| A | B |
|---|
| As a cell becomes larger, its volume increases _____ than its surface area. | faster |
| As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases _____ than its volume. | slower |
| The rate at which a cell produces waste is determined by its ____. | volume |
| The rate at which a cell can get rid of waste is determined by its ____. | surface area |
| The rate at which a cell can take in nutrients is determined by its ____. | surface area |
| The amount of nutrients that a cell needs is determined by its ___. | volume |
| Besides the problem of taking in nutrients and getting rid of waste, what is another problem that cells face when they get too big? | DNA overload (Basically, the DNA is like a library and when cells get bigger, its like a city getting bigger wiithout increasing the number or size of its libraries) |
What is the color of the curve that would represent volume in a graph of volume versus surface area as cells grow?, 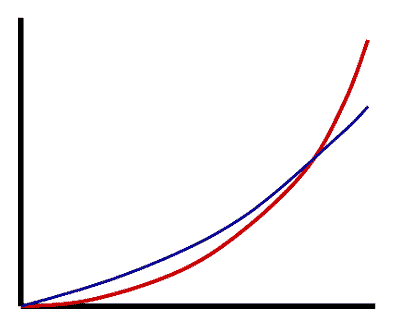 | the red curve,  |
What is the color of the curve that would represent surface area in a graph of volume versus surface area as cells grow?,  | the blue curve,  |
| What are the four phases of the cell cycle? | G1, S, G2, and M |
| Chromosomes are only visible when ___. | the cell is dividing |
| When the cell is most actively growing, it is in the ____ phase. | G1 |
| When DNA is replicating, the cell is in the ___ phase. | S |
| When the cell is preparing for mitosis, it is in the ____ phase. | G2 |
| When the cell is undergoing cell division, it is in the ___ phase. | M |
| In order, what are the four stages of mitosis? | Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (remember PMAT) |
| G1, S, and G2 all occur during ____. | interphase |
| Which phases of the cell cycle occur during interphase? | G1, S, and G2 |
| Cell division ends during ___. | cytokinesis |
| The ____ is a series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. | cell cycle |
| The ___ is a narrow region of the duplicated chromosome where sister chromatids are attached to each other. | centromere,  |
| The centromere region is where _____ are held together. | sister chromatids,  |
| After chromosomes undergo DNA replication, they consist of two identical ____ that are attached to each other. | sister chromatids,  |
| During which stages of mitosis are sister chromatids attached to each other? | prophase and metaphase |
| During which stage of mitosis do sister chromatids start to separate? | anaphase |
| During which stage of mitosis are sister chromatids lined up along the center of the cell? | metaphase (think metaphase = middle) |
| During which stage of mitosis does the nuclear envelope break down? | prophase |
| During which stage of mitosis do the chromosomes condense to become visible? | prophase |
| Centrioles help organize a fan-like group of protein fibers called the ____ that help pull the chromosomes apart. | spindle |
| In animal cells, ________ help organize a fan-like group of protein fibers called the spindle that help pull the chromosomes apart. | centrioles, 
