| A | B |
|---|
| A carrot has a diploid number of 18. What is it's haploid number? | 9 |
| Gametes are produced by the process of ___. | meiosis |
| Another word for sex cell is ___. | gamete |
| Which stage of meiosis do chromosomes form tetrads? | prophase I |
| During which stage of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell? | metaphase I |
| During which stage of meiosis do sister chromatids separate from each other? | anaphase II |
| For meiosis, when does DNA replication occur? | Interphase I only (Remember, there is no interphase II, and technically, interphase is not a stage of meiosis. It comes before meiosis, just like interphase also comes before the start of mitosis.) |
| What is the diploid number of chromosomes in humans? | 46 (also written as 2n=46) |
| What is the haploid number for humans? | 23 (also written as n=23) |
| The sex cells of fruit flies have 4 chromosomes each. What is the diploid number of chromosomes for fruit flies? | 8 (remember the diploid number is always twice the haploid number) |
| _________ chromosomes are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, but are not identical. | Homologous |
| _________ are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, and are identical. | Sister chromatids |
| A(n) _____ is a segment of DNA that has the instructions for making one protein. | gene |
| A chromosome is made of ___ DNA molecule(s) | one |
| When two homologous chromosomes are lined up right next to each other during meiosis, they are referred to as a ___. | tetrad |
| During which stage of meiosis might crossing over occur? | prophase I |
| When homologous chromosomes are lined up next to each other during meiosis, they might swap pieces of DNA. This phenomenon is called ___. | crossing over |
| Crossing over during meiosis is important because it increases ___. | genetic variation (= the number of different chromosomes, and therefore different combinations of traits, that offspring can inherit) |
Which diagram is mitosis?,  | Mitosis is on the left,  |
When chromosomes are lined up like this during meiosis, what are they referred to as?, 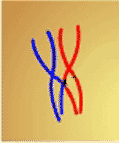 | A tetrad,  |
Which process from meiosis is shown below and during which stage would it occur?, 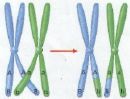 | The picture shows "crossing over" and it usually happens during prophase I.,  |
| A gene can be cut out of a DNA molecule using a _____. | restriction enzyme |
| DNA that has had genes from a different organism spliced into it is called ___. | recombinant DNA,  |
| Segments of DNA can be separated from each other based on their relative size using ____. | gel electrophoresis,  |
| A technique that can be used to make many copies of DNA in the lab is called ____. | PCR (polymerase chain reactions), 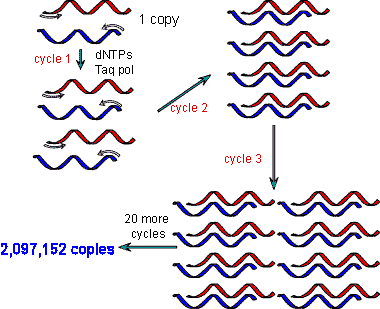 |
| Cells that have taken in DNA from outside the cell have undergone a process called ____. | cell transformation |
| An organism that has genes from other species is called a _____ organism. | transgenic |
| A(n) ___ is a member of a population of genetically identical cells produced from a single cell. | clone |
| Researchers were able to clone a sheep by taking the nucleus out of an egg cell, replacing it with the nucleus from _____ from another sheep, and placing the egg into the womb of a female sheep to grow as a zygote would. | an adult cell |
| The most common vector for getting recombinant DNA into a bacterial cell is a(n) ______. | plasmid |
