| A | B |
|---|
| sexual reproduction | involves two parents and combines their genetic material to produce a new organism that differs from both parents |
| asexual reproduction | involves only one parent and the produces offspring that are identical to the parent |
| mitosis | a cell's nucleus divides into two new nuclei and one copy of DNA is distributed into each daughter cell |
| heredity | the passing of physical characteristics from parent to offspring |
trait,  | each specific characteristic passed from one generation to the next,  |
| genetics | the scientific study of heredity |
| fertilization | a new organism begins to form when egg and sperm cells join in this process |
Gregor Mendel,  | founder of the modern study of Heredity and Genetics |
| purebred | organism that is the offspring of many generations that have the same form of a trait |
| gene | The factors that control a trait |
| allele | different forms of a gene |
dominant allele,  | A trait that always shows up in the organism when the gene is present,  |
recessive allele,  | A trait that is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present,  |
hybrid,  | organism that has two different alleles for a trait,  |
| probability | a number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur |
| punnet square | A chart that shows all of the possible ways that alleles can combine in a genetic cross |
phenotype, 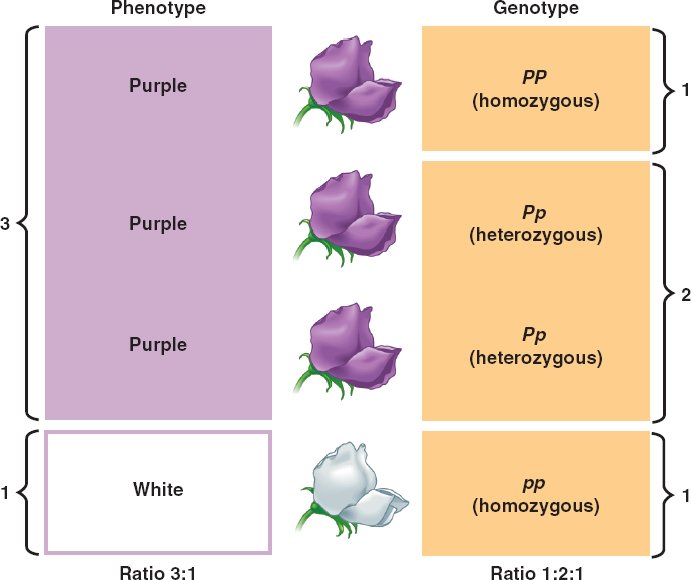 | physical appearance or visible traits of an organism,  |
genotype,  | genetic makeup of an organism,  |
| homozygous | An organism with two identical alleles for a trait |
| heterozygous | An organism that has two different alleles for a trait |
incomplete dominance,  | occurs when one allele is only partially dominant |
codominance,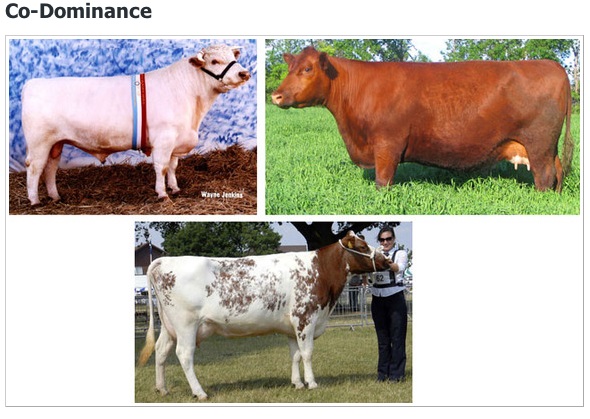  | occurs when both alleles for a gene are expressed equally. |
| multiple alleles | When there are three or more possible alleles that determine the trait |
| polygenic inheritance | This occurs when more than one gene affects a trait. |
| meiosis | the process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half as sex cells form. |
| chromosome | a threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes. |
DNA,  | deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information. |
RNA, 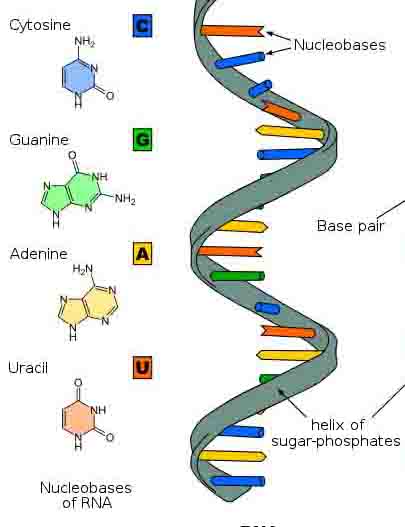 | ribonucleic acid, a nucleic acid present in all living cells. Its principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins, although in some viruses RNA rather than DNA carries the genetic information. |
| selective breeding | The process of selecting organisms with the desired traits to be parents of the next generation |
inbreeding,  | involves crossing two individuals that have similar desirable characteristics - can result in genetic disorders. |
| hybridization | breeders crossing two genetically different individuals. |
clone,  | An organism that has the exactly the same genes as the organism from which it was produced.,  |
| genetic engineering | Genes from one organism are transferred to the DNA of another organism. |
| gene therapy | The process of inserting copies of a gene directly into a person's cells. |