| A | B |
|---|
| The smaller structures inside the cell which have specific functions are called __. | organelles |
| Which organelle stores the DNA of a cell? | nucleus,  |
| Which two cell structures are found in plant cells but not animal cells? | Cell wall and chloroplasts, 
|
| The dark structure located inside the nucleus that manufactures ribosomes is called ____. | the nucleolus,  , , 
|
| What is located just inside the cell wall of plant cells? | the cell membrane,  |
| The ______ doesn't allow DNA to leave the nucleus. | nuclear envelope (a.k.a. nuclear membrane) |
| Which organelle do plants use for photosynthesis? | chloroplasts, 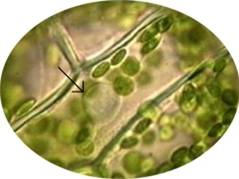 , , 
|
| Long strands of DNA wrapped around proteins are known as ___. | chromosomes (Remember, each chromosome is made up of 1 long double-stranded molecules of DNA wrapped around many histone proteins), 
|
| Which part of the cell regulates what enters or leaves the cell? | cell membrane,  |
Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called ____ that helps capture the energy from the sun for the process of ___., 
| chlorophyll, photosynthesis, 
|
| Everything inside the cell membrane except for the nucleus is called ____. | the cytoplasm, 
|
| The network of tube-like protein filaments that help give cells shape and support and also help with movement is called the ___. | cytoskeleton, 
|
| The structure that modifies, sorts and moves complex molecules made in the endoplasmic reticulum to other parts of the cell (or even to the outside of the cell) is called the ____. | golgi, 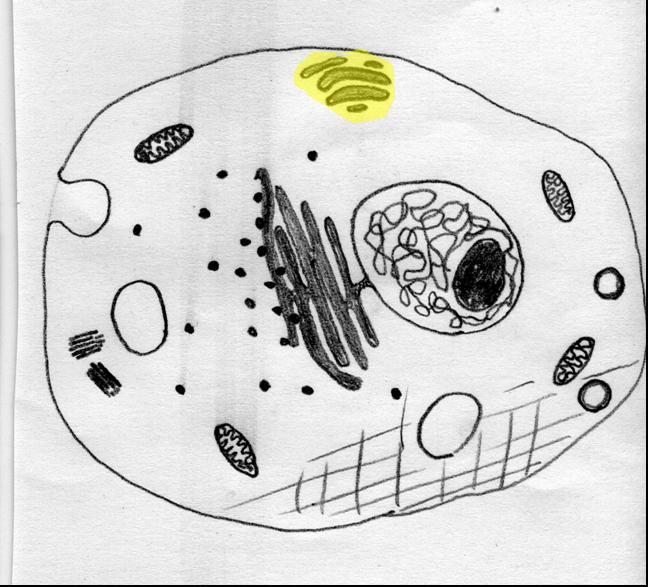 |
| The organelle that specializes in converting the chemical energy in food into molecules that the cell can more easily use for energy is called the ___. | mitochondria,  , , 
|
(true or false) Mitochondria are found only in animal cells., 
| False (plants need mitochondria also to break down the food they made during photosynthesis using the chloroplasts),  , , 
|
| The organelle where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled, along with proteins and other materials that are exported (sent out of) the cell is called ____. | the endoplasmic reticulum,  , , 
|
| The organelle that acts like a storage center is called ___. | a vacuole,  |
| The organelle that stores things and, in plant cells, also helps keep the cell from collapsing by storing large quantities of water, is called a(n) ____ . | vacuole,  |
| The small organelle that serves as the site where proteins are put together is called the ___. | ribosome,  , , 
|
| The organelle that contains strong enzymes for breaking down food molecules and recycling old cell parts is called the __. | lysosome, 
|
| Which organelle stores the body's genetic information? | the nucleus,  |
The nucleolus manufactures the parts used to make __., 
| ribosomes, 
|
| The cell membrane is located just ___ of the cell wall in plants | inside,  |
The short hair-like structures that help some single-celled organisms (like the one pictured below) swim, and that are also found on cells lining our throats, are called ___,  | cilia,  , , 
|
The longer tail-like structures that help some single-celled organisms (like the one pictured below) swim are called ___,  | flagella,  , , 
|
| What do all cells have in common? | A cell membrane and DNA for at least part of their life. (Also, all cells have ribosomes and cytosol) |
| All cells can be divided into these two categories based on whether they have a nucleus or not. | Prokaryotic (no nucleus, includes all types of bacteria) and Eukaryotic (all other types of life except the two kingdoms of bacteria) |
| Cells with a nucleus are called __. | Eukaryotic cells, 
|
| Cells without a nucleus are called ___. | Prokaryotic cells, 
|
| The movement of water molecules across a cell membrane is called ___. | osmosis |
| In a salt water solution, the salt is known as the ___. | solute |
| If a cell membrane allows glucose to pass through it, then the cell membrane is said to be ____ to glucose. | permeable, 
|
