| A | B |
|---|
| Astronomy | The study of the universe |
| Geology | The study of the Earth |
| Meteorology | The study of the atmosphere & weather |
| Oceanography | The study of the oceans |
| Inner Core | Earth layer composed of solid iron & nickel |
| Hypothesis | A possible explanation for an observed set of facts |
| Outer Core | Earth layer composed of liquid iron & nickel |
| Mantle | The thickest Earth layer; layer found below the crust; composed of silicon, oxygen, magnesium, & iron |
| Crust | The thinnest Earth layer; only layer man has dug or drilled into |
| Photosynthesis | Process by which plants produce food & Oxygen from Carbondioxide, Water & sunlight; respiriation is the opposite of this equation |
| Revolve | To orbit something |
| Rotate | To spin on an axis |
| 3 Things Eratosthenes needed to calculate the circumference of the Earth | Exact time of noon on June 21st, Distance between the 2 cities. The angle of the shadow from the obelisk in one city. |
| Degrees of a circle | 360 degrees |
| 3 ancient pieces of evidence that Earth is a sphere | The mast of ships is the first thing to be seen when a ship comes over the horizon, Change in constellations, The shadow of the Earth on the moon during a lunar eclipse is the arc of a circle |
| Reactants of Photosynthesis | Carbondioxide, water & sunlight |
| Products of Photosynthesis | Food (sugars & starches) & Oxygen |
| Person who made the 1st known scientific measurement of the circumference of the Earth | Eratosthenes |
| Oblate Spheroid (def) | A sphere that is flighted at the poles and bulges at the equator |
| Position of the North Star as a sailor goes north | Higher in the sky |
| Circumference (def) | The distance around the perimeter of a circle |
| Geo- | prefix meaning Earth |
| Oblate Spheroid (def) | The shape of the Earth; flattened at the poles bulging at the equator |
| Cause of Earth's Shape | Earth's Rotation |
| Mass (def) | The amount of matter in an object |
| Volume | The amount of space taken up by an object |
| Density | The amount of matter in a given space |
| Formula for Density | D=m/v |
| Average Human Body Temperature in Celcius | 37 degrees Celcius |
| Average Human Body Temperature in Fahrenheit | 98.6 degrees F |
| Boiling Point of water in Fahrenheit | 212 degrees F |
| Freezing point of water in Fahrenheit | 32 degrees F |
| Freezing point of water in Celcius | 0 degrees C |
| Boiling point of water in Celcius | 100 degrees C |
| 1ml = ___ cubic centimeters | 1ml= 1cubic centimeter |
| Metric Prefix meaning one hundred | Hecto |
| Metric Prefix meaning one thousand | Kilo |
| Person credited with the first use of the displacement method of dtermining the volume of an irregularly-shaped obj. | Archimedes |
| If a box has a mass of 2g & a volume of 1250ml, what is the density? | .0016 g/ml |
| .01 dkg = ____g | .1 g |
| 300 cl = ____ml | 3000 ml |
| 878.4 l = ____ kl | .8784 kl |
| 12.3 hl = ____cl | 123,000 cl |
| An irregularly shaped obj. is placed in a graduated cylinder. Without the obj. the cylinder reads 15 ml, with the obj. it reads 25 ml. What is the volume of the obj? | 10 ml |
| If the volume of an obj. is 4 ml & the density is 3g/ml, what is the mass? | 12 g |
| Exponent for 100 | 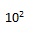 |
| deci (def) | 1/10 |
| centi- (def | 1/100 |
| Exponent for deci | 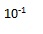 |
| Exponent for cent | 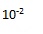 |
| 1st Greek to successfully estimated the Earth's Circumference | Eratosthenes |
| Open system (def) | The system & its surroundings freely exchange both energy & matter |
| Average Slope (def) | The change in elevation over a given distance. |
| Latitude (def) | Angular distance in degrees north or south of the equator |
| Latitude of the North Pole | 90 degrees N |
| Latitude of the South Pole | 90 degrees S |
| Synonym for Latitude | Parallels |
| Latitude of the Equator | 0 degrees lat. |
| Longitude (def) | Angular distance in degrees east or west of the prime meridian |
| Synonym for Longitude | Meridians |
| How many minutes are in a degree? | 60 minutes |
| How many seconds are in a minute? | 60 seconds |
