| A | B |
|---|
| What was the mechanism that Darwin and Wallace proposed to explain how evolutionary change could occur? | Natural Selection |
| Remains or traces of organisms from the past are called ______. | fossils |
| Paleontology is the study of _____. | fossils |
________ theory of evolution hypothesized that species evolve through "use" and "disuse" and the inheritance of acquired traits. This idea was later proved to be _____.,  | Lamarck's, wrong,  |
| Who was the other person who proposed a theory of Evolution similar to Darwin's around the same time period? | Alfred Russel Wallace |
| One of the observations that helped Darwin form his theory of evolution is that for any species, population sizes would increase ______ if all individuals that are born reproduce successfully. | exponentially (Thomas Malthus, an economist worried about the ability to feed a growing human population, influenced Darwin's thinking in this area) |
| Another set of observations that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that even though populations tend to grow exponentially, populations in nature tend to be ___ in size because resources are ____. | stable, limited |
| Production of more individuals than the environment can support leads to a _______ among individuals of a population, with only a fraction of the offspring surviving. | struggle for existence |
| An important observation that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that members of a population are not all ____. | alike |
| An important observation that helped Darwin formulate his theory of evolution is that individuals in a population have varying characteristics and much of this variation is _____. | heritable |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that individuals whose traits give them a high probability of surviving and ____________ are likely to leave more _________ than other individuals. | reproducing, offspring |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that the unequal ability of individuals to ________ and _________ will lead to a gradual change in a population, with favorable characteristics accumulating over generations. | survive, reproduce |
| An important part of Darwin's theory of evolution is that the unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce will lead to a ________ in a population, with ________ accumulating over generations. | gradual change, favorable characteristics |
| The process of humans modifying other species over many generations by selecting and breeding individuals that possess desired traits is called ________. | artificial selection (farmers have been doing this for the last 10,000 years) |
| Natural selection is differential _______ in reproduction that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | success |
| ________ is differential success in reproduction that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | Natural selection |
| Natural selection is differential success in __________ that results from the interaction between individuals that vary in heritable traits and their environment | reproduction |
| Natural selection can produce an increase, over time, in the adaptation of organisms to their ______. | environment |
| Natural selection can produce an increase, over time, in the _____ of organisms to their environment. | adaptation |
| In humans, the use of antibiotic drugs selects for pathogens that through __________ are resistant to the drugs’ effects | chance mutations |
| Homology is similarity resulting from common ______. | ancestry |
| ________ is similarity resulting from common ancestry. | Homology |
| ___________ structures between organisms are anatomical resemblances that represent variations on a structural theme that was present in a common ancestor. | Homologous,  |
The picture below shows ______ structures.,  | homologous,  |
Homologous structures are thought to have evolved from a common structure that has become different through ________ evolution.,  | divergent,  |
| __________ structures are thought to have evolved from a common structure that has become different through divergent evolution. | Homologous,  |
| Comparative ________ reveals additional anatomical homologies not visible in adult organisms. | embryology, 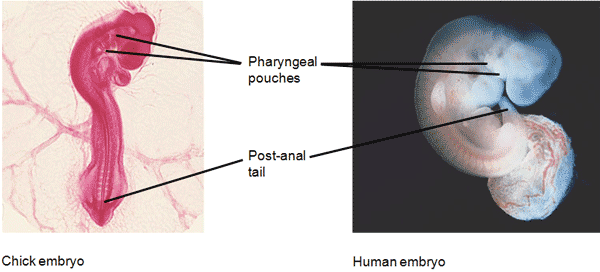 |