| In a salt water solution, the water is known as the ____. | solvent |
| The movement of particles across a cell membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration is known as ____. | diffusion |
| The cell membrane is said to be _______ permeable to substances because it lets some pass through but not others. | selectively |
| The type of substances that can most easily diffuse across a cell membrane are ____ substances. | small (It also helps if the substances are non-polar. Polar and ionic substances have a hard time diffusing through the phospholipid part of the cell membrane. They usually have to go through a transport protein) |
| The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a __________ | lipid bilayer (mostly phospholipids), 
|
| Larger molecules, polar molecules, and charged particles (ions) usually pass through _____ to get into or out of a cell. | transport proteins |
| Cells will shrink if placed into a _____ solution. | hypertonic |
| When energy is needed to force molecules across a cell membrane, _______ is taking place. | active transport |
| Cells will grow bigger if placed in a ____ solution. | hypotonic |
When osmotic pressure increases in plant cells, why don't the cells usually burst?, 
| Plant cells have a tough cell wall that keeps the cell from expanding enough to burst. |
| If a solution is 6% solutes, it will be ____ % water. | 94 |
| If a solution is 90% water, it will have ___ % solutes. | 10 |
| A solution that has the same concentration of solutes as the interior of a cell is known to be ____. | isotonic |
| Active transport requires _____. | energy |
| If a substance is crossing a cell membrane due to active transport, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ____ concentration. | low, high |
| If a substance is diffusing across a cell membrane, it is going from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ___ concentration. | high, low |
| The four types of proteins found in cell membranes are: | transport (like channel proteins), receptor, marker, and pumps |
When osmotic pressure decreases in a plant, the ______ shrink and the plant ____., 
| vacuoles, wilts |
| When osmotic pressure increases in plants, the ______ gets bigger and the plant ___. | vacuole, gets stiff |
| The type of cell membrane protein that allows larger molecules and ions to pass through by facilitated diffusion is called a ____. | transport protein (examples include channel proteins and carrier proteins) |
| The type of protein that a hormone could attach to on the outside of a cell membrane is called a ____. | receptor protein |
| The type of cell membrane protein that allows your body to recognize your own cells is called a ____ . | marker protein |
The process pictured below is called ____., 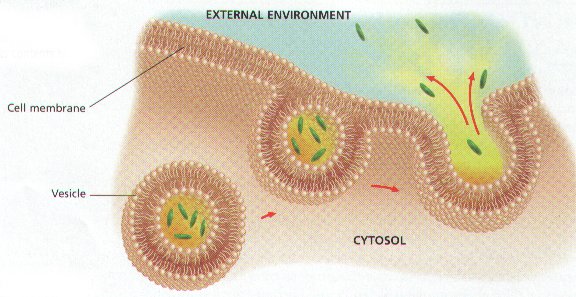 | exocytosis,  , , 
|
| A type of protein that travels through the blood stream and attaches to receptor proteins on a cell's surface in order to deliver a chemical message is known as a ____. | hormone |
The process pictured below is called ____., 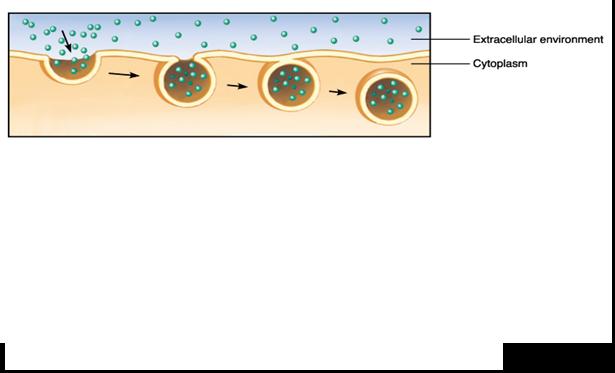 | endocytosis,  , , 
|
| When large molecules need the help of protein channels to cross the cell membrane, the process that is occurring is called ______. | facilitated diffusion |
| The type of endocytosis that takes in solid particles (usually food) is called ____. | phagocytosis |
| The type of endocytosis that takes in liquids is called ___. | pinocytosis |
| Name 3 types of active transport. | protein pumps, endocytosis and exocytosis. |
| The type of cell membrane protein that moves molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration is called a ___. | protein pump |
| Muscle, connective, and nerve are types of ____ in the body. | tissues |
| Heart, lungs, pancreas, and liver are examples of ____ in the body. | organs |
| A group of similar cells that perform a particular function in the body is called ___. | a tissue |
| The mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine are all part of the ____. | digestive system |
