| A | B |
|---|
| Monotheism | Belief in one god |
| Polytheism | Belief in many gods |
| The Phoenicians | civilization of sea-traders on the Mediterranean Coast |
| The Ten Commandments | from the Hebrews, and Moses this described moral and religious conduct |
| Mesopotamia | "The land between the two Rivers" |
| Artisans | people skilled in a particular craft |
| Cuneiform | the earliest writing system created by the Sumerians |
| Code of Hammurabi | The earliest written law code from Ancient Babylon |
| City-State | political unit typically with a walled city and the farmland that surrounded it |
| Abraham | Man who is credited with founding Judaism |
| The alphabet | the greatest contribution made by the Phoenicians |
| The Hebrews | The group who founded the first monotheisic religion |
| Jerusalem | the captial of the Kingdom of Israel constructed by David |
| The Diaspora | means "the scattering" and represents the state that the Hebrews lived in after being forced out of their homeland |
| Pictograms | a writing system where pictures or symbols represent entire word or ideasideas |
| "Eye for an Eye" | the philosophy of justice put forth by the Code of Hammurabi |
| The social structure of most early river civilizations | rigid with very little movement between classes |
| Imperial Bureaucracy | using a set of experts to advise the king and help rule a large empire |
| Nubia | Kingdom south of Egypt (upper Egypt) on Nile that was a rival civilization for the Egyptians |
| Babylon | 1st EMPIRE in Mesopotamia, contributed the 1st law Code (Hammurabi's code) |
| Upper Egypt | The SOUTHERN part of the nile River |
| Lower Egypt | The Nrthern part of the Nile and Nile Delta |
| Empire | a government that features a group that has conquered another group's land. |
| Pharaoh | the Egyptian leaders that were worshiped like they were a god |
| Theocracy | Rule by a religious leader (ex. Ancient Egypt) |
| Royal road | Built by the Persians, it helped connect their large empire |
| Cyrus the great | Persian ruler responsible for conquering most of Persia's empire. He was TOLERANT to those he conquered though. |
| Darius I | Persian Ruler who set up the system for administering/controlling the Persian Empire. He constructed the Royal Road. |
| Ramses II | most powerful Egyptian Pharaoh |
| Rosetta Stone | archaeological find that allowed people to translate the Egyptian heiroglyphics |
| Heiroglyphics | The Egyptian form of writing |
| Moses | Hebrew leader who led the EXODUS and contributed the Ten Commandments |
| Judaism | religion of the hebrews, it is the 1st monotheistic religion |
| The Torah | the holy text of Judaism (1st 5 books of old testament) |
| Zoroastrianism | the Persian religion that focused on a struggle between good and evil |
| Ahura Mazda | The god of Zoroastrianism |
| Yahweh | The Hebrew word for God |
| Diaspora | The "scattering" of the Jews after their conquest by several other groups |
| Epic of Gilgamesh | the 1st recorded story, it is a Sumerian Epic that tells of a legnedary King and his quest for immortality |
| Pyramid | built as tombs for the pharaohs, they housed the pharaoh's mummy and possessions |
| Ziggurat | Step Pyramids built in ancient Mesopotamia they were used as temples for their gods |
| Obelisks | large Egyptian statues meant to symbolize the Sun's rays |
| Cuneiform (image) |  |
| Hieroglyphics (image) |  |
| Phoenician Alphabet (image) |  |
| Ziggurat (image) |  |
| Obelisk (image) | 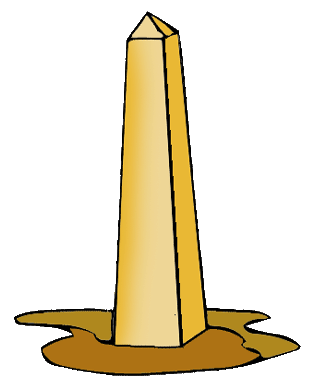 |