| A | B |
|---|
moon,  | A large object that travels with a planet through space. |
waxing crescent,  | Describes phases following a new moon in which less than half of the Moon appears to be lighted, but as more of the Moon's lighted side becomes visible. |
waning crescent,  | Describes phases that occur after a full moon, as less than half of the Moon appears to be lighted, and as the visible lighted side of the Moon is growing smaller. |
waxing gibbous,  | Moon phase in which more than half of the Moon appears to be lighted and as the visible portion of the moon is growing larger--moving towards a full moon. |
| full moon | Moon phase when all of the Moon's lighted half is visible; fourth phase after a new moon that happens 1/2 way through the moon's cycle.,  |
| new moon | Moon phase that occurs when the Moon is between Earth and the Sun, and the Moon cannot be seen because its lighted half is facing the Sun and its dark side faces Earth.,  |
| axis | An imaginary line that passes through Earth's center and the North and South poles, about which the Earth turns.,  |
tilt,  | 23.5 Degrees; the angle of the earth that is part of the reason for the seasons. |
rotation, 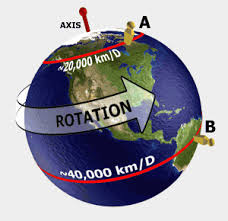 | Earth's spinning on its axis once every 24 hours, resulting in day and night. |
seasons, 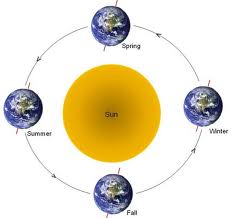 | Caused by the tilt of Earth on its axis as it revolves around the Sun; summer, fall, winter, spring |
| North Pole | The northernmost point of the Earth's axis., 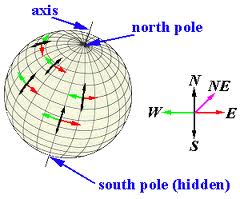 |
| South Pole | The southernmost point of the Earth's axis., 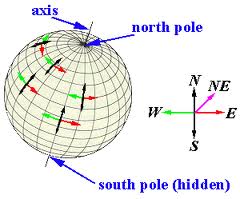 |
equator, 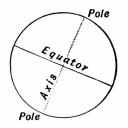 | An imaginary circle around the middle of the earth, halfway between the North Pole and the South Pole. |
| sun | A star that is the source of light and heat for the planets in the solar system.,  |
daylight, 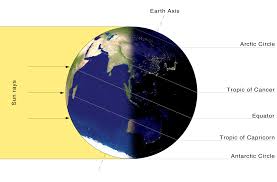 | Time during which the Sun is shining on your part of the Earth. |
| night | When part of the Earth is in darkness or shadow and not facing the Sun.,  |
moonlight,  | Rays from the sun that are reflected off the moon (which does not produce its own light). |
| lunar | Of, or relating to, the moon. luna=moon |
| solar | Of, or relating to, the sun. sol=sun |
lunar eclipse, 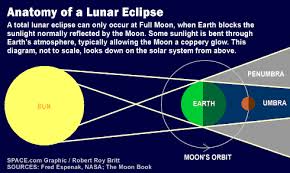 | An eclipse where the Earth comes between the Sun and the full Moon and the moon passes through Earth's shadow. |
solar eclipse,  | Occurs when the Moon passes directly between the Sun and Earth and casts a shadow over part of Earth |
| Earth | 3rd planet from sun; has an atmosphere that protects life & surface temperatures that allow water to exist as a solid, liquid, and gas,  |
sunrise,  | Happens as your part of the Earth begins spin out of darkness to face the sun and appears to "rise" above the horizon. |
| sunset | Happens as your part of the Earth slowly begins to turn away from the sun and into darkness and appears to "set" below the horizon.,  |
temperature,  | A measure of how hot (or cold) something is; a measure of the heat energy. |
