| A | B |
|---|
| weight | the measure of the force of gravity on an object. |
| volume | is the amount of space that matter occupies |
| mass | the amount of matter in an object |
| weather | the condition of the Earth's atmosphere at a particular time and place |
atmosphere,  | the envelope of gases that surrounds the planet |
Antoine Lavoisier,  | Founder of modern chemisrty,  |
| water vapor | water in the form of GAS! |
denisty,  | The amount of mass in a given volume |
| air pressure | the result of the weight of a column of air pushing on an area. |
| barometer | an instrument used to measure air pressure |
mercury barometer, 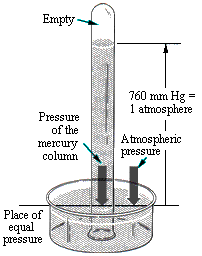 | used to measure changes in air pressure; consists of a glass tube partially filled with mercury resting in a dish of mercury,  |
aneroid barometer,  | An instrument that measures changes in air pressure without using a liquid.,  |
| millibars or inches of mercury | units for air pressure |
| altitude | elevation/distance above sea level |
troposhere, 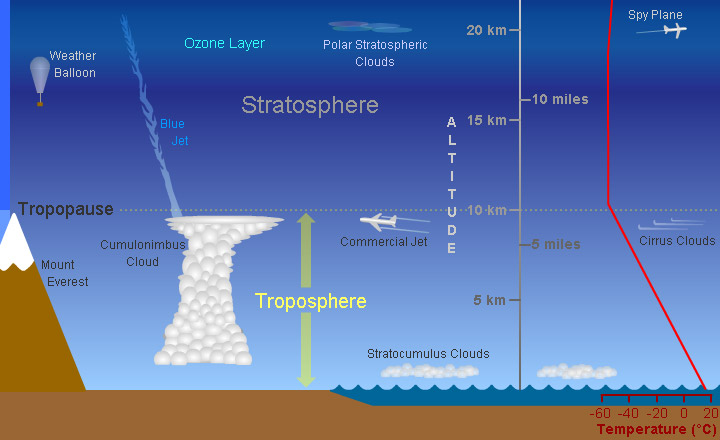 | lowest layer of the Earth's atmosphere. Where the Earth's weather occurs.,  |
stratosphere,  | 2nd layer of the atmosphere and contains the ozone layer,  |
Mesophere,  | middle of the atmosphere. protects the earth from being hit by most meteroids.,  |
thermosphere,  | The outermost layer of Earth's atmosphere,  |
ionosphere, 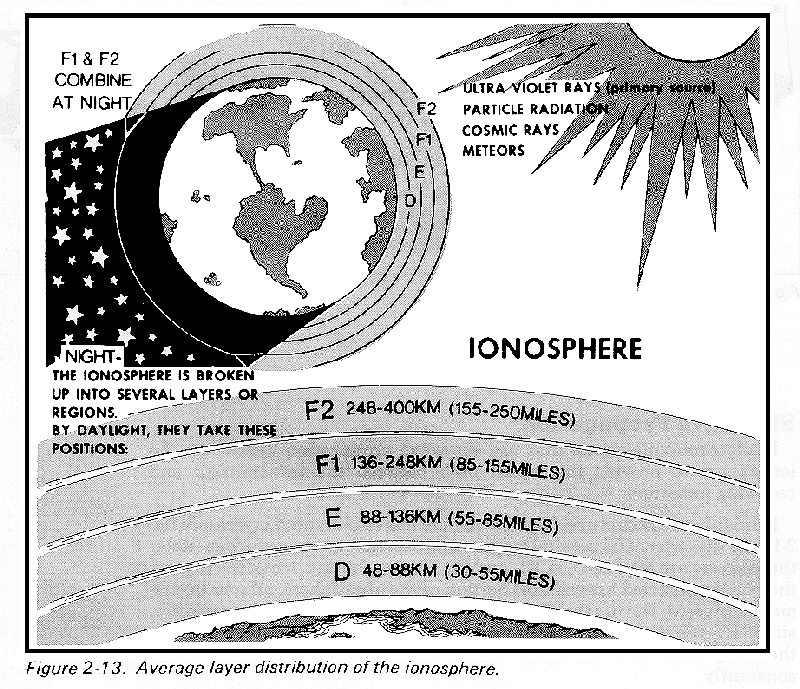 | The lower layer of the thermosphere. |
exosphere,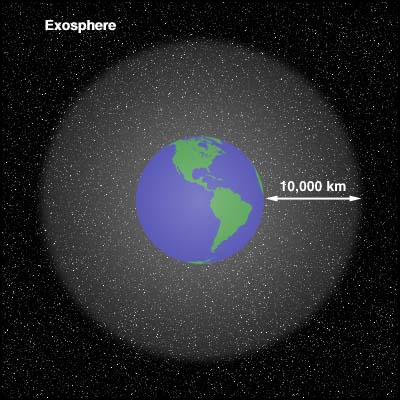  | Outer layer of the thermosphere that extends from 400km to about 10,000 km,  |
electromagnetic waves, 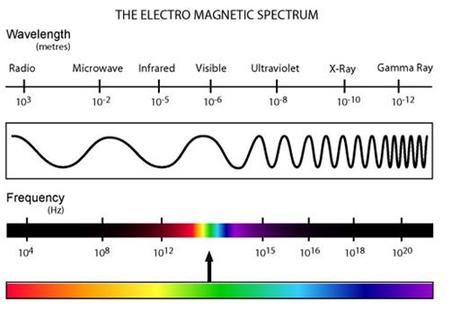 | How the energy from the sun reaches the earth. Can be divided into radio waves, microwaves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, x-rays, and gamma rays.,  |
visible light,  | all light that we can see. Including all colors of the rainbow |