| A(n) _______ is a small circular piece of DNA, common in bacteria, that often times has genes that give the bacteria antibiotic resistance. | plasmid |
| Inserting new helpful DNA into the body cells of an already born human can be accomplished through ______. | gene therapy |
Which process is shown below?,  | Gel electrophoresis,  |
| Gregor Mendel used ____ to study the inheritance of traits. | pea plants |
| Mendel removed the male parts from the flowers of some plants in order to ___. | prevent self-pollination |
| Mendel noticed that each "factor" in pea plants had two "forms." These "forms" would later be called ___. | alleles |
| The ______ states that some alleles are dominant while others are recessive. | principle of dominance |
| When Gregor Mendel crossed true-breeding tall plants with true-breeding short plants, the offspring were ___. | all tall |
| The person considered to be the father of genetics is ___. | Gregor Mendel |
| If the offspring from a true-breeding tall plant and a true-breeding short plant are allowed to self-pollinate, they will produce offspring in the F2 generation that are ___. | about 75% tall and 25% short (Remember, it asked about the F2 generation. The true-breeding parents would be the P generation. Their offspring who were allowed to self-pollinate were the F1 generation. The offspring that resulted from the self-pollination were the F2 generation) |
| Plants with the ___ form of a trait are always true-breeding. | recessive |
| Plants with the ____ form of a trait can be true-breeding while other plants with that trait might not be true-breeding. | dominant |
| True-breeding plants that produced constricted pods were crossed with true-breeding plants that produced inflated pods. The resulting offspring produced inflated pods. It can be concluded that the ____ pod allele is dominant. | inflated |
| When alleles ___ from each other, they separate. | segregate |
| Alleles segregate from each other when ___ form during the process of ___. | sex cells form during the process of meiosis. |
| Different forms of the same gene are called _____. | alleles |
| Dominant alleles are represented by a _______ letter. | capital (ex:T= tall in pea plants) |
| Recessive alleles are represented by a _______ letter. | lower case (ex: t = short in pea plants) |
| The types of alleles that an organism inherits is known as the ______. | genotype (example = Bb) |
| The physical expression of two alleles is known as the organism's _____. | phenotype |
| Bb would be called the organism's _____ while "brown eyes" would be the organism's _____. | genotype, phenotype |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is BB? | Brown eyes |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is Bb? | Brown eyes (remember that B is dominant) |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is bb? | blue eyes |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organism's genotype be if the organism was heterozygous? | Bb (remember that 'hetero' means 'mixed') |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organism's genotype be if the organism is homozygous dominant? | BB (remember that 'homo' means 'same') |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organism's genotype be if the organism is homozygous recessive? | bb (remember that 'homo' means 'same') |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 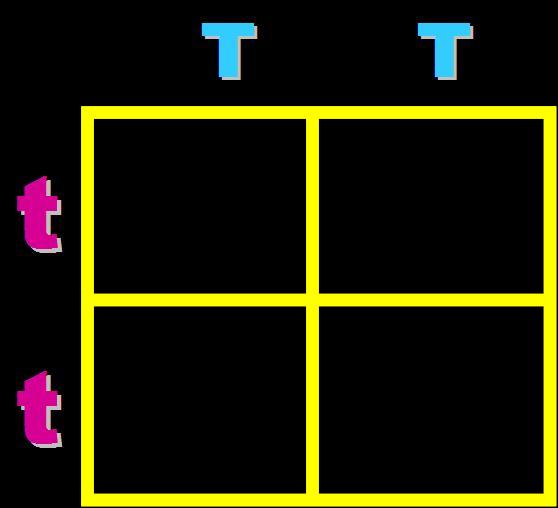 | Genotype = 100% Heterozygous (Tt) Phenotype = 100% tall, 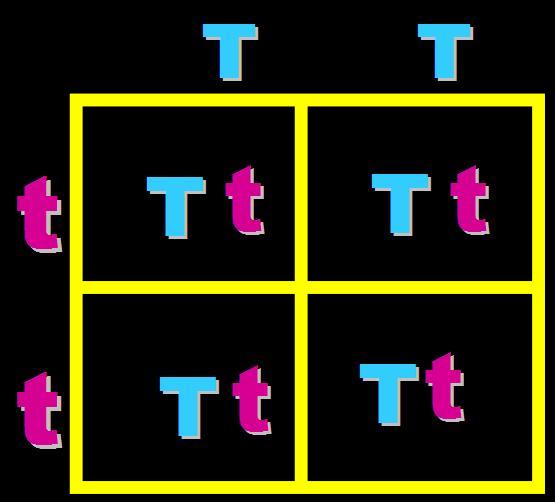 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 