| A | B |
|---|
| P-Waves | The first wave that is recorded on a seismograph, 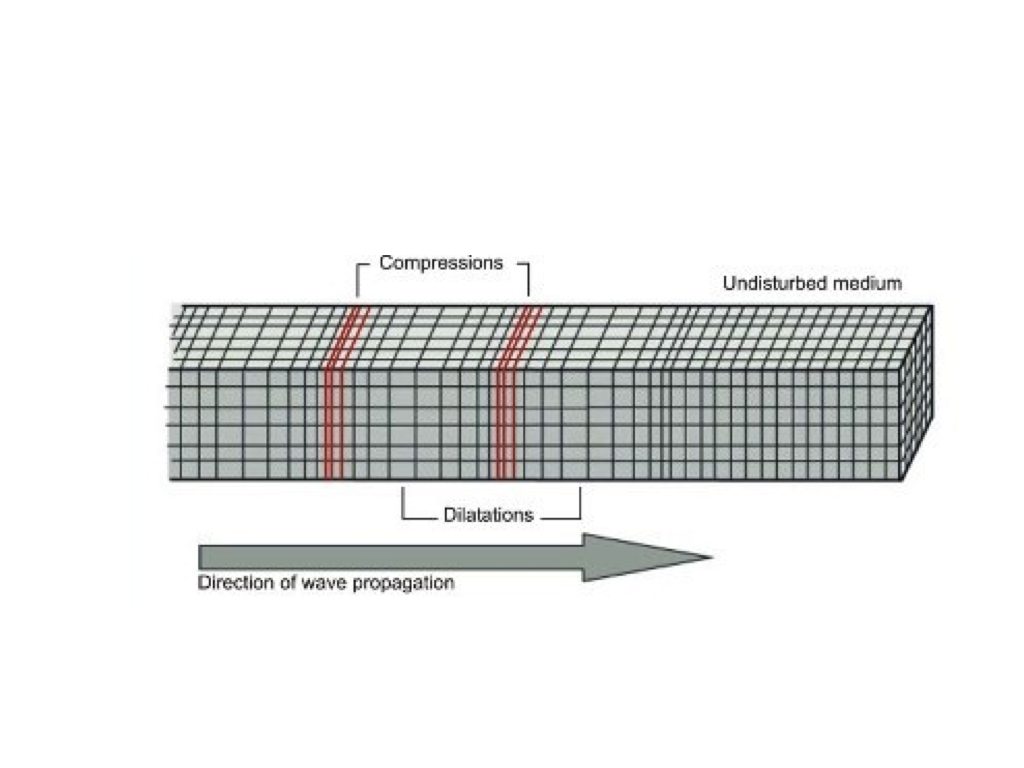 |
| S-Waves | Do not travel through the Earth's core |
| Lithosphere | The crust and upper-most solid part of the mantle which are pushed and pulled through plate tectonics. |
| Oceanic crust | The denser, thinner layer of the lithosphere which slides down during subduction. Example: basalt. |
| Continental crust | The less dense, thicker part of the lithosphere that slides on top during subduction. Example: granite. |
| Contour Lines | Show elevation on a topographic map |
| Isolines | A line on a map, graph or chart showing points of equal value. |
| Gradient | The change in value over distance |
| Profile | side view of a topographic map |
| Mass movement | When earth moves downslope due to gravity |
| Capillarity | The ability to retain water. The smaller the particles, the higher the capillarity |
| Porosity | The amount of pore space between particles. Well-sorted sediments have higher porosity. |
| Permeability | The ability for water to pass through sediments. Large pore spaces have higher permeability. |