| A | B |
|---|
| resin material applied to pits and fissures | denatal sealant |
| the process of changing a simple chemical into another substance that contains the same elements | polymerization |
| a type of material that is polymerized by a chemical reaction | self-cured |
| a type of meterial that is polymerized by a curing light | light cured |
| a process used to open fissures before sealant placement | microabraion |
| a sealant product that does not contain filler particles | unfilled rezin |
| a microscopic leakage at the interface of the tooth structure and the sealant or restoration | microleakage |
| salt or ester of acrylic acid | acrylate |
| a sealant firmly adheres to a tooth surface because of | sealant retention |
| purpose of dental sealants | prevent denatal caries/decay in the pits and fissures |
| whay are pits and fissures susceptible to caries | these areas are difficult to clean and flouride is less effective in these areas |
| what are the ways for sealant materials to harden | polymerization, light curing, self curing |
| why is clear sealant material less desirable | it is more difficult to evaluate |
| what is the difference between filled and unfilled sealants | filled sealants are wear resistant, are stronger and last longer |
| dental prevention includes | use of flouride, dietary considerations, plaque control, sealants and regular dental exams |
| where are sealants placed | pits and fissures |
| what is the range of shelf life of sealant materials | 18 to 36 months |
| what patient safety precautions should be considered when placing sealants | patients should wear protective eyewear and avoid contact of etchant with soft tissue |
| what is the main cause of sealant failure | moisture contamination |
| when will most sealant failures occur | 3 to 6 months |
| self-cured sealants polymerize to final set within how many minutes | 2 minutes |
| disclosing agent | coloring agent applied to teeth to make plaque visible |
| systemic flouride | swallowed and travels throughout body |
| topical flouride | applied directly to teeth |
| most common dental disease | cries |
| flouride combats decay by | slows demineralization and enhancing remineralization |
| what dental condition is result of too much flouride | flourosis |
| what is key dietary factor related to dental caries | carbohydrates |
| what type of toothbrush bristels are recommended | soft bristled |
| modified bass method | method of toothbrushing preferred |
| type of dental floss most effective | both waxed and unwaxed |
| whan are composites used | Class III or IV restoration because canines and incisros are so visible for esthetic purposes |
| Class III | affects interproximal surfaces (mesaila or diatal) of incisors and canines |
| Class IV | Affects larger surface (mesial or diatal) which includes incisal edge of and interproximal surfaces of ins=cisors and canine |
| When selecting shade of the composite resin | use natural lighting and involve patient in selection |
| dental dam is moisture control preferred for III and IV restorations because | provides better retraction and gingival tissue and maintains a drier environment |
| What is purpose of the mylar matrix system | replaces missing wall of cavity preparation and helps with conouring process in restoration process |
| primer and bonding resin are light cured | according to manufacturer instrcutions |
| Class III and IV composite restorations use what mylar matrix strip | clear |
| where are sectional bands disposed of | sharps containers |