|
| The division of the cytoplasm itself is called ___. | cytokinesis |
| In plant cells, cytokinesis is accomplished with the formation of a ___ between the two new cells. | cell plate |
| During which stage of mitosis are the chromosomes divided into the two opposite ends of the cell and the nuclear membrane reforms? | telophase |
| The two main stages of cell division are ___. | mitosis and cytokinesis, 
|
| One main difference between cell division in plants versus animals is that plants have ___. | a cell plate |
| One main difference between cell division in plants versus animals is that animals have ___. | centrioles |
| During normal cell division, a human cell with 46 chromosomes would produce two daughter cells with ___ chromosomes each. | 46 |
| A cell that has 5 chromosomes in G1 would have ___ chromosomes in G2 | 10 (remember they replicate during the S phase which occurs between G1 and G2) |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 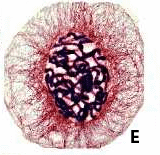 | Prophase,  |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 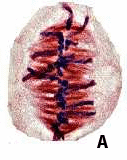 | Metaphase,  |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 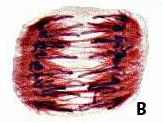 | Anaphase,  |
Which stage of mitosis is depicted in the picture below?, 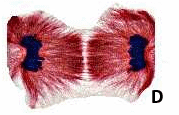 | Telophase,  |
Which stage of the cell cycle is depicted in the picture below?, 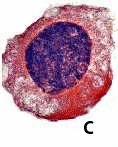 | Interphase,  |
The structures labeled A are,  | sister chromatids,  |
The structures labeled B are,  | spindle fibers,  |
The structure labeled C is,  | a centromere,  |
The plant cell labeled A is in ____.,  | anaphase,  |
The plant cell labeled B is in ____.,  | telophase,  |
The plant cell labeled C is in ____.,  | interphase,  |
The plant cell labeled D is in ____.,  | prophase,  |
The plant cell labeled E is in ____.,  | metaphase,  |
| Uncontrolled cell division is also known as ______. | cancer |
| When cells divide over and over again because of cancer, a lump of cells called a ____ forms. | tumor |
| How is the cell cycle controlled (ie - turned on, off, slowed down, sped up)? | Special proteins inside the cell act as on switches, or off switches to speed up or slow down the cell cycle as needed. |
| A(n) ____ can cause the proteins that control cell division to malfunction, causing the cell to divide uncontrollably. | mutation in DNA |
| ________ are a group of proteins that regulate the cell cycle by increasing or decreasing their concentration in the cell. | Cyclins |
| True or false: Interphase is a stage of mitosis. | False (Interphase happens before the stages of mitosis. The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Cytokinesis is not a stage of mitosis either. It is however part of the M phase (mitotic phase). |