______ structures are structures that no longer seem to have a function and are remnants of structures that served important functions in the organism's ancestors.,  | Vestigial,  |
| The human appendix is an example of a(n) ______ structure. | vestigial |
| Biologists also observe homologies among organisms at the molecular level such as ______ that are shared among organisms inherited from a common ancestor. | genes |
| _______ structures are very similar in look and purpose due to convergent evolution, but are not thought to have common origin. | Analogous,  |
Analogous structures (like the wings in the picture below) are very similar in look and purpose due to ______ evolution, but are not thought to have common origin.,  | convergent,  |
| Evolution above the species level (ie - the kind that creates new species) is called _______. | macroevolution p507 |
| ____ genes determine such basic features as where a pair of wings and a pair of legs will develop on a bird or how a flower’s parts are arranged. | Homeotic genes p526 |
| The products of one class of homeotic genes called ____ genes provide positional information in animal embryos. | Hox (Examples include the development of fins in fish and limbs in tetrapods) p526 |
| The number of years it takes for 50% of an original sample of a radioactive isotope to decay is called the isotope's _____. | half-life p512,  |
| The supercontinent formed near the end of the Paleozoic era when plate movements brought all the landmasses of Earth together is called ______. | Pangaea p520, 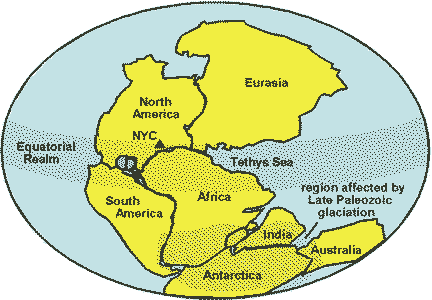 |
| The model of the origin of eukaryotes that proposes that mitochondria, chloroplasts, and perhaps other cellular structures were formerly small prokaryotes that lived symbiotically inside larger cells. | endosymbiont theory (aka - endosymbiotic theory) p516,  |
| The half-life of carbon-14 is 5700 years. If there was 10 grams of carbon-14 in a bone fragment 11,400 years ago, how much carbon-14 would still be left today? | 2.5 grams (After 5700 years, half of the 10 gram original sample would be left, so after 5700 years there would be 5 grams. In the next 5700 years, half of that 5 grams would be left, so after a total of 11,400 years ago, only 2.5 grams would be left) p512,  |
| Scientific data indicates that Earth formed about _____ years ago. | 4.6 billion p508 |
| The first genetic material was probably ____ due to its ability to catalyze reactions including its own self replication. | RNA p509 |
| The earliest known fossils date back about _____ years ago. | 3.5 billion pp507&514 |
| Earth's early atmosphere was much different than today's atmosphere in that it lacked _____. | oxygen p516 |
| In 1953, ______, created laboratory conditions similar to those hypothesized for early Earth and found that amino acids along with other organic compounds were able to form spontaneously. | Stanley Miller p509,  |
| What type of rocks are most fossils in? | sedimentary p510 |
| The _____ refers to a relatively brief period of time in geologic history when many present-day phyla of animals first appeared in the fossil record. This burst of evolutionary change occurred about 535 to 525 million years ago and saw the emergence of the first large, hard-bodied animals. | Cambrian Explosion p518 and G-5 |
| How long ago did dinosaurs go extinct? | 65 million years ago p524 |
| In classification, the taxonomy category above class (less specific than class) is called ______. | phylum p537 |
| In classification, the taxonomic category above genus (less specific than genus) is called _____. | family p537 |
| An evolutionary timing method based on the observation that at least some regions of the genome evolve at constant rates. | Molecular clock p549 |
| In classification, the taxonomic category above family (less specific than family) is called _____. | order p537 |
| A taxonomic category above the species level, designated by the first word of a species' binomial scientific Latin name. | genus p537 |
| In classification, the taxonomic category above order (less specific than order) is called _____. | class p537 |
| An evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade is called a(n) _____. | shared derived character p543 |
