| A | B |
|---|
| English scientist (mid 1600s-1700s) who studied gravity and the relationship of force, mass, & acceleration | Sir Isaac Newton |
| a push or pull | force |
| net force acting on an object that changes its speed, direction, or both | unbalanced force |
| net force acting on an object that does NOT change its speed or direction | balanced force |
| the total sum of forces acting on an object, taking into account direction and force applied | net force |
| tendency of an object to resist any change in motion—objects in motion or at rest remain that way unless . . . | inertia |
| the pull (attraction) of two objects to each other; its strength is based on the objects’ masses & distance apart | gravitational force (gravity) |
| the pull (attraction) force between opposite poles (N&S) or push (repulsion) force between similar poles (N vs. N or S vs. S) | magnetic force |
| the force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact; depends on the type of surface and amount of contact—sliding, rolling, fluid | friction |
| a change in an object’s distance relative to another object | motion |
| used to judge motion with respect to some other object or point—relative vs. exact | frame or point of reference |
| a measure of how quickly the object gets from one place to another; formula= Distance/Time | speed |
| occurs when an object maintains its same speed over an entire graph, a line without any curves up or down | constant speed |
| occurs when an object changes its speed, shown as a curving line (up = increase, down = decrease) | variable speed |
| the total distance divided by the total time of the trip, regardless of any changes in speed at any point | average speed |
| the speed of an object at one particular moment during the trip | instantaneous speed |
| speed in a given direction | velocity |
| any change in an object’s motion, positive (speeding up), negative (slowing down), or a change in direction | acceleration |
| A skateboarder moves for 10 seconds. In the first 5 seconds, he travels 20 meters. In the next 5 seconds, he travels 10 meters. Describe the skateboarder's motion. | He slowed down (negative acceleration) since he traveled 10 fewer meters in the same amount of time (5 seconds). |
| A skateboarder moves for 10 seconds. In the first 5 seconds, he travels 20 meters. In the next 5 seconds, he travels 10 meters. What was the skateboarder's average speed?. | average s= total d/ total t = 30/10 =3 meters per second |
| If the mass is =, but force is increased, then acceleration ________________. | increases (more force = more acceleration) |
| If the mass is =, but force is decreased, then acceleration ________________. | decreases (less force = less acceleration) |
| If the force is =, but mass is decreased, then acceleration ________________. | increases (less mass = more acceleration) |
| If the force is =, but mass is increased, then acceleration ________________. | decreases (more mass = less acceleration) |
Which way will the soccer ball go and why?, 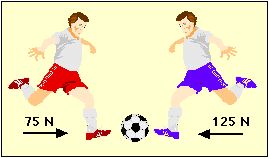 | To the left towards the boy in red shorts because 125 N left-75 N right = 50 N to the left net force,  |
What does this distance-time graph tell you about this object's motion?, 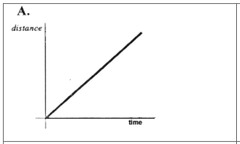 | It is moving at a constant speed--the line is a straight diagonal with no changes-- it travels the same distance in the same time the entire time,  |
What does this distance-time graph tell you about this object's motion?, 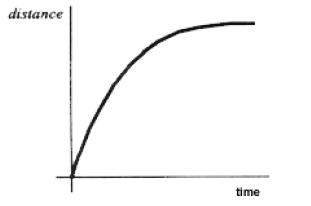 | It is slowing down--it travels less distance in the same amount of time as time continues,  |
What does this distance-time graph tell you about this object's motion?, 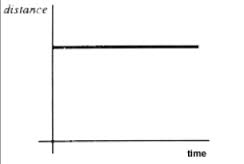 | It is stopped- no change in distance as time continues,  |
What does this distance-time graph tell you about this object's motion?,  | It is speeding up--it travels more distance in the same amount of time as time continues,  |
What does this distance-time graph tell you about this object's motion?, 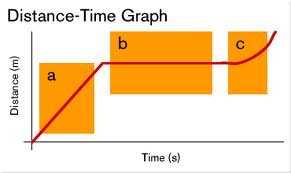 | During segment A, it is at a constant speed, then it stops during segment B, and it increases its speed during segment C,  |
What does this distance-time graph tell you about the motion of these two objects??, 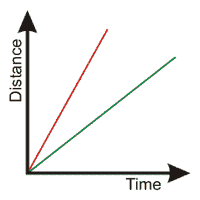 | Both objects are moving at a constant speed, but the red line object is moving at a faster speed.,  |
| The amount of gravitional force depends on the objects' _____________ and _______________. | mass and distance apart |
| A balled-up piece of paper and a flat sheet of paper are droppped. Why does the balled up piece hit first if gravitational force was the same? | The balled up piece has less air resistance (friction) acting against its motion than the flat piece. |