| True or false: Cytokinesis is a stage of mitosis. | False (Cytokinesis is not a stage of mitosis either. It is however part of the M phase (mitotic phase). Cytokinesis does start during telophase, but it is not a stage of mitosis. The only stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) |
| True or false: Mitosis is asexual reproduction. | False (Mitosis is part of asexual reproduction in single-celled eukaryotic organisms that divide to form new single-celled organisms that are genetically identical to the parent cell. However, the cells that divide in multicellular organisms including the stages of mitosis are not an example of asexual reproduction because they are not creating a new organisms). |
| Different forms of the same gene are called _____. | alleles |
| Dominant alleles are represented by a _______ letter. | capital (ex:T= tall in pea plants) |
| Recessive alleles are represented by a _______ letter. | lower case (ex: t = short in pea plants) |
| The types of alleles that an organism inherits is known as the ______. | genotype (example = Bb) |
| The physical expression of two alleles is known as the organism's _____. | phenotype |
| Bb would be called the organism's _____ while "brown eyes" would be the organism's _____. | genotype, phenotype |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is BB? | Brown eyes |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is Bb? | Brown eyes (remember that B is dominant) |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what will be the color of your eyes if your genotype is bb? | blue eyes |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organism's genotype be if the organism was heterozygous? | Bb (remember that 'hetero' means 'mixed') |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organism's genotype be if the organism is homozygous dominant? | BB (remember that 'homo' means 'same') |
| If B = brown eyes and b = blue eyes, what would the organism's genotype be if the organism is homozygous recessive? | bb (remember that 'homo' means 'same') |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 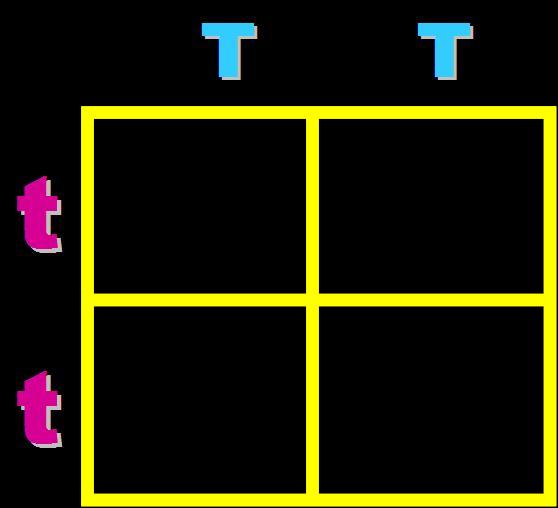 | Genotype = 100% Heterozygous (Tt) Phenotype = 100% tall, 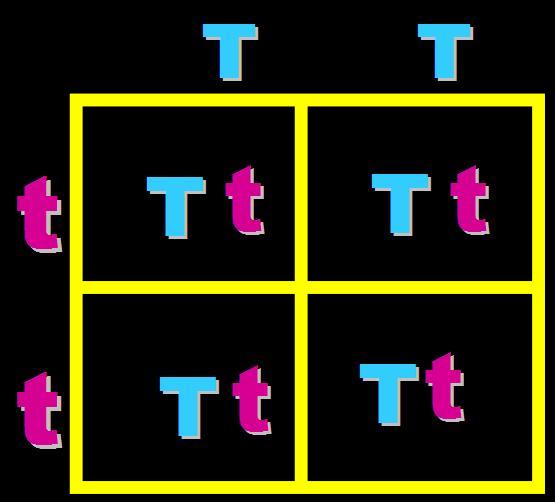 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 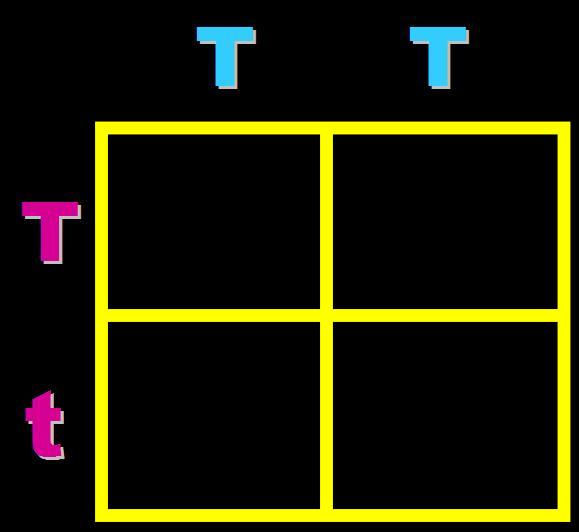 | Genotype = 50% homozygous dominant (TT) and 50% heterozygous (Tt) Phenotype = 100% Tall, 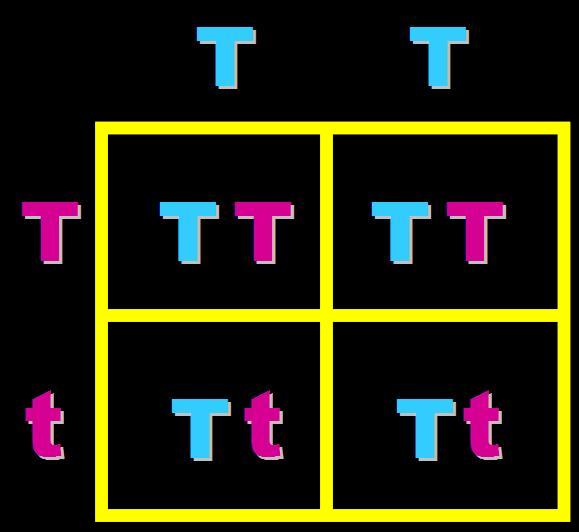 |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages., 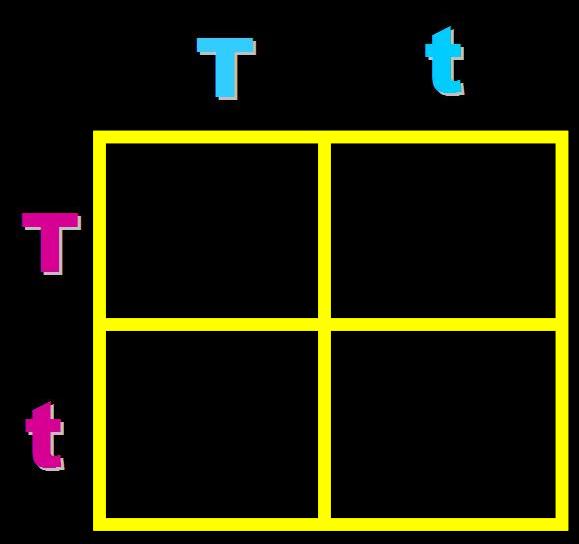 | Genotype = 25% Homozygous dominant (TT), 50% heterozygous (Tt) and 25% homozygous recessive (tt) Phenotype = 75% Tall and 25% short,  |
In pea plants, T=tall and t=short. What will the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring in this cross be? Give the expected percentages.,  | Genotype = 50% heterozygous (Tt) and 50% homozygous recessive (tt) Phenotype = 50%Tall and 50% short, 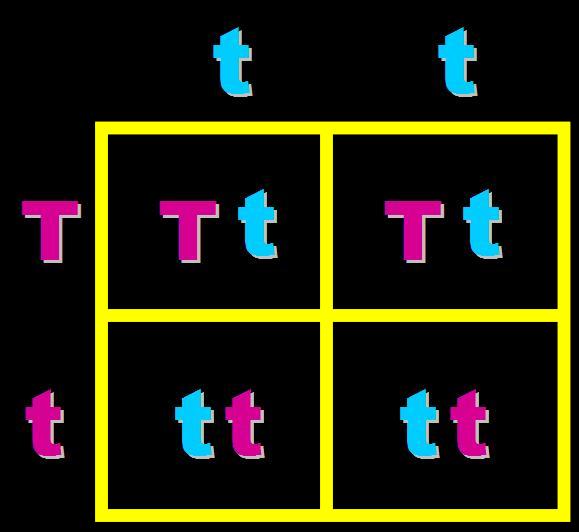 |
| How would your set up a Punnett Square for a cross between a short male pea plant and a heterozygous tall female? |  |
| Another word for heterozygous is ____. | hybrid |