| Latitude of the Tropic of Cancer | 23.5 degrees N |
| Latitude of the Tropic of Capricorn | 23.5 degrees S |
| Latitude of the Arctic Circle | 66.5 degrees N |
| Latitude of the Antarctic Circle | 66.5 degrees S |
| Longitude of the Prime Meridian | 0 degrees long. |
| Longitude of the International Date Line | 180 degrees long. |
| Place where the Prime Meridian is located. | Greenwich, England |
| Contour Lines (def) | Lines that connect points of equal elevation |
| Elevation (def) | Distance above sea level |
| Topographic Map (def) | Map showing the shape & elevation of the Earth's surface. |
| Contour Interval (def) | The difference in height between two adjacent contour lines |
| Index Contours (def) | Every 5th line is darkened & labeled with the elevation |
| Best most to scale representation of Earth | Globe |
| Hachures (def) | Lines drawn on a contour line to show a depression |
| Map Scale (def) | The relationship between the distance on the map & the actual distance on the Earth's surface. |
| Synonym for Map Scale | Map Legend |
| Magnetic Declination (def) | The difference in the angle between true north & magnetic north |
| Formula for average slope | change in elevation divided by the change in distance |
| How are contour lines drawn to show a steep slope? | Contour lines are drawn close together. |
| Cirrus Clouds (def) | Clouds are thin, feathery, very high & always made of ice crystals. These are easy to see when planes fly by & leave a jet trail |
| Stratus Clouds (def) | Low sheets or layers of cloud formed from horizontal air movement |
| Cumulus Clouds (def) | Clouds formed by vertically rising air currents piled in thick, puffy masses |
| Meaning of the prefix Nimbo- | Rain Cloud |
| Approximate difference in temperature between the air temperature & dew point temperature that will cause water to condense resulting in clouds & possibly precipitaion | A difference of 4 degrees or less |
| # of inches of snow for every 1 inch of rain | 10 inches |
| The higher the air rises, the (more)(less) moisture it can drop | More |
Windward (def), 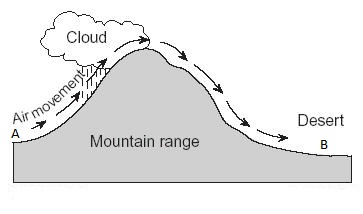 | Side of a mountain where rising air cools, water condenses and falls as rain,  |
Leeward (def),  | Side of a mountain where air is compressing and the sinking air is dryer.,  |
| 2 Chemical agents that cause of Acid Rain | Sulfates (from volcanoes & fuel burning) and nitrates (from car exhaust and industrial processes)) |
| 4 Dangers from Acid Rain | Changes pH of the soil, makes stone weater faster, kills plants & animals, & damages metals |
| Temperature Inversion (def) | Upside-down temperature condition occurring when surface air is colder than the air above. Cool polluted air is trapped by the warm air above it. |
| What conditions favor the formation of temperature inversions? | Clear dry nights in the area of a valley or depression |
| 2 things that aid in destroying temperature inversions | Wind & sunlight |
| What results from the uneven heating of the Earth's surface? | Winds |
| Isobars that are close together signify areas were winds are (blowing faster) (blowing slower). | Blowing faster |
| Winds blow from (high) (low) pressure to (high) (low) pressure | From high pressure to low pressure |
| Anemometer (def) | Instrument that measures wind speed |
| Weather/Windvane (def) | Instrument that shows wind direction |
| How are winds named? | For the direction the wind comes from |
| What causes winds to curve to their right in the northern hemisphere? | Coriolis Effect |
| As altitude increase, what does temperature do? | Decreases |
| As altitude increases what does pressure do? | Decreases |
| As temperature increase, what does pressure do? | Decreases |
| Are temperture & pressure positively or negatively correlated? | Negatively (Inversely) |
| Sea Breeze (def) | Cool breeze off of the ocean due to air on land heating up and rising away |
| Land Breeze (def) | Warm breeze off of the land due to cool air sinking over the land at night |
| Which direction does a Nor' easter blow? | Southwest |
| Name the 4 types of fronts | Warm, Cold, Stationary, & Occluded |
| Air Mass (def) | A large body of air that has the same properties as the surface over which it develops |
