____ is a human genetic disease caused by a recessive X-linked allele; characterized by excessive bleeding following injury. | Hemophilia p291 |
| _______ is a human genetic disease caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21; characterized by mental retardation and heart and respiratory defects. | Down syndrome p299 |
| Down syndrome is a human genetic disease caused by the presence of ___________; characterized by mental retardation and heart and respiratory defects. | an extra chromosome 21 p299 |
| _______ are genes located close enough together on a chromosome to be usually inherited together. | Linked genes p292 |
| ______ is an error in meiosis (can also occur in mitosis), in which both members of a pair of homologous chromosomes, or both sister chromatids, fail to move apart properly. | Nondisjunction p297 |
| ______ is a deficiency in a chromosome resulting from the loss of a fragment through breakage OR a mutational loss of one or more nucleotide pairs from a gene. | A deletion p298 |
| A gene located on a sex chromosome (on the X or Y or both) is called a(n) _____. | sex-linked gene (Genes that are located on both the X and Y chromosomes would be located in the homologous regions of the sex chromosomes. They would be inherited like autosomal genes and would not show a sex-linked pattern of inheritance) p290 |
| A(n) ______ is an aberration in chromosome structure due to fusion with a fragment from a homologous chromosome, such that a portion of a chromosome is repeated. | duplication p298 |
| ______ is a chromosomal alteration in which the organism possesses more than two complete chromosome sets. | Polyploidy p298 |
| _____ is an abberation in chromosome structure resulting from the attachment of a chromosomal fragment to a nonhomologous chromosome. | Translocation p298 |
| A translocation is an abberation in chromosome structure resulting from the attachment of a chromosomal fragment to a _________ chromosome. | nonhomologous p298 |
| The reciprocal exchange of genetic material between nonsister chromatids during prophase I of meiosis is called _____. | crossing over p294 |
| Four types of chromosomal mutations are ___. | Deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations p298 |
The type of mutation shown below is a(n) _____.,  | chromosomal deletion p298,  |
The type of mutation shown below is a(n) _____.,  | chromosomal duplication p298,  |
The type of mutation shown below is a(n) _____.,  | chromosomal inversion p298,  |
The type of mutation shown below is a(n) _____.,  | chromosomal translocation p298,  |
What would be the sex of the person who owns these chromosomes?,  | male (notice the X and the Y chromosome at the last pair) pp289-290,  |
What type of genetic disorder does the owner of these chromosomes have?,  | Down syndrome (notice the extra chromosome at the 21st pair) p299,  |
| In humans, color blindness is an X-linked recessive allele. What are the expected phenotypes of the offspring if both parents have normal vision but the mother is heterozygous? | 100% normal vision girls and 50% of the boys are expected to be color-blind. p291, 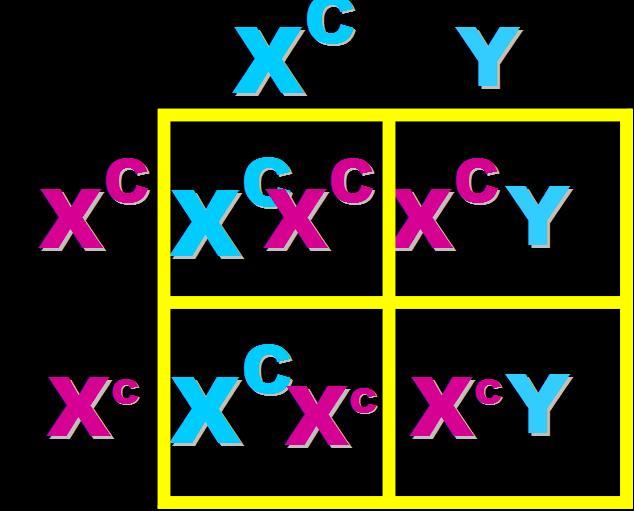 |
| What accounts for recombination of linked genes? | Crossing over p294 |
| ___________ are the source of all new alleles, which can lead to new phenotypic traits. | Random mutations p297 |
| In which kingdom is polyploidy fairly common? | Plants p298 |
| Name two other places besides the nucleus where DNA can be found in eukaryotic cells. | Mitochondria and chloroplasts (these organelles, as well as some other plastids in plants, contain their own DNA. It replicates when the organelles do. The existence of these extranuclear genes in these organelles lends support to the endosymbiotic theory of organelle origin. Defects in animal mitochondrial genes are passed down from the mother because mitochondria an animal inherits comes almost exclusively from the egg) p301 |