| Another word for homozygous is ____. | purebred |
| Another word for purebred is ____. | homozygous, 
|
| Another word for hybrid is ____. | heterozygous |
| The number of different types of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the letter ___. | n |
| A carrot has a diploid number of 18. What is it's haploid number? | 9 |
| Gametes are produced by the process of ___. | meiosis, 
|
| Another word for sex cell is ___. | gamete |
| What are the two main types of gametes? | sperm and egg |
| Which stage of meiosis do chromosomes form tetrads? | prophase I |
| During which stage of meiosis do homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell? | metaphase I |
| During which stage of meiosis do sister chromatids separate from each other? | anaphase II |
| What happens between meiosis I and meiosis II that reduces the number of chromosomes? | DNA replication does not occur. |
| For meiosis, when does DNA replication occur? | Interphase I only (Remember, there is no interphase II, and technically, interphase is not a stage of meiosis. It comes before meiosis, just like interphase also comes before the start of mitosis.) |
| What is the diploid number of chromosomes in humans? | 46 (also written as 2n=46) |
| What is the haploid number for humans? | 23 (also written as n=23) |
| The sex cells of fruit flies have 4 chromosomes each. What is the diploid number of chromosomes for fruit flies? | 8 (remember the diploid number is always twice the haploid number) |
| _________ chromosomes are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, but are not identical. | Homologous, 
|
| _________ are chromosomes that have the same types of genes, and are identical. | Sister chromatids (This is technically not true if crossing over occurs during meiosis. The sister chromatids may be different) |
| A(n) _____ is a segment of DNA that has the instructions for making one protein. | gene |
| A chromosome is made of ___ DNA molecule(s) | one |
| When two homologous chromosomes are lined up right next to each other during meiosis, they are referred to as a ___. | tetrad |
| An organism's gametes have ___ the number of chromosomes as are found in the organism's body cells. | half |
| During which stage of meiosis might crossing over occur? | prophase I |
| When homologous chromosomes are lined up next to each other during meiosis, they might swap pieces of DNA. This phenomenon is called ___. | crossing over |
| Crossing over during meiosis is important because it increases ___. | genetic variation (= the number of different chromosomes, and therefore different combinations of traits, that offspring can inherit) |
Which diagram is mitosis and which is meiosis?,  | Mitosis is on the left and meiosis is on the right.,  |
When chromosomes are lined up like this during meiosis, what are they referred to as?, 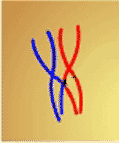 | A tetrad,  |
Which process from meiosis is shown below and during which stage would it occur?, 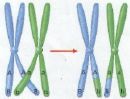 | The picture shows "crossing over" and it usually happens during prophase I.,  |