| composite placeent instrument is used for | carry composite material fro cavity prep; to place, condense, and carve composite material in cavity prep |
| composite burnisher function | form occlusal anatomy in composite restorations; acheives final contouring of anatomy, pits, fissures and grooves |
| acorn burnisher | has a gold titanium nitirde coating that does not scratch, stick, or discolor composite material |
| composite burnisher | titanium nitride coating |
| applicator use | apply conditioning, primer, and bonding material to cavity prep; used with bonding, sealants and orthodontic band brackets |
| applicator and composite wells are disposed of in | garbage |
| composite material well | holds etchant, primers, bonding and composite |
| curing light | harden light cured materials bonding, composite, sealants |
| what increments are materials bonded in | 2mm or less to ensure complete setting |
| protective shield | must be worn to protect eyes during light curing |
| L.E.D and halogen radiometers | used to test the visible light output of LED and Halogen curing lights |
| Halogen radiometer is what color | white |
| LED radiometer is what color | Blue |
| what happens if there is loss of light output of curing light | effects amount of time needed (takes longer) to cure dental material |
| finishing strip | finish and smooth interproximal surfaces of restoration |
| Class I restoration | one surface lesion involves pit and fissures of tooth |
| Class II restoration | extension of class I cavity onto proximal surface of the premolars and molars |
| 1. periostial elevator | detach gingival tissues around the neck of the tooth |
| 2. Straight elevator | loosen tooth from the periodontal ligament/ Root Tip Picks removes the root tips |
| 3. 150 forceps | extraction on Maxillary |
| 4. 151 forceps | extraction on Mandibular |
| 5. Cowhorn forceps | extraction |
| 6. Surgical curette | used following the extraction,removes diseased tissue or abscesses |
| 7. Rongeur | has a spring between the handles and the blade, used to trim the alveolar bone |
| 8. bone file | used after the rongeur to smooth rough margins of the alveolus after the extraction |
| 9. Scalpel | surgical knife used to make a precise incision into the soft tissue |
| 10. Hemostat | multipurpose instruments that are used to grasp and hold things |
| 11. Needle holder | looks and operates similarly to a hemostat, used to grasp a suture needle firmly |
| 12. Surgical scizzors | straight or curve blades used to trim soft tissue |
| 13. Suture scizzors | used to cut only suture material designed with a small notch on the cutting edge |
| 14. Cheek and tongue retractor | hold and retract the cheeks and tongue during surgical procedure |
| 15. Mouth prop or bite block | allows the patient to rest and relax the jaw muscles |
| 16. Surgical chisel | used to remove or reshape bone if needed |
| 17. Surgical mallet | used to remove or reshape bone if needed |
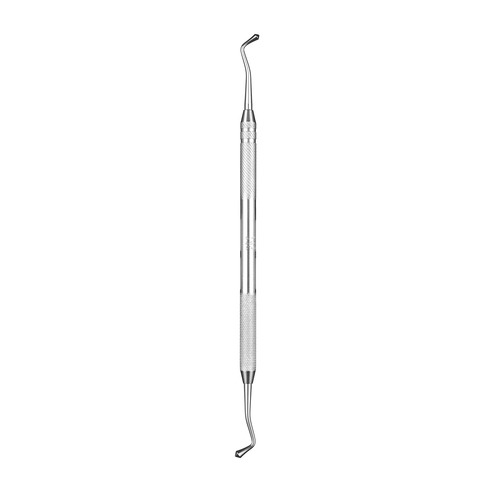 | ACORN BURNISHER |
 | AMALGAM CARRIER |
 | AMALGAM CONDENSOR |
 | BEAVERTAIL BURNISHER |
 | DISCOID/CLEOID CARVER |
 | COMPOSITE CARRIER |
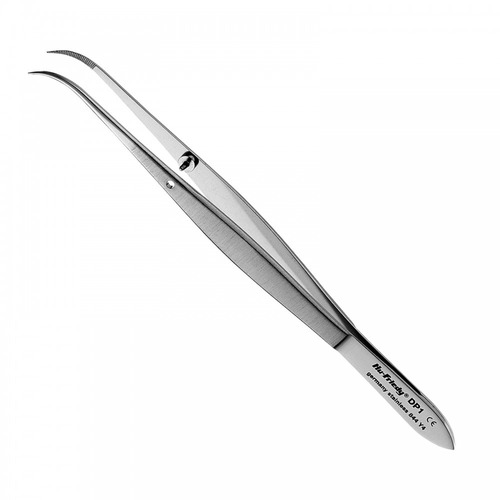 | COTTON FORCEPS |
 | EXPLOERER |
 | FOOTBALL BURNISHER |
 | HALF HOLLENBACK |
 | MATRIX BAND |
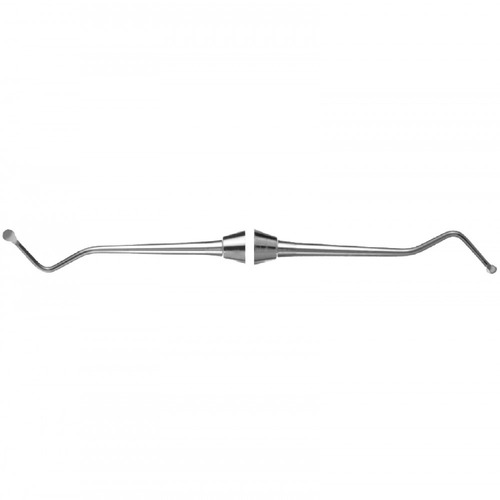 | SPOON EXCAVATOR |
 | WELL |
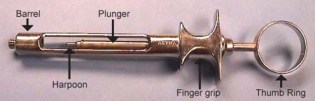 | ANESTHETIC SYRINGE |
 | APPLICATOR |
 | COMPOSITE PLACEMENT INSTRUMENT |
 | COMPOSITE BURNISHER |
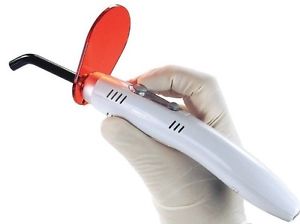 | CURING LIGHT |
 | FINISHING STRIPS |
 | COMPOSITE MATERIAL WEL |