| A | B |
|---|
| the height above sea level, also known as elevation, measured in kilometers | altitude |
| the force of air molecules pushing down on the Earth’s surface, measured in mb using a barometer | air pressure |
| a measurement of the amount of heat (kinetic energy of molecules) using a thermometer in *C or *F | temperature |
| the layer closest to Earth’s surface, contains the majority of its gases and all of its weather systems | troposphere |
| 2nd layer away from Earth, contains Ozone Layer that absorbs & protects us from UV radiation | stratosphere |
| 3rd layer away from Earth, protects us from meteors, which break up in this layer | mesosphere |
| the outer layer furthers from the Earth, includes the vacuum of space—exosphere | thermosphere |
| gas that is 78% of atmosphere | nitrogen |
| gas that is 21% of atmosphere | oxygen |
| gases that are 1% of atmosphere | trace gases |
| trace gas that is 0.04% of atmosphere, increased by burning fossil fuels & major cause of global warming | carbon dioxide |
| the gaseous form of water 0-4% | water vapor |
| cycle in which soil bacteria, decaying organisms , and plants maintain Earth’s atmosphere | nitrogen cycle |
| cycle in which plant photo-synthesis & plant/animal respiration maintain Earth’s atmosphere | carbon cycle |
| cycle in which evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and transpiration maintain Earth’s atmo | hydrologic (water) cycle |
| the process of maintaining the gases in Earth’s atmosphere at their current levels | equilibrium |
| coal, oil, & natural gas are burned to provide energy, major cause of air pollution | fossil fuels |
| the loss of this stratosphere gas increases UV radiation exposure, which causes skin & other cancers | ozone |
| dust, soot, and dirt stirred up by farming and burning trash & other materials, cause eye/lung irritation | particulates |
| low pH rain, caused when sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides mix with water vapor; damage to plants, fish | acid rain |
| a combination of smoke & fog caused when polluting chemicals and sunlight react; eye/lung irritant | smog (photochemical smog) |
| the CO2-caused increase in atmospheric temperature since late 19th C causing climate change | global warming |
| . the US federal government agency that monitors and enforces air quality standards, created 1970 | Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) |
| the US legislation that was created to monitor and reduce air pollution | Clean Air Act |
| the concept of taking care of the Earth | stewardship |
| As altitude increases, air pressure ____________. | decreases |
| The layers of the atmosphere are determined by changes in their ________________. | temperatures (getting warmer or cooler) |
In what two layers did the temperatures decrease as altitude increased?, 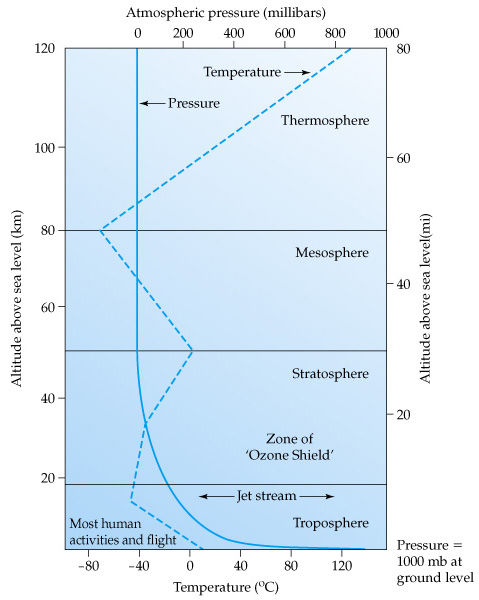 | Troposphere & Mesosphere both get colder as altitude increases,  |
Why does the stratosphere show an increases in temperature as altitude increases?,  | The ozone absorbs the UV radiation, so it gets warmer as altitude increases.,  |
Which of Earth's atmospheric gases is shown as "X" in this pie chart?, 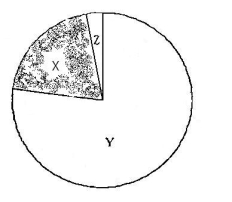 | oxygen is 21% of our atmosphere,  |
Which of Earth's atmospheric gases is shown as "Y" in this pie chart?,  | nitrogen is 78% of our atmosphere,  |
Which of Earth's atmospheric gases is shown as "Z" in this pie chart?,  | Trace gases are 1% of our atmosphere. They include carbon dioxide and others.,  |
| One way that the government can reduce air pollution is to _________________ | enforce the Clean Air Act end encourage businesses to use alternative energy sources |
| One way that businesses can reduce air pollution is to _________________ | use alternative energy sources, encourage workers to carpool, use scrubbers in smokestacks |
| One way that individuals can reduce air pollution is to _________________ | carpool, use public transportation, not burn trash, use alternative enrgy sources like hybrid cars, etc. |