| True or false: Meiosis is an example of sexual reproduction. | False (Meiosis is something that needs to occur before sexual reproduction can occur, because you need sex cells in order for sexual reproduction to happen. But the production of gametes is not sexual reproduction) |
| True or false: Interphase is part of meiosis. | False (Interphase is something that occurs before meiosis) |
| The type of inheritance where neither allele is dominant and they tend to produce a mix of the two traits such as blue + white = light blue would be _____. | incomplete dominance |
| The type of inheritance where both alleles are dominant, such as red fur + white fur = red and white fur hairs in roan cattle is known as ____. | codominance |
| The type of inheritance where there is more than two alleles for a single trait, such as A, B, and O alleles for blood type, is known as ____. | multiple alleles |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,IA, what is your blood type? | type A |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,i, what is your blood type? | Type A |
| If your genotype for blood type is IB,IB, what is your blood type? | Type B |
| If your genotype for blood type is IB,i, what is your blood type? | type B |
| If your genotype for blood type is IA,IB, what is your blood type? | Type AB |
| If your genotype for blood type is ii, what is your blood type? | Type O |
| Genes that are located on the 23rd pair of chromosomes (but only on the X, not the Y chromosome) are known as ____. | sex-linked genes |
| If you have an X and a Y chromosome, what is your gender? | male |
| If you have two X chromosomes, what is your gender? | female |
What are the expected blood types (and frequencies of each) of the offspring of this cross? (Change the A's to IA's, the B's to IB's and the O's to i's),  | 25% type AB blood, 25% type A blood, 25% type B blood, 25% type O blood,  |
| How would you set up a Punnett Square for a cross between a heterozygous blood type A male and a heterozygous blood type B female? | (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's),  |
In humans, colorblindness is a sex-linked recessive allele. What are the expected phenotypes of the offspring if both parents have normal vision but the mother is heterozygous?,  | 100% normal vision girls and 50% of the boys are expected to be colorblind., 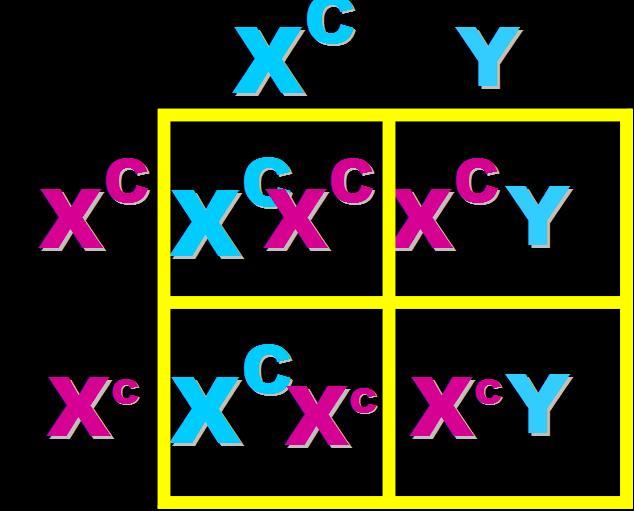 |
| How would you set up a cross between a male with type AB blood and a female with type O blood? (The A stands for IA, the B's stand for IB and the O stands for i) | (Change the A's to IA's the B's to IB's and the O's to i's), 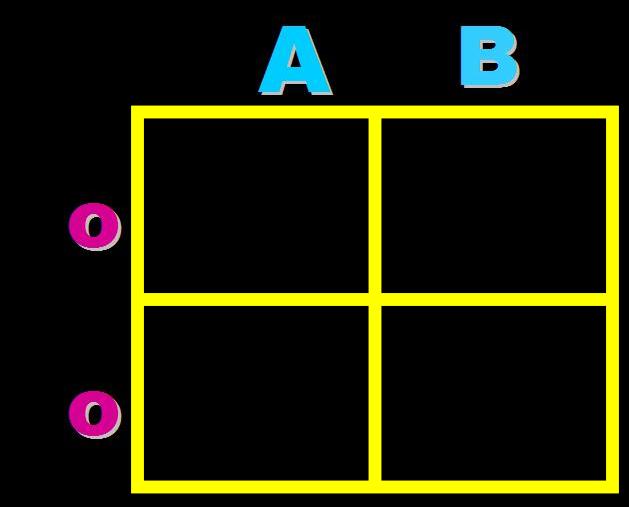 |
What are the expected blood types of the offspring and what are the odds of each? (Change the A's to I<sup>A</sup>'s the B's to I<sup>B</sup>'s and the O's to i's),  | 50% of the offspring are expected to have type A blood and 50% are expected to have type B blood. All offspring will be heterozygous. Remember that the O allele is recessive.,  |