orbit,  | n. The path that a planet or another object follows as it travels around another object in space. v. to move around a center point |
satellite,  | A natural object (like the Moon) or a man-made object (like the machines sending radio, tv or telephone signals through space) that revolves around (orbits) another object in space. The Moon is a _______ of the Earth. |
| phase | One of the different shapes of the moon as it is lit up by the Sun and seen from Earth., 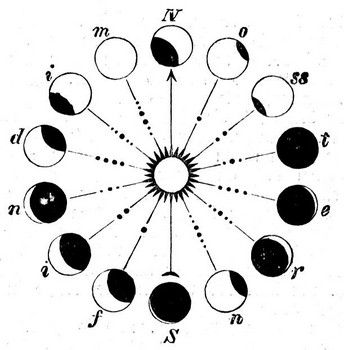 |
half-moon,  | When half of the moon is lit up by the sun, occurs on days 7 and 21 of a lunar cycle. |
| lunar month | The time it takes the moon to complete a full cycle of its orbit around the earth--about 29 days.,  |
cycle,  | A series of events that happen over and over again, such as the phases of the moon. |
| planet | A large body of rock or gas in space that orbits a star and does not produce light of its own.,  |
solar system,  | n. The planets and all the other objects that revolve around a star, such as the Sun |
| space | Anything outside the Earth's atmosphere, for example, anything flying higher than 100 miles above Earth.,  |
atmosphere, 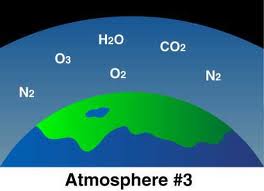 | A mixture of gases that surrounds a planet, moon, or sun. |
asteroid,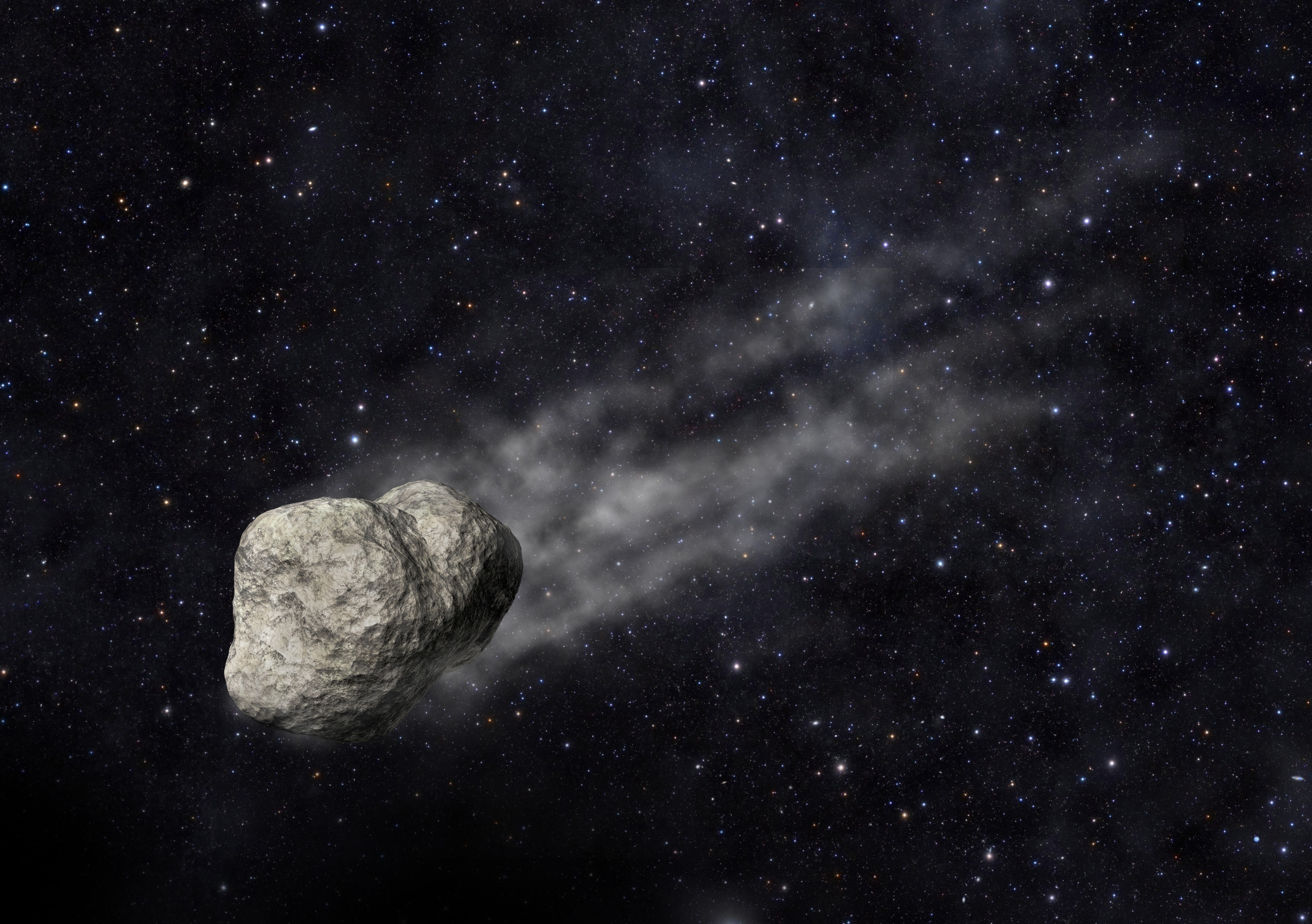  | A small, rocky object that orbits the sun; most asteroids are located in a band between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. |
| meteoroid | Any of the small rocks or space dust that hits the earth's atmosphere as it travels through space.,  |
meteorite,  | A meteoroid that falls from space, passing through the Earth's atmosphere and hitting the Earth's surface. |
comet,  | n. A ball of frozen gases, dust, ice and rock that orbits the Sun; comets evaporate as they near the Sun, forming long, glowing tails of gas and dust |
star,  | A mass of hot gases that gives off energy and light that are produced by reactions at its center; visible from Earth as a point of light. |
| stellar | Of or related to a star. stell=star |
telescope,  | A device built to observe far away things (like planets) by making them seem closer. |
| galaxy | A collection of stars, star systems, dust, and gas that are held together by gravity.,  |
Milky Way,  | A large spiral galaxy that is home to Earth and the rest of our solar system, including about a trillion stars. |
light-year,  | The distance light travels through space in one year (9.5 trillion km). |
| universe | n. All of space and everything in it; everything in existence,  |
| shadow | A dark area caused when an object blocks light from falling on a surface.,  |
reflection,  | The light energy that bounces off objects. |
| refraction | The bending of light rays when they pass through an object.,  |
solstice, 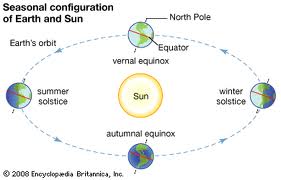 | One of two days each year, when Earth's axis is most tilted toward or away from the Sun, resulting in the shortest day of the year (December 22) and longest day of the year (June 21). |
| equinox | Each of the two times of the year (March 21-spring and September 23-fall) when the sun is directly over the equator at noon, and days and nights are of equal length., 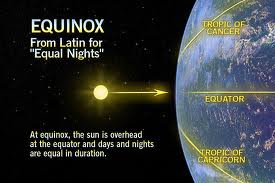 |