| The taxonomic category above the kingdom level (less specific than kingdom) is called _____. | domain p537 |
| When writing a scientific name, what is capitalized and what font style is used? | Only the first letter of the genus name is capitalized. Italics are used for all letters.37 |
| The scientific name is composed of the organisms ______ name and _____ name. | genus and species name p537 |
| Felis catus and Felis concolour belong to the same ____. | They belong to the same genus, but not species. Since they belong to the same genus, they automatically belong to the same family, order, class, phylum, kingdom and domain also. p537 |
| Put the following terms in order from largest group to smallest as far as the number of species that belong to each: Class, Domain, Family, Genus, Kingdom, Order, Phylum, Species, | Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (Remember the phrase, "Did King Phillips court order fresh grilled salmon?") p537 |
| A genus is composed of a number of related ____. | species p537 |
| Cat is a(n) _______ name that is different from country to country or language to language but Felis catus is a _______ name that is used by all scientists throughout the world. | common, scientific p537 |
| What genus does Ursus maritimus belong in? | Ursus (the first part of a scientific name is always the name of the genus to which the organism belongs) p537 |
| Homo sapien belongs to which species? | sapien (the second name of the scientific name is always the species name to which the organism belongs) p537 |
| The animals Panthera leo (lion) and _____ tigris (tiger) belong to the same genus. | Panthera p537 |
| In biology, an evolutionary innovation is also referred to as a(n) ____. | shared derived character (for example, feathers were an evolutionary innovation that set feathered dinosaurs, and later, birds, apart from all other reptiles. Therefore feathers are a type of derived characteristic that today would only be seen in birds and not other animals) p543 |
| The branch of biology concerned with naming and classifying the diverse forms of life is called _____. | taxonomy p537 |
| The second broadest taxonomic category after domain is called _____. | kingdom p537 |
| Similarities in structure due to similar natural selection pressures instead of common ancestry are called analogies and are due to ______ evolution. | convergent p540,  |
| Homologies (phenotypic and genetic similarities due to shared ancestry) may look quite different from each other due to ____ evolution. | divergent p540 |
| Name the three domains and label each as being either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. | Archaea (prokaryotic), Bacteria (prokaryotic), Eukarya (eukaryotic) pp551&552 |
| Which prokaryotic domain seems to be most closely related to the Eukarya based on molecular studies? | Archaea (Analysis of other genes however suggest that the domain bacteria might be more closely related to Eukarya. For example, genes that influence metabolism in yeast are more similar to those in the domain Bacteria. To further complicate matters, horizontal gene transfer between domains early on make it difficult to know where genes originated from) p552 |
| From which domain are chloroplasts and mitochondria thought to have originated from? | Bacteria p552 |
| _____ is the process by which genes are transferred from one genome to another through mechanisms such as viral infection, exchange of transposable elements or plasmids, and perhaps even the fusion of organisms. | Horizontal gene transfer (It appears that there may have been horizontal gene transfer between bacteria and early eukaryotic organisms) p553 |
| Organisms that must consume organic molecules for a source of carbon to build other organic molecules are called _____. | heterotrophs (The two types of heterotrophs are photoheterotrophs and chemoheterotrophs.) p564 |
| Any organism that can use some form of carbon dioxide as its carbon source is called a(n) _____. | autotroph (The two types of autotrophs are photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs) p565 |
| The assimilation of atmospheric nitrogen by certain prokaryotes into nitrogenous compounds that can be directly used by plants is called ____. | nitrogen fixation p564 |
