| A | B |
|---|
17th Amendment,  | Direct election of Senators |
19th Amendment,  | Women's right to vote |
Gilded Age,  | Period of lavish lifestyles and income inequality |
John D. Rockefeller,  | Created monopoly in the Oil industry |
Andrew Carnegie,  | Made Pittsburg the steel capital of the USA |
Cornelius Vanderbilt,  | Created an empire in the railroad industry |
Transcontinental Railroad,  | Allowed settlers to move west |
J.P. Morgan,  | Banker and Financier |
The Wright Brothers,  | successful built and flew first airplane |
Thomas Edison,  | invented practicle electric light bulb |
Alexander G. Bell,  | invented the telephone |
Booker T. Washington,  | advocated education to end segregation |
W.E.B. Du Bois,  | founded the NAACP |
Ida B. Wells,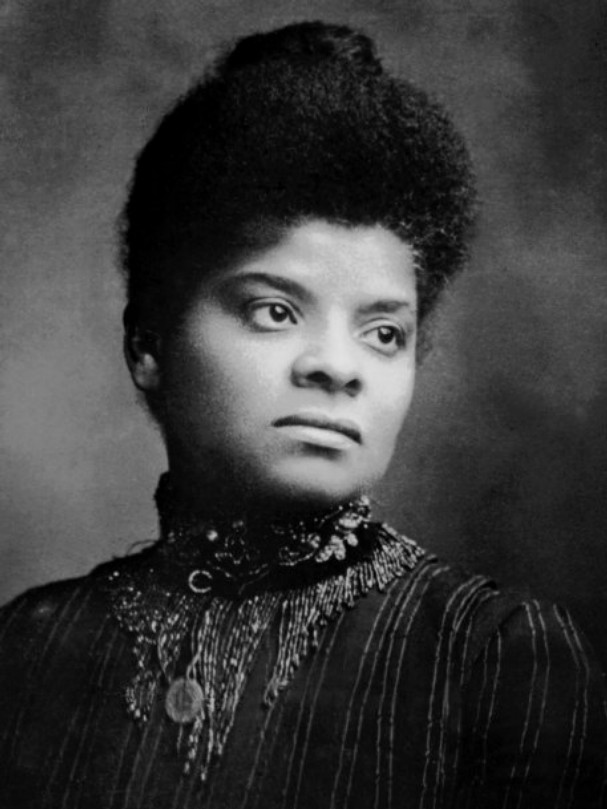  | led a campaign against lynching |
Samuel Gompers,  | founded the skilled American Federation of Labor |
Eugene V. Debs,  | founded the American Railways Union |
Knights of Labor,  | First major Labor Union in the USA open to skilled & unskilled workers |
Cowboys,  | drove cattle from Texas to railheads on the Great Plains |
The Homestead Act,  | Act of Congress offered Americans free land in the West |
Henry Ford,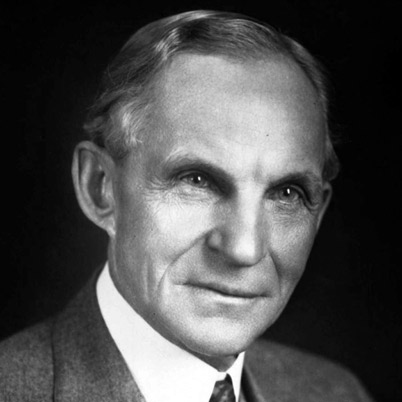  | develped the assembly line method to improve production |
Plessy v. Ferguson,  | Court case established doctrine of separate but equal |
Chinese,  | This immigrant group provided labor for the transcontinental Railroad |
Haymarket Square,  | Site where anarchists threw a bomb at police during a labor protest |
Pullman strike,  | ARU strike that disrupted rail traffic in Chicago |
Homestead Steel Strike,  | Industrial strike broken by a private army hired by the factory |
Recall,  | ability of the people to vote and remove elected officials |
| Initiative | ability of the people to draft laws for the legislature to vote on |
Referendum,  | ability of the people to vote on new laws themselves |
secret ballot,  | reform that guarantees no one knows who you vote for |
subway,  | New York city built the first of these |
Susan B. Anthony,  | Fought from women's right to vote |
Ellis Island,  | immigration processing center in New York City |
Statute of Liberty,  | Many immigrants saw this when entering New York harbor |
| Freedom and economic opportunity | The reason millions of immigrants came to America |
Theodore Roosevelt,  | Offered a progressive plan called Square Deal |
Woodrow Wilson,  | Offered a progressive plan called New Freedom |
Rocky Mountains and Great Plains,  | Area of USA rapidly settled by ranchers and farmers in late 1800s |
| Southerners and African Americans | These groups moved west in particular after the Civil War seeking opportunities |
| Immirgration prior to 1871 | Mainly came from Northern and Western Europe |
Immigration after 1871,  | mainly from Southern and Eastern Europe |
mechanical reaper,  | invention made farming more productive and profitable |
public schools,  | helped assimilate new immigrants into US Society |
the melting pot,  | the process of many immigrants blending together to become Americans |
| Detroit, Pittsburg, New York, Detroit & Cleveland | growing industrial cities where immigrants settled |
| Laissez-Faire | economic philosophy that limits government involvement in the economy |
Progressives,  | wanted government controlled by the people, government regulation and social justice |
muckrakers,  | wrote about child labor, corruption and business practices |
Sherman Anti-Trust,  | Outlaws business practices that limit trade and competition |
| Clayton Anti-Trust Act | Act prohibits price-fixing by businesses |
| Labor issues | working conditions, hours and wages |