rocket,  | A device that burns fuel at extremely hot temperatures, forcing out gas in one direction, in order to move in the opposite direction through the atmosphere and into space. |
| Space Shuttle | n. A reusable orbiter vehicle for traveling into space, carrying people or equipment. It takes off like a rocket and lands like an airplane.,  |
| astronaut | A person who is trained to travel into outer space or to the stars. astro=star,  |
cosmonaut,  | A person who is trained to travel into outer space or through the universe, especially one who is from Russia. cosmos=universe |
probe,  | A spacecraft or robot that explores a region and uses sensors to collect scientific data, including visual image. Although a probe has no human crew and is completely controlled from Earth, astronomers have learned a great deal about our solar system from probes. |
| space station | A large man-made satellite or base on which people such as astronauts can live, work and conduct experiments for extended periods of time before returning to Earth.,  |
gravity, 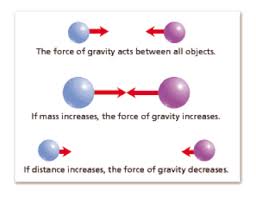 | n. It is a force that pulls two objects in the universe toward toward each other, such as between a person and the Earth. It is the force that keeps planets in their orbits. The more mass something has, the stronger it pulls on other objects. |
| space colony | Like a town built in space on the Moon or Mars that has its own supply of air and food and on which thousands of people could live for many years without returning to Earth.,  |
waning gibbous,  | Moon phase in which more than half of the Moon appears to be lighted and as the visible portion of the moon is growing smaller--moving towards a new moon. |
terraform,  | v. to change a planet, making it more like Earth |
| year | n. the time it takes the Earth to travel once around the sun,  |
NASA,  | n. National Aeronautics and Space Administration, a government agency of the United States responsible for developing advanced airplane and space exploration technology. |
union,  | n. the joining together of independent units into a single government |
mass,  | n. the amount of matter in an object; whether an object is a solid, a liquid, or a gas, the object always has mass; measured by how much something weighs |
justice,  | n. the establishment of rights according to the rule of law |
preamble,  | n. the introduction to a constitution that states the reasons for the laws that follow |
outer planets,  | plural n. the five planets in our solar system farthest from the sun; Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto |
inner planets, 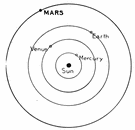 | plural n. the four planets in our solar system closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars |
| equality | n. the state or condition in which all people have the same freedoms and opportunities,  |
constitution,  | n. the basic principles and laws of a nation, state, or social group that determine the powers of the government and guarantee certain rights to people in it. |
colony,  | n. a settlement that retains close ties to its homeland |
| rover | n. a vehicle used to explore the surface of a planet or moon,  |