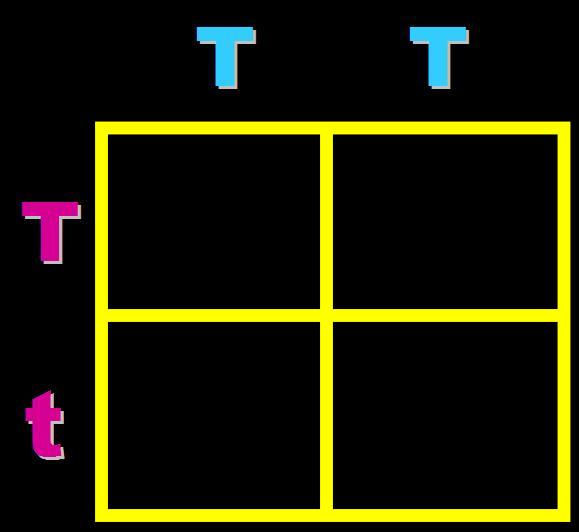 | Genotype = 50% homozygous dominant (TT) and 50% heterozygous (Tt) Phenotype = 100% Tall, 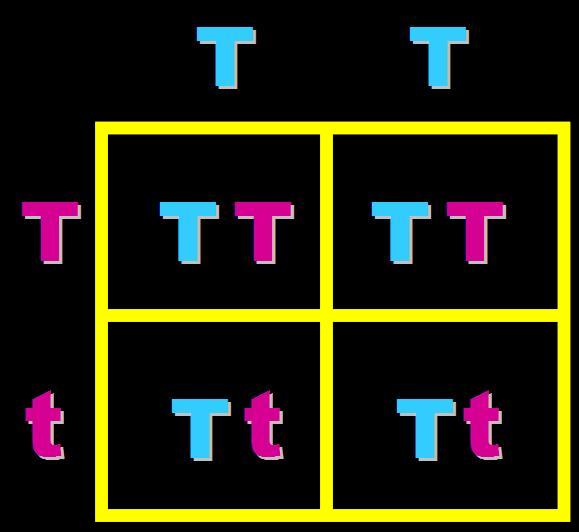 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 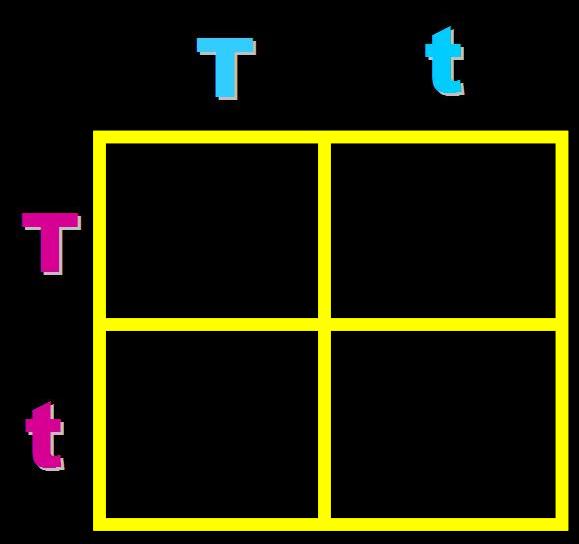 | Genotype = 25% Homozygous dominant (TT), 50% heterozygous (Tt) and 25% homozygous recessive (tt) Phenotype = 75% Tall and 25% short,  |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages.,  | Genotype = 50% heterozygous (Tt) and 50% homozygous recessive (tt) Phenotype = 50%Tall and 50% short, 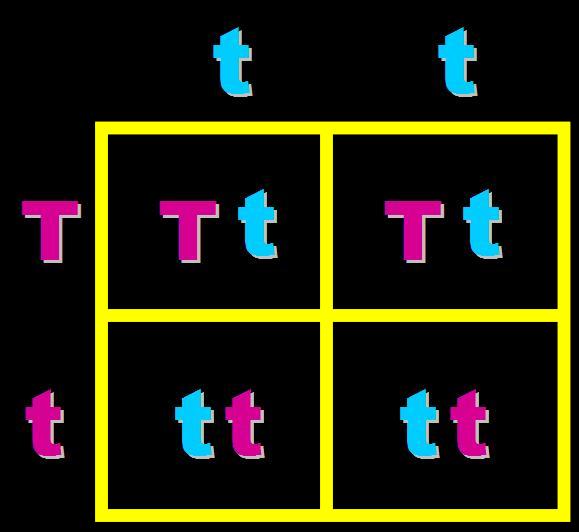 |
| How would your set up a Punnett Square for a cross between a short male pea plant and a heterozygous tall female? |  |
| Another word for heterozygous is ____. | hybrid |
| Another word for homozygous is ____. | purebred |
| Another word for purebred is ____. | homozygous, 
|
| Another word for hybrid is ____. | heterozygous, 
|
| The process of making proteins inside cells is called ______. | protein synthesis |
| Inside which organelle is DNA located? | nucleus (Remember, prokaryotes don't have a nucleus, so their DNA is located out in the cytosol/cytoplasm) |
Which type of nucleic acid can't leave the nucleus?, 
| DNA |
| On which organelle are proteins made? | ribosomes (This is true of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotic ribosomes are a little bit smaller, but otherwise very similar to the eukaryotic ribosome), 
|
| Where are ribosomes located? | out in the cytosol (Most of the time, they are free-floating. Sometimes, they attach to ER to make rough ER), 
|
| The process of making a strand of m-RNA in the nucleus is called _____. | transcription |
| What are four differences between RNA and DNA? | 1) RNA is single-stranded instead of double 2) RNA has the nucleotide uracil in place of thiamine 3) RNA can leave the nucleus and DNA can't 4) RNA includes the sugar called ribose while DNA includes the sugar called deoxyribose |
Which nucleotide do you find in RNA but not DNA?, 
| uracil |
| Uracil bonds to _____ at the nitrogenous base. | adenine |
| The process of using the code on RNA to make a long chain of amino acids in the correct order to form a protein is called _____. | translation |
| Which type of molecule brings amino acids to the site of protein synthesis? | transfer RNA (t-RNA) |
| Which molecule attaches to a ribosome and serves as a code for putting amino acids together? | messenger RNA (m-RNA) |
How many nucleotides are needed to code for 1 amino acid?, 
| 3 |
| How many different types of amino acids are used to make proteins? | 20 |
Each set of 3 nucleotides on a strand of m-RNA is called a(n) _____., 
| codon |
| How many nucleotides are found at the bottom of a molecule of t-RNA and are involved with bonding to m-RNA? | 3 (The part labeled B in the diagram below), 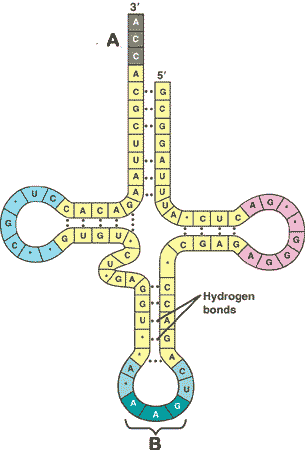 |
| How many amino acids are found attached to a molecule of t-RNA? | 1,  |
A change in the sequence of nucleotides in a molecule of DNA is called a(n) ____., 
| mutation |
| Mutations that are harmful are usually weeded out by ______. | natural selection |
| Mutations in a gene that are helpful usually become part of the gene pool as a new ____. | allele (a different form of a gene) |
Which amino acid would the codon sequence AGU call for?,  | Serine,  |
| Which enzyme is required for transcription? | RNA Polymerase (remember, you are making RNA during transcription) |