| A group of organs that work together to perform a specific function is called ___ | an organ system |
| What are the four levels of organization in multicellular organism, starting with the simplest and ending with the most complex? | cells, tissues, organs, organ systems |
| What are the four phases of the cell cycle? | G1, S, G2, and M |
| Chromosomes are only visible when ___. | the cell is dividing |
| When the cell is most actively growing, it is in the ____ phase. | G1 |
| When DNA is replicating, the cell is in the ___ phase. | S |
| When the cell is preparing for mitosis, it is in the ____ phase. | G2 |
| When the cell is undergoing cell division, it is in the ___ phase. | M |
| In order, what are the four stages of mitosis? | Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (remember PMAT) |
| G1, S, and G2 all occur during ____. | interphase |
| Which phases of the cell cycle occur during interphase? | G1, S, and G2 |
| Cell division ends when ____ has been completed. | cytokinesis |
| The ____ is a series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. | cell cycle |
| The ___ is a narrow region of the duplicated chromosome where sister chromatids are attached to each other. | centromere,  |
| The centromere region is where _____ are held together. | sister chromatids,  |
| After chromosomes undergo DNA replication, they consist of two identical ____ that are attached to each other. | sister chromatids,  |
| During which stages of mitosis are sister chromatids attached to each other? | prophase and metaphase |
| During which stage of mitosis do sister chromatids start to separate? | anaphase |
| During which stage of mitosis are sister chromatids lined up along the center of the cell? | metaphase (think metaphase = middle) |
| During which stage of mitosis does the nuclear envelope break down? | prophase |
| During which stage of mitosis do the chromosomes condense to become visible? | prophase |
| Centrioles help organize a fan-like group of protein fibers called the ____ that help pull the chromosomes apart. | spindle |
| In animal cells, ________ help organize a fan-like group of protein fibers called the spindle that help pull the chromosomes apart. | centrioles, 
|
| The division of the cytoplasm itself is called ___. | cytokinesis |
| In plant cells, cytokinesis is accomplished with the formation of a ___ between the two new cells. | cell plate |
| During which stage of mitosis are the chromosomes divided into the two opposite ends of the cell and the nuclear membrane reforms? | telophase |
| The two main stages of cell division are ___. | mitosis and cytokinesis, 
|
| One main difference between cell division in plants versus animals is that plants have ___. | a cell plate |
| One main difference between cell division in plants versus animals is that animals have ___. | centrioles |
| During normal cell division, a human cell with 46 chromosomes would produce two daughter cells with ___ chromosomes each. | 46 |
| A cell that has 5 chromosomes in G1 would have ___ chromosomes in G2 | 10 (remember they replicate during the S phase which occurs between G1 and G2) |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 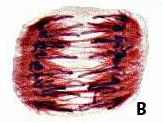 | Anaphase,  |
The structures labeled A are,  | sister chromatids,  |
The structures labeled B are,  | spindle fibers,  |
The area labeled C is called the ____,  | centromere,  |
| Uncontrolled cell division is also known as ______. | cancer |
| When cells divide over and over again because of cancer, a lump of cells called a ____ forms. | tumor |
| A(n) ____ can cause the proteins that control cell division to malfunction, causing the cell to divide uncontrollably. | mutation in DNA |
| How many phosphate groups does ATP have? | Three (that's why it is called adenosine tri-phosphate) |
| How many phosphate groups does ADP have? | Two (that's why it is called adenosine di-phosphate) |
| Energy is released from an ATP molecule when __. | a phosphate group is removed. |
| When ATP releases energy, ___ is formed. | ADP |