| The larger participant in a symbiotic relationship, serving as home and feeding ground to the symbiont is called the ____. | host p570 |
| A staining method that distinguishes between two different kinds of bacterial cell walls is called the ____. | gram stain p557,  |
| The sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface and sometimes helping to glue the cell to surfaces is called the ____. | capsule (Its called a capsule if it is dense and well defined. If it is less well organized, it is called a slime layer) p558,  |
| A thick-coated, resistant cell produced within a bacterial cell exposed to harsh conditions is called a(n) ____. | endospore p560, 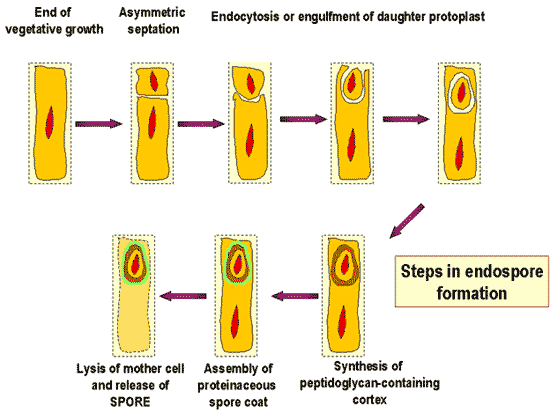 |
| Movement toward or away from a stimulus is called _____. | taxis p558 |
| A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of a bacterial chromosome is called a(n) ____. | plasmid (plasmids are also found in some eukaryotes, such as yeast) p560, 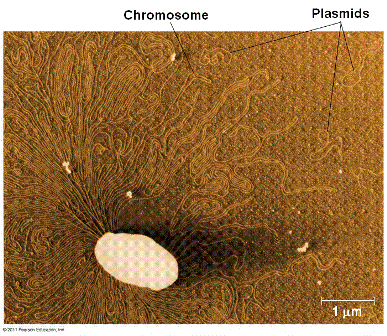 |
| An ecological relationship between organisms of two different species that live together in direct contact is called _____. | symbiosis p570 |
| An organism that absorbs nutrients from the body fluids of living hosts would be classified as a(n) ____. | parasite p570 |
| A bacterium that absorbs nutrients from nonliving organic materials such as corpses, fallen plant material, and the wastes of living organisms and converts them into inorganic forms would be classified as a(n) ____. | decomposer p570 |
| A symbiotic relationship in which the symbiont benefits at the expense of the host is called ____. | parasitism p570 |
| A symbiotic relationship in which both participants benefit is called ____. | mutualism p570 |
| A symbiotic relationship in which the symbiont benefits but the host is neither helped nor harmed is called _____. | commensalism p570 |
Prokaryotic cells lack _______, 
| a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles pp559&560 |
| Cells that have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles are called ____ cells. | eukaryotic G-13, 
|
| Bacteria that stain purple are known as _______ . | gram-positive bacteria p557,  |
| Bacteria that don't stain purple are known as ______. | gram-negative bacteria p557,  |
| Mutualism, parasitism and commensalism are all types of ____. | symbiosis p570, 
|
| Some bacteria have a whip-like tail called a ____. | flagellum p558, 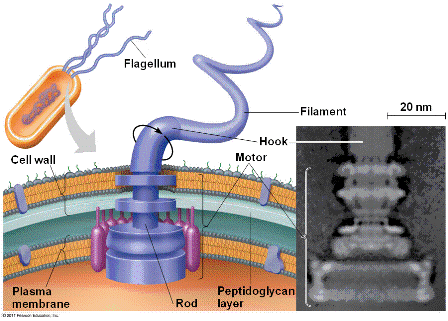 , , 
|
| The structure just outside the cell membrane of a bacterium is called the ___. | cell wall p557,  |
| Which gas in the atmosphere do some bacteria capture and turn into fertilizer that plants can use? | nitrogen p564 |
| Medicines that kill bacteria as well as other living microorganisms are known as ____. | antibiotics p564, 
|
| Specialized pili, called sex pili, link prokaryotes during ______, a process in which one cell transfers DNA to another cell. | conjugation p562, 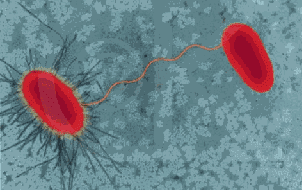 |
| What is the scientific name of the bacteria that reside in the intestines of mammals, including humans? | E. coli (Escherichia coli) p572 |
| What do you call the photosynthetic oxygen producing bacteria? | Cyanobacteria (a.k.a. - Blue-green bacteria) |
| ______ is the movement of an organism toward or away from chemicals, such as oxygen, nutrients, or pheromones). | chemotaxis p558 |
| Prokaryotes reproduce asexually in a process called _____. | binary fission p560,  |
| Under ideal conditions, some prokaryotes (including E. coli) can divide every ______. | 20 minutes (At this rate, 1 bacterium could become a million in less than 7 hours. At this rate, 1 bacterium could give rise to enough bacteria to outweigh the Earth in only two days!) p560 |
| The uptake of foreign DNA by prokaryotes from their surroundings is called ____. | transformation p562 |
| In the process of _____, DNA can be transferred from one prokaryote to another by a virus called a bacteriophage. | transduction p562, 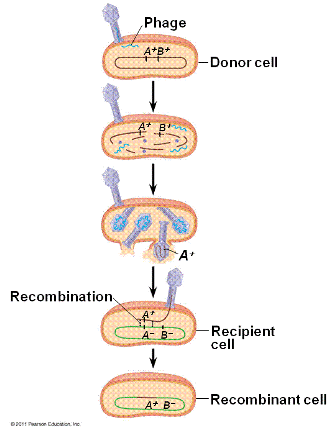 |
| Describe a typical bacterial chromosome. | One double-stranded circular DNA molecule associated with a small amount of protein (below is a diagram of bacterial chromosome replication) p559,  |
| In prokaryotes, the direct transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined is called _____. | conjugation (can happen in eukaryotic ciliates also in a sexual process in which the two cells exchange haploid micronuclei) p562,  |
