| A | B |
|---|
angle, 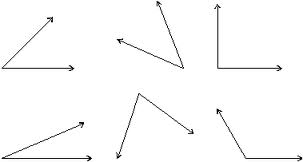 | where two rays or line segments meet at a common vertex (endpoint) or where two sides of a figure meet. |
acute angle, 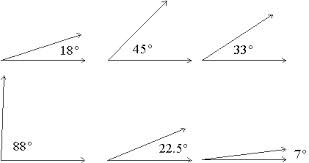 | Any angle less than 90 degrees but more than 0 degrees |
obtuse angle, 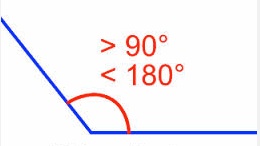 | Any angle measuring greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees |
ray, 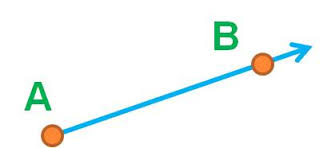 | Has a starting point but no ending point |
line,  | A path that is endlessly straight with no beginning or ending point |
line segment, 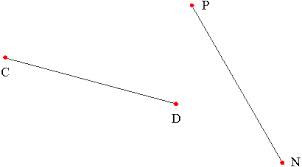 | A section of a line that has two endpoints, usually named by letters |
point, 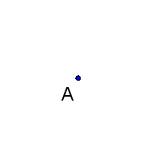 | A specific position in space, usually named by a letter |
vertex, 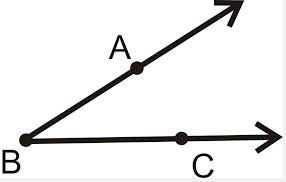 | A point where two or more rays meet or a point where the arms of an angle meet |
degrees, 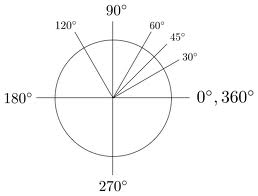 | Unit for measuring the size of angles |
| inner scale | One measure of degrees on a protractor; used to measure an angle that passes through the zero mark on the inside of the protractor |
outer scale, 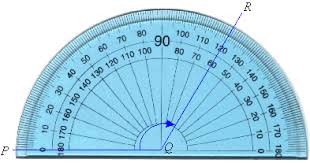 | One measure of degrees on a protractor; used to measure an angle that passes through the zero mark on the outside of the protractor |
right angle, 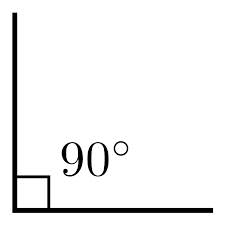 | Angle measuring exactly 90 degrees |
protractor, 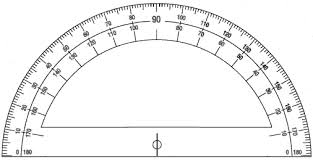 | Tool for measuring the size of an angle in degrees |
perpendicular, 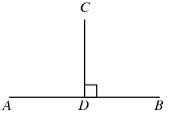 | Two lines intersect at a 90 degree angle |
parallel, 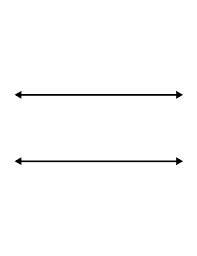 | Two lines that are always the same distance apart and never cross |
| four | Number of angles in a square or rectangle; same as its number of sides |
| three | Number of angles in a triangle; same as its number of sides |
| eight | Number of angles in an octagon; same as its number of sides |
| angle | The corner of a figure like a square or triangle; where two sides of a figure meet |
vertex,  | The point that is always in the MIDDLE when using letters to name an angle <aBc |
straight angle, 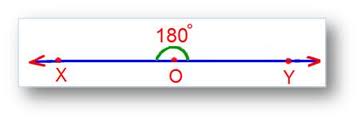 | Angle with a measure of exactly 180 degrees |
arm, 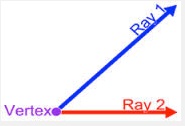 | Another name for a ray or line segment that is part of an angle |
baseline,  | Lines up with the arm of an angle that goes through the zero mark; straight edge of protractor |
center mark, 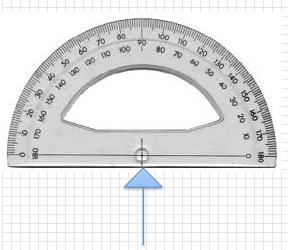 | Must be aligned with the vertex of an angle |
| line segment |  |
| line | 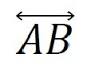 |
| ray |  |