| A | B |
|---|
| Eastern Hemisphere | eastern half of the globe, 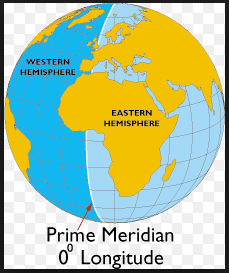 |
| Empire | a state that conquers other territories or people and then rules them,  |
| State | a body of people occupying a definite territory and politically organized,  |
| Western Hemisphere | western half of the globe, 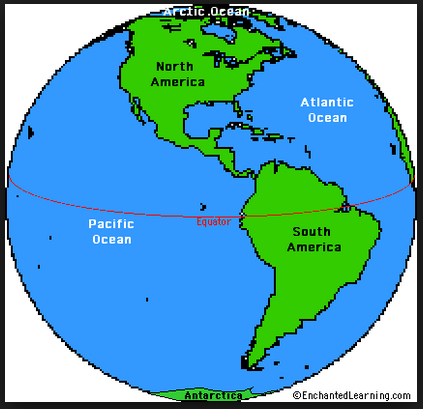 |
| humanism | movement during the Renaissance during which scholars studied the classical texts of ancient Greece and Rome,  |
| Renaissance | rebirth of classical knowledge, “birth” of the modern world,  |
| sonnett | Poem with 14 lines, usually in iambic pentameter with a definite rhyme scheme,  |
| compass | an instrument that indicates direction by using a magnetic needle,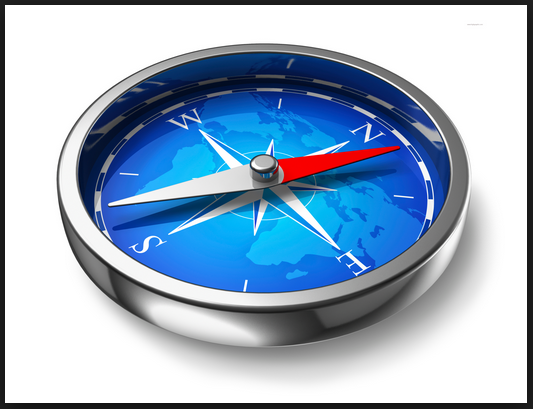  |
| exchange | trade, the giving and taking of one thing in return for another,  |
| maritime | relating to navigation or commerce on the sea,  |
| porcelain | fine grained ceramics (also known as "china"),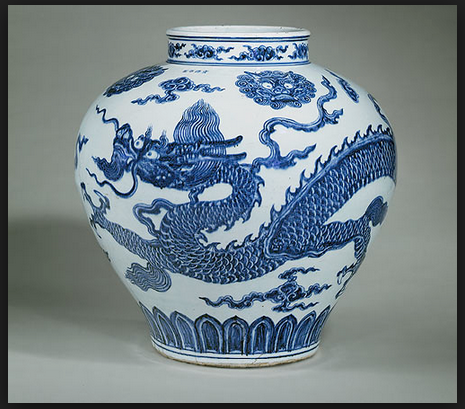  |
| silk road | trade routes from Asia to the Mediterranean Basin, 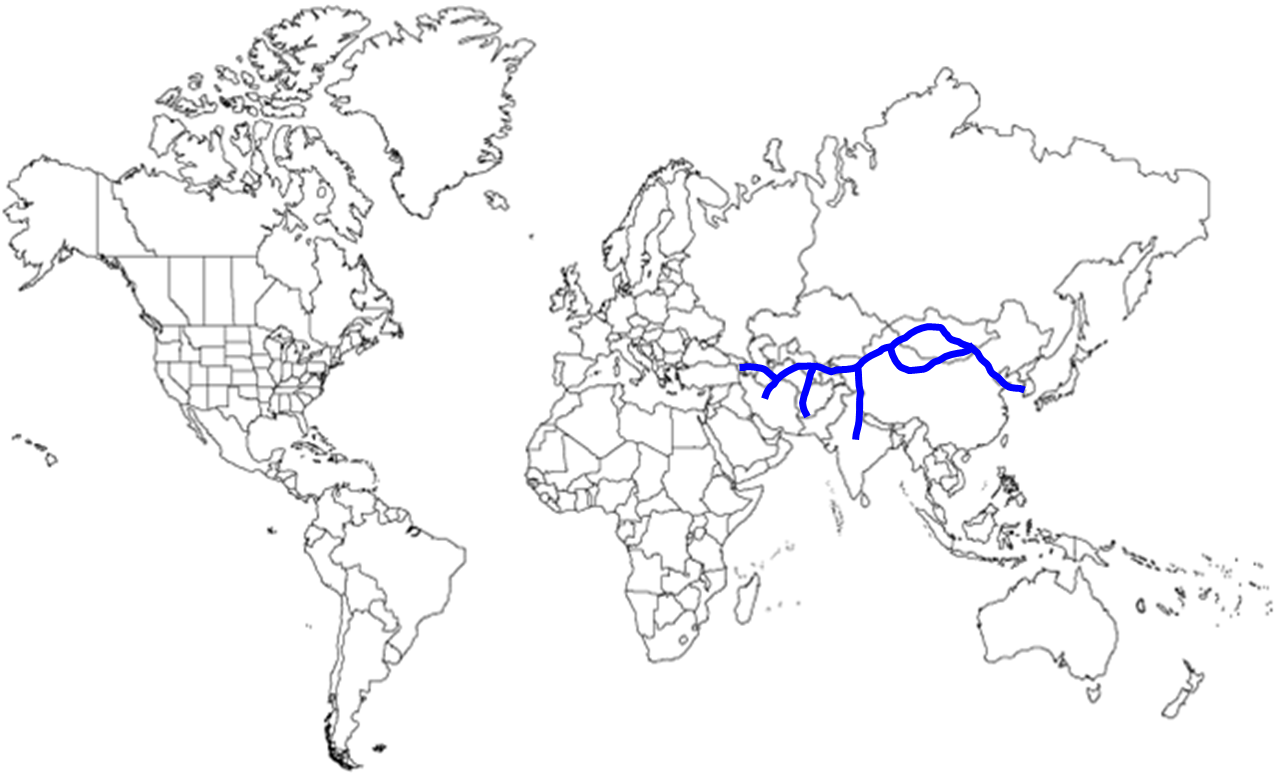 |
| textiles | cloth, woven fabric,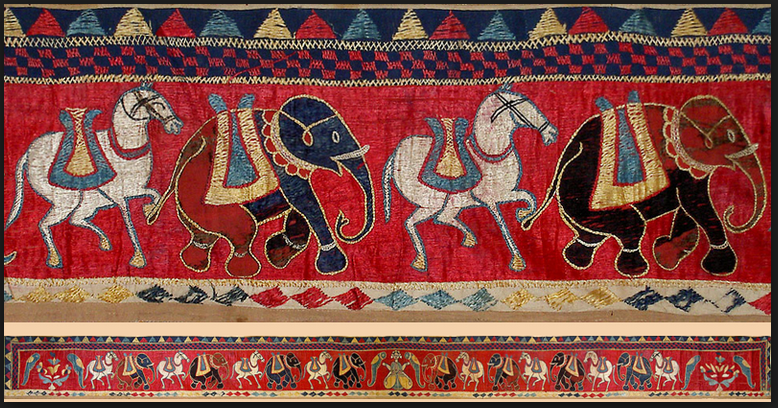  |