| ATP provides ____ for the mechanical function of cells. | energy |
| The energy in most food comes originally from ___. | sunlight |
| The formation of ADP from ATP ____ energy. | releases |
| The formation of ATP from ADP ____ energy. | requires |
What is the name of the molecule pictured below?,  | ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate). Notice the three phosphate groups.,  |
What is the name of the molecule pictured below?, 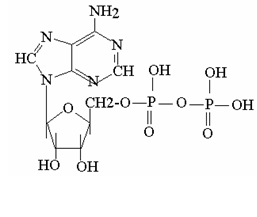 | ADP (adenosine di-phosphate). Notice it has two phoshate groups),  |
| How many kilocalories are found in a gram of carbohydrates? | about 4 kilocalories (a.k.a. Calories) |
| How many calories are in a kilocalorie? | 1000 |
| How many kilocalories are found in a gram of protein? | about 4 kilocalories (a.k.a. Calories) |
| How many kilocalories are found in a gram of lipids, such as fat or olive oil? | about 9 kilocalories (a.k.a. Calories) |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using energy from the glycolysis stage? | 2 ATP can be produced for every one molecule of glucose that goes through glycolysis. |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using energy from chemical reactions in the Krebs Cycle? | 2 ATP can be produced for every one molecule of glucose during the Krebs Cycle. |
| How many ADP can be turned back into ATP using the high energy electrons from one molecule of glucose during the electron transport chain? | During the electron transport chain, between 32 and 34molecules of ATP can be produced using the energy of high energy electrons stripped from one molecule of glucose. |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of glycolysis occur? | In the cytosol (cytoplasm) |
| In which part of the cell do the chemical reactions of the Krebs Cycle occur? | In the mitochondria,  |
| What is the only stage in cellular respiration that requires molecular oxygen? | The electron transport chain (oxygen removes the spent electrons from the end of the electron transport chain during aerobic cellular respiration) |
| Why is oxygen needed during aerobic cellular respiration? | Oxygen is needed to take the electrons away after they go through the electron transport chain. If they don't get taken away, the electron transport chain gets clogged with electrons and stops working. |
| How many ATP can be recharged using the energy stored in one molecule of glucose if oxygen is available? | Between 36 and 38 |
| Which of the three stages of cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide as a waste product? | Krebs Cycle |
| Which of the three stages of cellular respiration produces water as a waste product? | The electron transport chain. |
| What is the major difference between aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration? | Aerobic cellular respiration requires oxygen while anaerobic does not. |
| What is the purpose of turning pyruvic acid into alcohol or lactic acid if no oxygen is available? | Allows glycolyis to make more pyruvic acid which allows glycolysis to continue making 2 ATP per molecule of glucose. |
| Which two molecules carry high energy electrons and deposit them into the electrons transport chain? |  |
| What are the two main reactants of cellular respiration? | ., 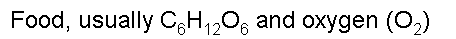 |
| What are the two main products of cellular respiration? | .,  |
| How many ATP can be generated from one molecule of glucose under anaerobic conditions? | 2 ATP per molecule of glucose can be generated under anaerobic conditions. |
| Glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of ____________ by the end of glycolysis. | pyruvic acid (a.k.a. pyruvate) |
| Where do the NADH's, generated during glycolysis and Kreb's Cycle, dump off their high energy electrons and hydrogen ions? | The NADH's dump off their high energy electrons to the system I proton pump of the electron transport chain. However, if the electron transport chain is backed up due to lack of oxygen, pyruvic acid from glycolysis will accept the electrons and hydrogen to form lactic acid. This way, NAD+ can be regenerated and used to keep glycolysis running. |
