| A | B |
|---|
| Organisms, such as plants, that make their own food are called ___. | autotrophs |
| Organisms that can't make their own food and must obtain their energy from food they consume are called ___. | heterotrophs |
| How many phosphate groups does ATP have? | Three (that's why it is called adenosine tri-phosphate) |
| How many phosphate groups does ADP have? | Two (that's why it is called adenosine di-phosphate) |
| Energy is released from an ATP molecule when __. | a phosphate group is removed. |
| When ATP releases energy, ___ is formed. | ADP (+ the phosphate group that came off) |
| ATP provides ____ for the mechanical function of cells. | energy |
| The energy in most food comes originally from ___. | sunlight |
| The formation of ADP from ATP ____ energy. | releases |
| The formation of ATP from ADP ____ energy. | requires |
| The energy required to convert ADP into ATP usually comes from burning ___. | carbohydrates |
What is the name of the molecule pictured below?,  | ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate). Notice the three phosphate groups.,  |
What is the name of the molecule pictured below?, 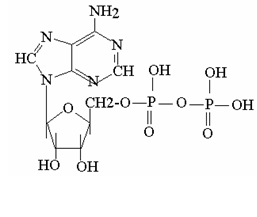 | ADP (adenosine di-phosphate). Notice it has two phoshate groups),  |
Besides plants, what are two other types of organisms that can conduct photosynthesis?, 
| Bacteria and protists both have members that do photosynthesis. |
| A student notices bubbles coming off of an aquatic plant when it is exposed to bright sunlight. These bubbles are most likely ___. | oxygen (because the plant is doing photosynthesis), 
|
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into ___., 
| oxygen and high energy sugars or starches |
What are three things needed for photosynthesis?, 
| water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight |
| Plants gather the sun's energy with light absorbing molecules called ___. | pigments |
| Which type of pigment is used to capture most of the sun's energy? | chlorophyll, 
|
| An orange pigment that captures some of the sun's energy is called ___. | carotene |
| Most plants appear green because chlorophyll ____ green light. | reflects |
| Which region of the visible spectrum is not absorbed well by chlorophyll? | green |
| Which region of the visible spectrum is not absorbed well by carotene? | orange |
| What is a granum (singular of grana)? | It's a stack of thylakoids inside a chloroplast. |
| The region of the chloroplast that is outside of the thylakoids is called the ___. | stroma |
| Where in the chloroplast can chlorophyll be found? | Within the thylakoid membrane |
Where do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place?, 
| Within the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast |
What are the products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?, 
| Oxygen gas, ATP and NADPH |
Where do the electrons that travel through the electron transport chain of photosynthesis originally come from?, 
| They are stripped from water molecules. |
| What happens to water molecules when they are stripped of electrons during photosynthesis? | The water molecules fall apart, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen gas. |
During which stage of photosynthesis is water needed?, 
| light-dependent reactions |
During which stage of photosynthesis is carbon dioxide needed?, 
| the Calvin Cycle (a.k.a. the light-independent or dark reactions) |
During which stage of photosynthesis is oxygen produced?, 
| light-dependent reactions |
During which stage of photosynthesis is the energy from ATP and NADPH used to produce high energy sugars?, 
| the Calvin Cycle (a.k.a. the light-independent or dark reactions) |
| Which products of the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis are needed during the Calvin Cycle? | NADPH and ATP |
For a tree doing photosynthesis, where does the carbon dioxide that is needed during the Calvin Cycle come from?, 
| the atmosphere |
The Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis is another name for the _____., 
| light-independent reactions |
| What is the product of the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis? | High energy sugars |
| Where does the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis take place? | In the stroma of the chloroplast |
What is the name of this entire structure?,  | chloroplast,  |
What is #1 pointing to?,  | A thylakoid inside a chloroplast,  |
What is #2 pointing to?,  | The grana of the chloroplast (a granum is a single stack of thylakoids),  |
What is #3 pointing to?,  | The stroma of the chloroplast,  |
What is the overall chemical equation for photosynthesis?, 
| .,  |