| Front (def) | Boundary between two air masses; storms & precipitation occur here |
| What does a fully darkened station model circle represent? | A completely overcast sky |
| What does a flag (pennant) represent on a station model shaft? | 50 knots |
| What does one long feather on a station model shaft represent? | 10 knots |
| What does a short feather on a station model shaft represent? | 5 knots |
| Which direction does the shaft of a station model point? | Into the wind. This example has the wind coming from the SE, 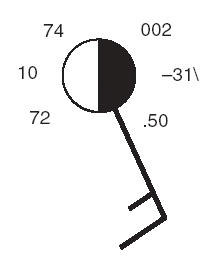 |
| Pressure gradient (def) | Rate of change in pressure |
| Layer of the atmosphere where the jet stream is found | Upper Troposphere |
| Direction Tornados usually move | From the southwest to the northeast |
| Where in the atmosphere do tornados usually form? | Usually form along a front |
| Tornado Alley Examples | Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, & Missouri |
| Meteorologist (def) | Person who studies the weater |
| Station Model (def) | Symbols used by (NWS) the National Weather Service to depict current weather in one particular area |
| Station Model symbol that means rain | Dots |
| Station Model symbol that means fog | 3 Horizonal lines like an = sign with an extra line |
| Station Model symbol that means snow | Asterick * |
| Weather Watch (def) | A cautionary statement issued by the NWS indicating that atmospheric conditions are favorable for the development of a particular weather or hydrologic phenomenon. |
| Weather Warning (def) | A cautionary statement issued by the NWS indicating that a specific hazardous weather or hydrologic event is imminent or actually occurring |
| pH of Acid Rain | 4.6 or lower |
| pH of "Normal" Rain | 5.6 |
| Why does hot air rise? | Hot air is less dense than the air around it |
| Why does cool air sink? | Cool air is more dense than the air around it |
| What are the 2 most abundant gases in our atmosphere with %? | Nitrogen 78% & Oxygen 21% |
What city has clear skies and warm weather?, 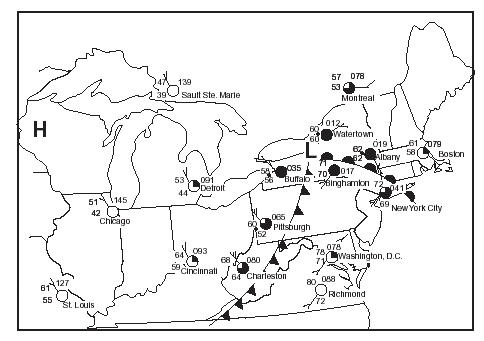 | St. Louis,  |
Which state has stormy weather: NY or Wisconsin?,  | NY. It has the L for low pressure,  |
Whis letter represents the leeward side of the mountain?,  | B,  |
What direction does Mill flow?, 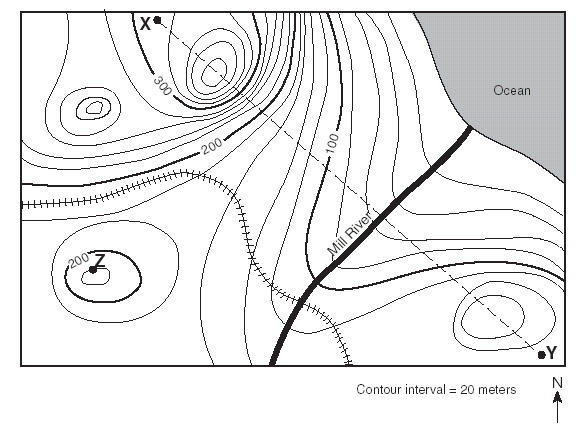 | NE contour lines bend & point up stream, river flows downstream,  |
What is the elevation of point Z?,  | 220 meters,  |
If the contour line for point Z had hachures on it, what would be the elevation of point Z?,  | 200 meters. The 1st depression contour is the same elevation as the last contour line around it because you come back down from the peak to go into the crater.,  |
| Temperature at which water is most dense | 4 degrees C |
| On Planet X, City A & B are exactly north & south of each other. The distance between City A & City B is 1000 m. At noon on a certain day, the sun is directly overhead at City A casting no shadow, but casts a shadow measuring 190 at City B. What is the circumference of Planet X? | 1894.74 m, 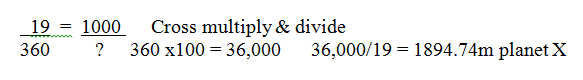 |
| Greenhouse Effect (def) | A warming of Earth's atmosphere do to an increase in certain gases such as carbon dioxide & methane |
| Chloroflurocarbons (def) | CFC's; destroy the Ozone layer in stratosphere |
| Which cools more slowly: water or land? | water |
| Which heats more quickly: water or land? | Land |
| Why does the Equator have a hotter climate than NJ? | The Equator gets more days of direct concentrated sunlight |
| How does air temperature relate to water vapor in the atmosphere | Air with higher tempertures can hold more water vapor |
| What kind of weather is predicted when a barometer rises? | High pressure = good weather |
| What kind of weather is predicted when a barometer falls? | Low pressure = Bad weather |
| Sea Breeze (def) | Occurrs when warm air over land rises and is replaced by cool air of the ocean |
| Land Breeze (def) | Occurs when warm air over the ocean rises and is replaced by cool air from land |
| 3ml = |  |
| List the layers of the atmosphere from the Earth up. | Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere |