| A | B |
|---|
| Biology means the study of | life |
| What are the building blocks of all matter? | atoms |
| The nucleus of an atom is made up of ____ and ____ | protons and neutrons |
| Electrons have a ___ charge | negative |
| Protons have a ___ charge | positive |
| Neutrons have a ___ charge | neutral (no) charge |
| Which type of particle orbits the nucleus? | electrons |
| Positive charges are attracted to ____ charges | negative |
| Positive charges are repelled by ____ charges | positive |
| Negative charges are repelled by ____ charges | negative |
| An electron would be attracted to a _____ | proton |
| The large center region of an atom is called the ___ of the atom | nucleus |
| Each element is different because they have a different number of ____. | protons |
| All of the elements are listed in the ____. | periodic table |
| The ____ is equal to the number of protons in an atom. | atomic number |
| The number of protons + the number of neutrons is equal to the ____ | mass number |
| The mass number is equal to the | number of protons and neutrons |
| The atomic number is equal to the number of ____ in an atom | protons |
| The number below the chemical symbol on the periodic table that has a few decimal places is known as the ____. | average atomic mass |
| If an element has a mass # of 23 and an atomic # of 11, how many protons will it have? Neutrons? | 11 protons and 12 neutrons |
| The most abundant element in Earth's atmosphere is ___. | Nitrogen (= 77% of the atmosphere) |
| The most abundant element in the universe as well as our bodies is called ___. | hydrogen |
| The element that forms the backbone of organic molecules is ___. | carbon |
| Two or more elements bond together to form ____. | compounds |
| A compound which has bonds formed by sharing electrons is called a ___. | molecule (technically, a molecule like oxygen which is made of two oxygen atoms is also a molecule because it is held together with covalent bonds, but it is not a compound because it does not have two or more different elements in it) |
| How many oxygen atoms are in H20? | One (there are two hydrogens) |
| What is the chemical formula for a molecule of glucose? | C6H12O6 (the numbers should be subscripts) |
| In a chemical equation, the _____ are on the left side of the arrow. | reactants |
| In a chemical equation, the ___ are on the right side of the arrow. | products |
| The process of using energy from the sun to make food molecules like glucose is called ____. | photosynthesis, 
|
What are the products of photosynthesis?, 
| food (usually glucose) and oxygen |
What are the reactants of photosynthesis?, 
| water and carbon dioxide |
Which two molecules are needed for photosynthesis to occur?, 
| water and carbon dioxide, 
|
What are the waste products of cellular respiration?, 
| carbon dioxide and water, 
|
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?, 
| oxygen and glucose |
| Glucose is a type of ____. | sugar |
| A reaction that gives off energy (loses energy) is called an _____ reaction | exothermic, 
|
| A reaction that requires more energy than it gives off is called an ___ reaction. | endothermic, 
|
Cellular respiration is an example of an ___ reaction, 
| exothermic reaction, 
|
| Burning wood is an example of an ____ reaction. | exothermic, 
|
Photosynthesis is an example of an ___ reaction., 
| endothermic, 
|
| Atoms or molecules that become charged because they gain or lose electrons are called ___. | ions |
| A negatively charged ion would be ____ by another negatively charged ion. | repelled |
| A positively charged ion would be ____ by another positively charged ion. | repelled |
| A negatively charged ion would be ___ by a positively charged ion. | attracted |
| A uniform mixture of substances is know as a ___. | solution |
| In a glass of salt water, the ___ would be the solvent. | water |
| In a glass of salt water, the ___ would be the solute. | salt |
| In a solution of sugar and water, the sugar would be the ___. | solute |
| In a solution of sugar and water, the water would be the _____. | solvent |
| Acidic solutions have a pH that is ____ seven. | below |
| Basic solutions have a pH that is ___ seven. | above |
| Distilled water has a pH of ___. | seven |
| A liquid with a pH of 1 would be described as being ___. | strongly acidic |
| A liquid with a pH of 6 would be described as being ___. | weakly acidic |
| A liquid with a pH of 8 would be described as being ___. | weakly basic |
| A liquid with a pH of 13 would be described as being ___. | strongly basic |
| As temperature ____, particles move faster and faster | increases |
| As temperature ____ particles move slower and slower. | decreases |
| Increasing the ___ or ___ of the reactants will cause a reaction to speed up. | temperature, concentration |
| A(n) ______ is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction. | catalyst, 
|
A biological catalyst is known as ____., 
| an enzyme, 
|
| Chemicals that have carbon and hydrogen in them and were produced by once living things are called ___. | organic chemicals |
| All organic chemicals have the elements ____ and ___ in them and most also have ____. | carbon, hydrogen, (most have oxygen also) |
| Give some examples of organic chemicals | carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, fossil fuels, 
|
| Water and carbon dioxide are ____ molecules. | inorganic |
| The building blocks of larger molecules are known as ____. | monomers |
| Many monomers linked together make up a ____. | polymer |
| A polymer is a large molecule made up of many ____. | monomers |
| The root word "poly" means ____. | many |
| The root word "mono" means ___. | one |
| The four categories of biological macromolecules are ___, ___, ___, and ___. | carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, 
|
| The type of macromolecule that is used primarily as a source of energy is ___. | carbohydrates, 
|
| Bread, pasta, cereal and fruits are high in which type of macromolecule? | carbohydrates, 
|
| The monomers of complex carbohydrates are ___. | simple sugars (a.k.a. monosaccharides), 
|
| glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of ____. | simple sugars (or monosaccharides), 
|
| Sucrose is commonly called ____. | table sugar |
| Sucrose is a type of carbohydrate made of glucose bonded to fructose. Therefore, it is a ___. | disaccharide |
| Another term for simple sugars is ___. | monosaccharides, 
|
| Many monosaccharides bonded together are called a ____. | polysaccharide, 
|
| Lactose is a type of _____ found in milk. | sugar |
| Lactose can be broken down into galactose and glucose by the enzyme known as ___. | lactase |
Plants store their carbohydrates as the polysaccharide known as ____., 
| starch |
Animals store carbohydrates in their liver and muscles as the polysaccharide known as ___., 
| glycogen, 
|
| The cell walls of plants are made of the polysaccharide known as ____. | cellulose, 
|
| ____ is a tough polysaccharide that can only be broken down by bacteria and some fungi. | Cellulose |
There is a lot of cellulose in the plant cell walls of grass. It is very difficult to breakdown into the simple sugars that make it up. Therefore, cows rely on _____ in their stomach to break it down for them., 
| bacteria |
Gycogen is stored in an animal's ___ and ____., 
| muscles and liver |
Starch, glycogen and cellulose are all types of ___., 
| carbohydrates, 
|
| Sugars are classified as ___. | carbohydrates, 
|
The type of macromolecule that is used mostly for building structures in an organism is called ___., 
| protein |
| Hormones are usually made of ___. | protein |
| The building blocks of proteins are ____. | amino acids, 
|
| The monomers of proteins are ___. | amino acids, 
|
A long straight chain of amino acids is called a ____., 
| polypeptide |
A polypeptide that folds into a 3-D structure that has a specific function is called a(n) ___., 
| protein |
Lean meat is highest in the macromolecule known as ____., 
| protein |
The most important quality of an enzyme is its ___., 
| shape. |
| A protein whose shape has been changed due to heat or harsh chemicals is known as a(n) ____ protein. | denatured |
Organic catalysts are known as ___., 
| enzymes |
| An enzyme ____ a chemical reaction without being changed itself. | speeds up |
| DNA and RNA are types of ____ | nucleic acids, 
|
| The type of molecule that stores genetic information is called ___. | DNA |
| The monomers of nucleic acids are ____. | nucleotides, 
|
| DNA is made up of four different types of ____. | nucleotides |
| adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are ____ | nucleotides |
The order of nucleotides in DNA determines the order of ____ in a _______, 
| amino acids, protein, 
|
A change in the order of nucleotides in DNA is known as a ____., 
| mutation |
A type of nucleic acid that is single-stranded is ___., 
| RNA |
A type of nucleic acid that is double stranded is ___., 
| DNA |
| Fats, oils, and waxes are classified as ___. | lipids |
| The main function of lipids in an animal's body is to ____. | store energy for later use |
| Red meats, dairy and fried foods are high in the type of macromolecules known as ___. | lipids |
| The building blocks of most lipids are ___ . | 3 fatty acids and glycerol |
| Besides being used to store energy, lipids are also used for ___. | insulation and protecting internal organs |
| Fats that are solid at room temperature and are not particularly good for you are a type called ___. | saturated fats |
| Fats that are liquid at room temperature and are considered healthy to eat are called ___. | unsaturated fats |
| ____ are high in saturated fats. | Red meats |
| Fats from vegetable oils tend to be ___. | unsaturated (these tend to be healthier for you than saturated fats) |
| Phospholipids make up the majority of the ___. | cell membrane |
| Cell membranes are made up of mostly ___. | phospholipids |
Enzymes are almost always made of ____., 
| proteins (although the sex hormones testosterone and estrogen are actually lipids) |
The chemical or chemicals that an enzyme works on is called the ___., 
| substrate |
| The part of the enzyme that the substrate fits into is called the ___. | active site |
| The chemical process in which molecules are broken down in the body is known as ___. | catabolism, 
|
| The chemical process in which larger molecules are built up is known as ___. | anabolism, 
|
| The sum of all catabolic and anabolic reactions in the body is known as ___. | metabolism, 
|
Five things that can affect how well an enzyme works are ___., 
| temperature, concentration, pH, inhibitors, and mutations in the DNA that codes for the enzyme |
| Steroids are classified as _______. | lipids,  |
| Lipids with a ring structure are called ______ | steroids., 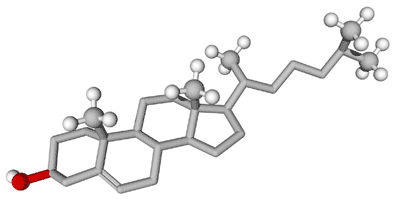 |