| A trait, like human skin color, that involves several different genes is called a(n) _____. | polygenic trait (remember, "poly" means many and "genic" refers to genes) |
The following diagram is an example of a(n) ___.,  | pedigree chart,  |
| Different forms of the same gene are called _____. | alleles |
| Which law states that the two alleles for a heritable character separate during gamete formation and end up in separate gametes? | The Law of Segregation |
| A dihybrid cross between 2 individuals that are heterozygous for two independently assorting characterisitics (such as seed color and seed shape), produces the classic ________ ratio. | 9:3:3:1 ratio,  |
| Which law states that each pair of alleles segregate independently of other pairs during gamete formation? When is this law not true? | Law of independent assortment. This law does not hold true if the alleles for two different characteristics are located on the same chromosome. |
| New alleles for a gene are formed by _________ that survive the ________ process. | mutations, natural selection |
The following picture is an example of a ______.,  | karyotype,  |
| Humans have ____ autosomes and ____ sex chromosomes in a normal karyotype. | 44, 2,  |
| Humans have 44 __________ and 2 _________ in a normal karyotype. | autosomes, sex chromosomes |
| Give three examples of disorders caused by sex-linked inheritance. | color-blindness, hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
| Females usually inactivate one of their X chromosomes, turning it into a _______. | Barr body |
| Abnormal number of chromosomes in a human's karyotype are caused by a problem in separating chromosomes properly during meiosis called ___________. | nondisjunction,  |
| ______ is a condition in which a person is born with 3 copies of a homologous pair instead of the usual two. | Trisomy (The person below has trisomy-21, otherwise known as Down Syndrome, because of their extra chromosome at the 21st pair.),  |
Trisomy-21 (see picture below) causes __________ .,  | Down syndrome (The picture below shows a child with Down syndrome. People with Down syndrome have characteristic features of eyes wide apart, heavy eyelids, below average height, and below average (but not always) intelligence. Other complications lead to a lower than average life-expectency), 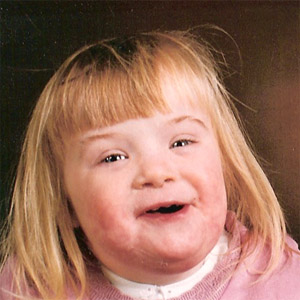 |
| A person who inherits only one X chromosome and no Y chromosomes will be a _____ with ______ syndrome. | female with Turner's syndrome (they are sterile, with their sex organs not developing at puberty) |
| A person with two X and one Y chromosome is a _____ with _____ syndrome. | male with Klinefelter's syndrome (usually sterile with poor muscular development) |
| Both Turner's and Klinefelter's syndrome involve an abnormal number of sex chromosomes. This is caused by _____ during meiosis. | nondisjunction,  |
| During which process would nondisjunction occur? | meiosis,  |