| Any organism that needs only carbon dioxide in some form as a carbon source is called a(n) ____. | autotroph (The carbon dioxide can be in the dissolved form of the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-) p564 |
| A catabolic pathway in which inorganic molecules other than oxygen accept electrons at the "downhill" end of the electron transport chain is called ____. | anaerobic respiration (Examples of alternate electron acceptors include the nitrate ion, NO3-, and the sulfate ion, SO4-2) G-2, p564 |
| A catabolic process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose, or other organic molecules, without an electron transport chain and that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid, is called ____. | fermentation (Anaerobic respiration is different from fermentation because it has an electron transport chain with something other than oxygen accepting the electrons. Since it has an electron transport chain, anaerobic respiration produces many more ATP than fermentation) G-14, p564 |
| Any organism that causes disease, including quite a few prokaryotic species, is called a(n) ____. | pathogen (Although pathogenic prokaryotes are the best known of the prokaryotes, they represent only a small fraction of prokaryotic species. There are no known pathogenic Archaeans. Bacteria cause about half of all known human diseases.) p570 |
| Where are two places that you would find bacteria that have symbiotic relationships with humans? | Skin and intestines (There may be up to 150 bacterial species with a density of 10 million cells per square centimeter. Our intestines are home to 500 - 1000 species of bacteria, most of them mutualistic that help us process our food. Because bacterial cells are so small, there are actually more bacterial cells in and on a human body than there are human cells) p571 |
| The disease caused by a bacterium that uses Deer Ticks as vectors for transmission to humans is called _____. | Lyme disease (If you see one of these ticks or the bull's-eye rash in the photo below, see your doctor right away. Try to save the tick and bring it to the doctor also.) p571, 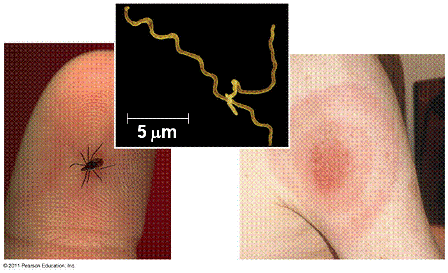 |
What is "E" in the picture below?,  | flagella p573,  |
| What type of organism is required to change milk into cheese or yogurt? | Bacteria p572 |
| A(n) _____ is a unicellular photosynthetic alga with a unique, glassy, cell wall containing silica. | diatom p585,  |
| _____ are short cellular appendages specialized for locomotion, formed from a core of nine outer doublet microtubules and two inner single microtubules ensheathed in an extension of the plasma membrane. | Cilia p584,  |
| Under the old five kingdom system, the ____ kingdom included all eukaryotic organisms that couldn't be classified as plants, animals, or fungi. Under the new three domain system, advances in molecular biology have made scientists realize that _____ should actually be broken down into several kingdoms with some possibly being placed back into the plant, animal or fungal kingdoms. Therefore, _____ is an informal term used to describe mostly unicellular organisms that are not plants, animals, or fungi. | protist (the answer for all of the blanks) p575 |
| ______ is a type of diplomonad that causes severe diarrhea and is often picked up by drinking untreated water from rivers or lakes contaminated with feces containing the parasite in the dormant cyst stage. | Giardia (This is often the cause of sickness on camping trips when water is not filtered or boiled.) pp578&580 |
What type of protist is pictured below?,  | Diatom (Diatoms, with their glass walls, are a major component of both oceans and lakes. They come in a wide variety of shapes. It's estimated that there are 100,000 living species. When they die, they form sediments called diatomaceous earth, which is used commercially in pool filtration systems. They play a major role in the carbon cycle by removing carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. When they die and sink to the bottom, they tend not to decompose well, so the carbon stays out of the carbon cycle) p585,  |
| A type of protozoan that moves by means of cilia is called a(n) _____. | ciliate (The paramecium in the picture below is a classic example of a ciliate. If you look closely, you can make out the small hairlike cilia.) p584,  |
The protozoan pictured below is a(n) ______.,  | paramecium p584,  |
| Protists that are animal-like in that they capture and consume food are called _______. | protozoans p551 |
| A(n) ______ is a unicellular photosynthetic alga with two flagella situated in perpendicular grooves in cellulose plates covering the cell. | dinoflagellate (The alga that causes red tide is a dinoflagellate. Some dinoflagellates are bioluminscent which means that they can glow in the dark.) p582,  |
The protist pictured below is called a(n) _____.,  | euglena (a common freshwater alga) p581,  |
| Photosynthetic protists are commonly called _____ and can be either unicellular or multicellular. | algae p576 |
| Algae and photosynthetic bacteria that drift passively in the pelagic zone of an aquatic environment are called ____. | phytoplankton p582 |
| A short cellular appendage specialized for locomotion, formed from a core of nine outer doublet microtubules and two inner single microtubules ensheathed in an extension of plasma membrane. | cilium (The plural is cilia. The key word here is short. Otherwise it could be a flagellum) p584 |
| A type of protozoan characterized by great flexibility and the presence of pseudopodia is called a(n) _____. | Amoeba p589,  |
| _______ are cellular extensions of amoeboid type cells used in moving and feeding. | Pseudopodia p589,  |
| The most common type of multicellular seaweeds, including kelp, are classified as _____ algae. | brown (The giant kelp in this kelp "forest" are brown aglae.) p586,  |
| The term _____ refers to mostly microscopic organisms that drift passively or swim weakly near the surface of oceans, ponds, and lakes. | plankton (Some larger organisms such as multicellular floating seaweed, most jellyfish, and the Mola Mola fish are classified as plankton also. The fish is classified as plankton because it is not a strong enough swimmer to swim against ocean currents.) p582 |
| The type of protists that are believed to have given rise to true plants are called _______. | green algae p590 |
| Algal blooms of certain types of dinoflagellates cause a phenomenon called ______ in which toxins produced by these algae cause massive fish kills. | red tide p583,  |
| An explosive growth in the population of algae is known as a(n) ________. | algal bloom p583 |
Red tide is caused by a neurotoxin released by a type of ________.,  | dinoflagellate p583,  |
| One type of entamoeba is a parasite that causes _______ which causes people to get life-threatening diarrhea from drinking contaminated water. | amebic dysentery (This is the third leading cause of death due to parasites after malaria and schistosomiasis.) p596 |
The _______ shown below is an example of a colonial organism, meaning that it is a colony of individual cells that work together.,  | Volvox p579,  |
What is "A" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | flagellum p581,  |
What is "D" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | contractile vacuole (used to get rid of water that is continually entering the cell in the freshwater hypotonic environment) p581,  |
What is "E" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | nucleus p581,  |
What is "F" in the picture of this euglena below?,  | chloroplast p581,  |
What is "A" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | cilia p584,  |
What is "B" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | food vacuoles p584,  |
What is "G" in the picture of this paramecium below?,  | contractile vacuole (Contracts to squeeze water out of the cell so that it doesn't explode due to being in the freshwater hypotonic environment.) p584,  |
| True or False: Individual organisms evolve. | False: Although natural selection acts upon individuals, only populations evolve as organisms can't acquire new adaptations after they start to develop. |
| _____________ is change in the genetic makeup of a population from generation to generation. | Microevolution |
| A __________ is a localized group of individuals that are capable of interbreeding and producing ______ offspring | population, fertile |