| What are three types of RNA? | m-RNA (messenger RNA), t-RNA (transfer RNA) and r-RNA (ribosomal RNA) |
| Where does transcription occur? | In the nucleus (In prokaryotes, it occurs out in the cytosol because prokaryotic organisms don't have a nucleus) |
| Where does translation occur? | Out in the cytoplasm on ribosomes. |
| Genes contain instructions for assembling ___. | proteins |
| Proteins are made out of ____. | amino acids |
The picture below is called the ____.,  | genetic code (All organisms, from prokaryotic bacteria all the way up to humans, use this same genetic code),  |
| What type of proteins are made by the endoplasmic reticulum and what type of ER makes them? | The rough ER usually makes proteins that will be exported from the cell (For example, hormones like insulin would be made using the ribosomes on rough ER and then further modified in the golgi before transported to the cell membrane by vesicles. The digestive enzymes in lysosomes would also be made in the ER and further modified in the golgi) |
| What is the name of the organelle that can modify proteins after they have been made in the rough ER? | golgi |
| What type of proteins are usually made on free-floating ribosomes in the cytosol? | Proteins that will stay in the cytosol (like enzymes) |
| A mutation that involves one or a few nucleotides is called a(n) ____. | point mutation |
| Another word for a point mutation is a ____ mutation. | gene |
| What are the three types of point mutations? | substitution, insertions and deletions |
| Which types of point mutations cause frameshift mutations? | insertions and deletions |
| A type of point mutation that causes a change in every amino acid following the mutation is called a(n) ____ mutation. | frameshift |
| A point mutation will cause the cell to make an incomplete protein if the mutation results in an early ____ codon. | stop |
| A picture of all 46 chromosomes paired in homologous pairs is called a(n) _____. | karyotype,  |
| The karyotype of a person with Down syndrome would show ___. | three chromosomes at the 21st pair.,  |
| The failure of chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis is called ___ and can lead to conditions such as ____. | nondisjunction, Down syndrome,  |
| Nondisjunction is the failure of chromosomes to separate properly during ____ and can lead to a person being born with an extra ____. | meiosis, chromosome,  |
| Four types of chromosomal mutations are ___. | Deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations |
The type of mutation shown below is a(n) _____.,  | chromosomal deletion,  |
The type of mutation shown below is a(n) _____.,  | chromosomal duplication,  |
The type of mutation shown below is a(n) _____.,  | chromosomal inversion,  |
The type of mutation shown below is a(n) _____.,  | chromosomal translocation,  |
A picture like the one below is called a(n) ____.,  | karyotype,  |
What would be the sex of the person who owns these chromosomes?,  | male (notice the X and the Y chromosome at the last pair),  |
What type of genetic disorder does the owner of these chromosomes have?,  | Down syndrome (notice the extra chromosome at the 21st pair),  |
| What do you call a point mutation that changes a nucleotide in a codon, but doesn't change the resulting amino acid? | Silent mutation (Silent mutations are almost always caused by a base-pair substitution that causes the 3rd nucleotide in a codon to change. As you can see in the genetic code chart below, changing the third base often times does not change the amino acid that is called for.),  |