| radiation | direct transfer of electromagnetic waves |
| infrared radiation | has wavelengths that are longer than red light. It is not visible, but can be felt as heat. |
ultraviolet radiation,  | An invisible form of energy with shorter wavelengths then violet light. Ultraviolet radiation can cause sunburns.,  |
| scattering | When dust sized particles and gases in the atmosphere disperse light in all directions. |
| reflect | to cast back (light, heat, etc.) from a surface |
| absorb | to take up or receive by chemical or molecular action |
| radiate | to emit rays, as of light or heat |
greenhouse effect,  | The trapping of heat near a planet's surface by certain gases in the planet's atmosphere. |
| temperature | the average amount of energy of motion of each particle of a substance. |
| absolute zero | the temperature where all the motion of all particles in a substance stops. -273ºC or -459 ºF |
| thermal energy | measures the total energy of motion in the particles of a substance. |
| thermometer | a device that measures temperature. |
convection, 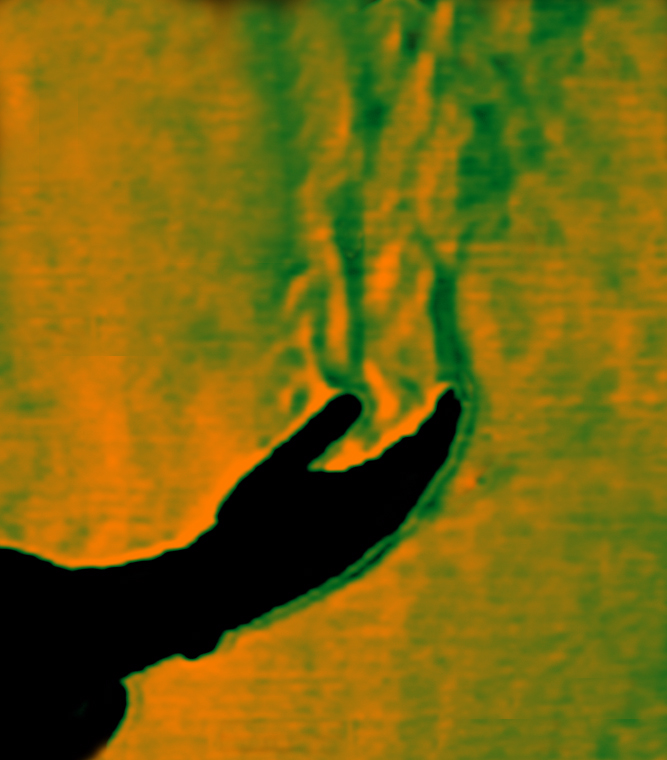 | the transfer of energy by the movement of a fluid (,  |
conduction,  | The transfer of heat between two substances,  |
| convection currents | formed by the upward movement of warm air and the downward movement of cool air. Heat is transferred mostly by convection within the troposphere. |
| Wind | The movement of air parallel to the Earth's surface. Just don't break it! |
anemometer,  | used to measure wind speed |
| windchill factor | A measuring of cooling combining temperature and wind speed |
| local winds | Winds that blow over short distances. |
global winds, 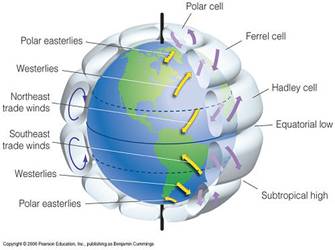 | Winds that blow steadily from specific directions over long distances.,  |
| Coriolis Effect | The way the Earth's rotation makes winds curve. |
Latitude,  | Parallel lines that measure the distance north or south of the equator. |