| Some steroids, like testosterone and estrogen, can act as ______. | hormones (hormones are any molecule that travels through the blood stream and connects with another cell to give it a message. Usually they are proteins, like insulin) |
| The plant in the windowsill has five flowers is an example of _____ data. | quantitative |
| The information that you gather in your experiment is called your ____. | data |
| The science that seeks to understand the living world is called ___. | biology |
| A logical interpretation based on prior knowledge and experience is called a(n) ____. | inference |
| A proposed scientific explanation for a set of observations is called a(n) ____. | hypothesis |
| Data that is recorded as descriptions is called ____ data | qualitative |
| Data that is directly measured and recorded as a number is called ____ data. | quantitative |
| The following two statements are about the same man. Which of the two statements is an observation and which is an inference? A) The man was tired. B) The man's heartrate was 140 beats per minute. | Statement A was an inference, while statement B is an observation. Usually, people whose heartrates are high are tired, but the man could have also just received a big fright. |
| Who makes decisions on what to do based on scientific data (for instance, what to do when scientists say that certain types of pollution cause global warming)? | You, the voter. Scientists only make recommendations and politicians only listen to people who vote. |
| Which of the characteristics of life best explains why bears hibernate when it starts to get cold? | Living things respond to their environment. |
| Cell specialization in multicellular organisms allows cells to ____. | perform different functions |
| The process by which organisms regulate their internal conditions to keep them fairly constant is called ___. | homeostasis |
| A group of organisms of the same type living in the same area is called a ___. | population |
| A group of many different types of organisms living together in the same area is called a ___. | community |
| Most multicellular organisms reproduce ____. | sexually |
| Most unicellular organisms reproduce ___. | asexually |
| A biologist who studies plants is called a ___. | botanist |
| A biologist who studies animals is called a ___. | zoologist |
| A biologist who studies ancient life is called a ___. | paleontologist |
| The largest level at which organisms can be studied is at the level of the ___. | biosphere |
| The combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down material is called ____. | metabolism, 
|
| The smallest thing that can be considered to be living is a ___. | cell |
| An organism that is made of only one cell is called a _____ organism. | unicellular |
| The directions for how an organism grows and develops is coded into a molecule called ____. | DNA |
| Changing form as an organism grows is called ___. | development |
| Something that an organism responds to is called a ____. | stimulus |
| When one type of organism changes over very long periods of time (many many generations), it is called ____. | Evolution |
| Groups of atoms bonded together with covalent bonds are called ____. | molecules |
| Groups of cells can be organized into ____, _____, and ____. | tissues, organs and organ systems |
| All the living and non-living things in an area are called _____. | an ecosystem |
| What are the two types of cells that all living things are made of? | Prokaryotic and eukaryotic |
| What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? | Eukaryotic cells store their DNA inside an organelle called the nucleus (Other differences include the fact that prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells and lack any type of membrane bound organelle, although the do have an organelle called a ribosome, but it is not surrounded by a membrane) |
| Which type of organisms are made of prokaryotic cells? | Bacteria (Prokaryotes can be found in two different kingdoms; the archaebacteria in the domain Archaea and the Eubacteria in the Bacteria domain) |
| Which type of organisms are made of eukaryotic cells? | Everything other than bacteria (These include the plant, animal, fungi, and protist kingdoms) |
| What are the tiny structures with specific functions called that are located in the cytosol of cells (mostly eukaryotic cells)? | organelles (Eukaryotic cells are the only type of cell that has membrane-bound organelles, like the nucleus, golgi, vacuoles, etc. These sac-like membranes form separate areas inside the cell where specialized functions can be carried out and specific substances can be stored. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes, which are often referred to as organelles also, but they are solid structures, not hollow sac-like structures like the membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells) |
| What surrounds both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and regulates what goes in and out of the cell? | A plasma membrane (Can also be called a cell membrane. Don't get this confused with the cell wall, which all prokaryotes have and many eukaryotes as well. Animals and some protists don't have a cell wall) |
| What are four things that both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have in common? | Plasma membrane, DNA, cytosol, and ribosomes |
| The small solid (not membrane-bound) organelle found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that helps the cell build different types of proteins is called a(n) _____. | ribosome |