| What do you call a point mutation that ends up causing a stop codon to be read earlier than normal so that the resulting protein is smaller than it should be? | Nonsense mutation (because the protein will be non-functional and its structure will make no sense) |
| The type of inheritance where neither allele is dominant and they tend to produce a mix of the two traits such as blue + white = light blue would be _____. | incomplete dominance |
| The type of inheritance where both alleles are dominant, such as red fur + white fur = red and white fur hairs in roan cattle is known as ____. | codominance |
| The type of inheritance where there is more than two alleles for a single trait, such as A, B, and O alleles for blood type, is known as ____. | multiple alleles |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,IA, what is your blood type? | type A |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,i, what is your blood type? | Type A |
| If your genotype for blood type is IB,IB, what is your blood type? | Type B |
| If your genotype for blood type is IB,i, what is your blood type? | type B |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,IB, what is your blood type? | Type AB |
| If your genotype for blood type is ii, what is your blood type? | Type O |
| Genes that are located on the 23rd pair of chromosomes (but only on the X, not the Y chromosome) are known as ____. | sex-linked genes |
| If you have an X and a Y chromosome, what is your gender? | male |
| If you have two X chromosomes, what is your gender? | female |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring of this cross? (Change the A's to IA's, the B's to IB's and the O's to i's),  | 25% type AB blood, 25% type A blood, 25% type B blood, 25% type O blood,  |
| How would you set up a Punnett Square for a cross between a heterozygous blood type A male and a heterozygous blood type B female? | (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's),  |
In humans, colorblindness is a sex-linked recessive allele. What are the expected phenotypes of the offspring if both parents have normal vision but the mother is heterozygous?,  | 100% normal vision girls and 50% of the boys are expected to be colorblind., 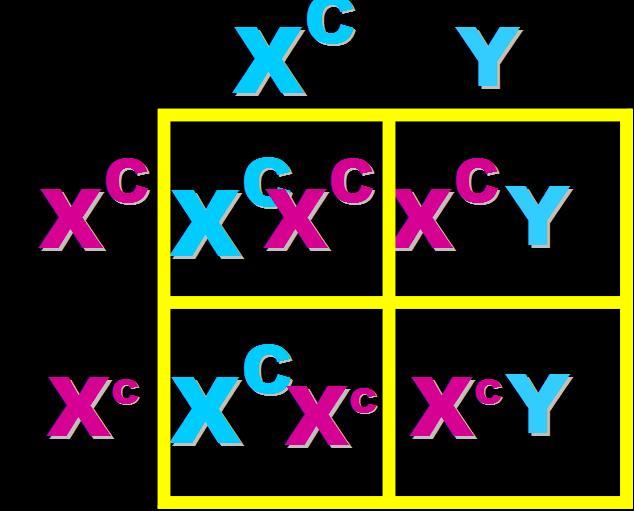 |
| How would you set up a cross between a male with type AB blood and a female with type O blood? (The A stands for IA, the B's stand for IB and the O stands for i) | (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's),  |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring and what are the odds of each? (Change the A's to I<sup>A</sup>'s the B's to I<sup>B</sup>'s and the O's to i's),  | 50% of the offspring are expected to have type A blood and 50% are expected to have type B blood. All offspring will be heterozygous. Remember that the O allele is recessive.,  |
| A trait, like human skin color, that involves several different genes is called a(n) _____. | polygenic trait (remember, "poly" means many and "genic" refers to genes) |
The following diagram is an example of a(n) ___.,  | pedigree chart,  |
| Different forms of the same gene are called _____. | alleles |
| Which law states that the two alleles for a heritable character separate during gamete formation and end up in separate gametes? | The Law of Segregation |
| A dihybrid cross between 2 individuals that are heterozygous for two independently assorting characterisitics (such as seed color and seed shape), produces the classic ________ ratio. | 9:3:3:1 ratio,  |