| The _________ is the total aggregate of genes in a population at any one time | gene pool |
| The Hardy-Weinberg theorem describes a population that is _________. | not evolving |
| What is the Hardy-Weinberg equation? | ., 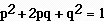 |
| In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, p + q =____ | 1 (remember, p and q represent the frequencies of the two alleles being considered. Their frequencies have to add up to 1, or 100%) |
| In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, p squared and q squared equal the frequencies of the ________ genotypes. | homozygous |
| In the Hardy-Weinberg equation, 2pq equals the frequencies of the ________ genotype. | heterozygous |
| _______ are changes in the nucleotide sequences of DNA. | Mutations |
| A _____ mutation is a change in one base in a gene. | point mutation |
| _______ is the main cause of differential success in reproduction. | Natural selection |
| _______ is defined as random deviation from the expected allele frequencies over time | Genetic drift |
| _________ results from the migration of fertile individuals or gametes between populations. | Gene flow |
| _______ is the primary mechanism of adaptive evolution. | Natural selection |
| ______ causes the accumulation and maintenance of favorable genotypes in a population. | Natural selection |
Which type of selection effect does the graph below show?,  | Directional,  |
Which type of selection effect does the graph below show?,  | Disruptive,  |
Which type of selection effect does the graph below show?,  | Stabilizing,  |
| Selection due to the sexual preferences of males or females within a species is called __________. | sexual selection |
| The evolutionary creation of new species is called ______. | speciation |
| Evolution above the species level (ie - the kind that creates new species) is called _______. | macroevolution |
| Evolutionary change that occurs within one species but doesn't immediately lead to speciation is called ______. | microevolution |
| The biological species concept defines a species as a population or group of populations whose members have the potential to _______ in nature and produce ______ but are unable to do the same with members of other populations. | interbreed, viable fertile offspring |
| _______ isolation is the existence of biological factors that impede members of two different species from producing viable fertile offspring. | Reproductive |
| ______ barriers cause biological isolation by impeding mating between species or by hindering the fertilization of ova if members of different species attempt to mate. | Prezygotic |
| Habitat isolation, temporal isolation, behavioral isolation, mechanical isolation, and gametic isolation are all examples of _______. | prezygotic barriers |
| ______ barriers cause biological isolation due to the inability of the hybrid zygote to develop into a viable fertile adult. | Postzygotic |
| Reduced hybrid viability, reduced hybrid fertility, and hybrid breakdown are examples of ______. | Postzygotic barriers |
| _______ speciation happens when a new species forms while geographically isolated from its parent population. | Allopatric |
| _______ speciation happens when a small population becomes a new species without geographic separation. | Sympatric ("patric" refers to homeland/country while "sym" means same. Sympatric speciation occurs in an organism's homeland while allopatric speciation occurs in a different homeland from the parent population) |
| Allopatric speciation occurs when gene flow is interrupted or reduced when a population is divided into two or more _______ isolated subpopulations. | geographically |
| _______ is the evolution of diversely adapted species from a common ancestor upon introduction to new environmental opportunities. | Adaptive radiation (Darwin's finches from the Galapagos are a classic example),  |
| The _______ model of evolutionary change describes evolution as happening in short fast spurts followed by long periods of little change. | Punctuated Equilibrium, 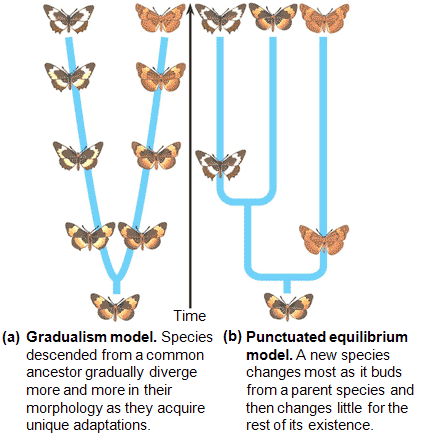 |
| The _______ model of evolutionary change describes evolution as happening slowly and steadily. | Gradualism,  |
| Evolutionary change often occurs due to adaptations to a _______. | changing environment |