Where would the proteins involved with the electron transport chain be located?,  | B,  |
Where would the Kreb's Cycle take place?,  | D,  |
Where would glycolysis take place?,  | F,  |
Where would protons (hydrogen ions) be building up due to being actively transported during the electron transport chain?,  | C,  |
Where are the proteins involved with the electron transport chain located?,  | B,  |
Which letter indicates where aerobic cellular respiration takes place?,  | B,  |
| What happens to carbon dioxide that you generate inside cells during cellular respiration? | The carbon dioxide will diffuse out of the cell and enter the bloodstream. The bloodstream will pass the lungs where it will allow the carbon dioxide to diffuse into the lungs. From there, it is exhaled. |
| What do humans produce if they are not getting enough oxygen to process their food aerobically? | Lactic acid |
Besides plants, what are two other types of organisms that can conduct photosynthesis?, 
| Bacteria and protists both have members that do photosynthesis. |
| A student notices bubbles coming off of an aquatic plant when it is exposed to bright sunlight. These bubbles are most likely ___. | oxygen (because the plant is doing photosynthesis), 
|
Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into ___., 
| oxygen and high energy sugars or starches |
What are three things needed for photosynthesis?, 
| water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight |
| Plants gather the sun's energy with light absorbing molecules called ___. | pigments |
| Which type of pigment is used to capture most of the sun's energy? | chlorophyll, 
|
| Most plants appear green because chlorophyll ____ green light. | reflects |
| Which region of the visible spectrum is not absorbed well by chlorophyll? | green |
| What is a granum (singular of grana)? | It's a stack of thylakoids inside a chloroplast. |
| The region of the chloroplast that is outside of the thylakoids is called the ___. | stroma |
| Where in the chloroplast can chlorophyll be found? | In the thylakoids |
Where do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis take place?, 
| Within the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast |
What are the products of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?, 
| Oxygen gas, ATP and NADPH |
Where do the electrons that travel through the electron transport chain of photosynthesis originally come from?, 
| They are stripped from water molecules. |
| What happens to water molecules when they are stripped of electrons during photosynthesis? | The water molecules fall apart, producing hydrogen ions and oxygen gas. |
During which stage of photosynthesis is water needed?, 
| light-dependent reactions |
During which stage of photosynthesis is carbon dioxide needed?, 
| the Calvin Cycle (a.k.a. the light-independent or dark reactions) |
During which stage of photosynthesis is oxygen produced?, 
| light-dependent reactions |
During which stage of photosynthesis is the energy from ATP and NADPH used to produce high energy sugars?, 
| the Calvin Cycle (a.k.a. the light-independent or dark reactions) |
| Which products of the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis are needed during the Calvin Cycle? | NADPH and ATP |
The Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis is another name for the _____., 
| light-independent reactions |
| What is the product of the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis? | High energy sugars |
| Where does the Calvin Cycle of photosynthesis take place? | In the stroma of the chloroplast |
What is the name of this entire structure?,  | chloroplast,  |
What is #1 pointing to?,  | A thylakoid inside a chloroplast,  |
What is #2 pointing to?,  | The grana of the chloroplast (a granum is a single stack of thylakoids),  |
What is #3 pointing to?,  | The stroma of the chloroplast,  |
What is the overall chemical equation for photosynthesis?, 
| .,  |