| Which law states that each pair of alleles segregate independently of other pairs during gamete formation? When is this law not true? | Law of independent assortment. This law does not hold true if the alleles for two different characteristics are located on the same chromosome. |
| New alleles for a gene are formed by _________ that survive the ________ process. | mutations, natural selection |
The following picture is an example of a ______.,  | karyotype,  |
| Humans have ____ autosomes and ____ sex chromosomes in a normal karyotype. | 44, 2,  |
| Humans have 44 __________ and 2 _________ in a normal karyotype. | autosomes, sex chromosomes |
| Abnormal number of chromosomes in a human's karyotype are caused by a problem in separating chromosomes properly during meiosis called ___________. | nondisjunction,  |
| ______ is a condition in which a person is born with 3 copies of a homologous pair instead of the usual two. | Trisomy (The person below has trisomy-21, otherwise known as Down Syndrome, because of their extra chromosome at the 21st pair.),  |
Trisomy-21 (see picture below) causes __________ .,  | Down syndrome (The picture below shows a child with Down syndrome. People with Down syndrome have characteristic features of eyes wide apart, heavy eyelids, below average height, and below average (but not always) intelligence. Other complications lead to a lower than average life-expectency), 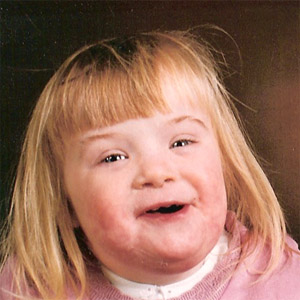 |
| During which process would nondisjunction occur? | meiosis,  |
| The shape of DNA is described as a _____. | double helix |
| The monomers of DNA are ____. | nucleotides, 
|
How many different types of nucleotides are found in a molecule of DNA?, 
| four |
| What are the three parts to a nucleotide? | 1) nitrogenous base, 2) a sugar (In the case of DNA it is deoxyribose sugar. Thats where the D in DNA comes from. Deoxyribonucleic Acid), 3) phosphate group,  |
| DNA is a _____ stranded molecule. | double |
Which nucleotide always bonds to thymine (T) across the middle where the nitrogenous bases meet?, 
| adenine (A) |
| In DNA, which nucleotide always bonds to adenine (A) across the middle where the nitrogenous bases meet? | thymine (T) |
| Which nucleotide always bonds to cytosine (C) across the middle where the nitrogenous bases meet? | guanine (G) |
| Which nucleotide always bonds to guanine (G) across the middle where the nitrogenous bases meet? | cytosine (C) |
| During DNA replication, if the original strand of DNA has the base sequence CGGTATC, the new strand across from it will have the sequence of nucleotides ____. | GCCATAG |
| In which organelle is DNA located in inside the cell? | In the nucleus (as part of a chromosome) |
| A chromosome is made of one long ______________ wrapped around histone _________. | molecule of DNA, proteins |
| DNA that is tightly coiled around histone proteins is known as a _____. | chromosome |
| How many chromosomes do most human cells hold? | 46, 23 pairs (as you can see for yourself in this karyotype),  |
| How many chromosomes do human sex cells have? | 23 total (1 of each type) |
| A segment of DNA that holds the code for a particular protein or trait is called a ____. | gene |
| The process of making a copy of a molecule of DNA is called ___. | DNA replication |
| Which enzyme adds nucleotides to the sides of the unzipped DNA molecule during DNA replication? | DNA polymerase |
| _______ results in 2 DNA molecules, each with one new strand and one original strand. | DNA replication |
| Which enzyme helps unzip DNA molecules? | Helicase |