| Trans-Saharan | trade routes crossing Africa’s Sahara Desert, 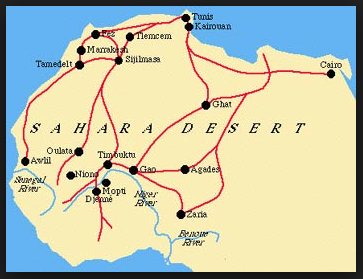 |
| Leonardo da Vinci | This multi-talented Italian artist, painter, inventor, sculptor, architect and mathematician was the ultimate Renaissance man,  |
| Niccolo Machiavelli | This writer of the Renaissance believed that the key to gaining and maintaining power was to not let oneself be restricted by moral principles.,  |
| Michelangelo | This artist, most famous for painting the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, was also a magnificent sculptor and architect,  |
| Erasmus | The leading Christian Humanist,  |
| Shakespeare | Renaissance writer of plays and sonnets,  |
| Cultural Diffusion | the process by which a cultural item spreads from group to group or society to society.,  |
| Ottoman Empire | found on three continents (Asia, Africa & Europe); famous for conquering Constantinople, and trading in coffee & ceramics, 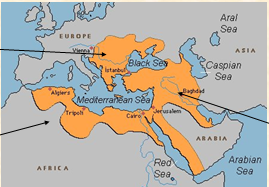 |
| Mughal Empire | found in northern India; famous for trading textiles & spices, and bringing Islam to India, 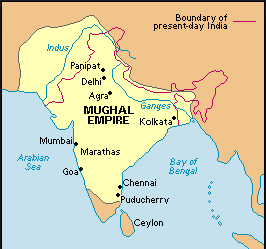 |
| Aztec Empire | found in central Mexico; famous for trading corn, and for practicing human sacrifice,  |
| Inca Empire | found in South America; famous for building roads,  |