| A | B |
|---|
| a vasoconstrictor is added to a local anesthetic because | lengthens the duration of action of the local anesthetic |
| this may increase risk of prolonged bleeding for patients | aspirin |
| this cement is exothermic and must be mixed on a glass slab | zinc phosphate |
| glass ionomer cement differs from other cements in the unique property of | releasing fluoride |
| after receiving a gel or foam fluoride treatment, how long should the patient wait before eating or drinking | 30 minutes |
| when assembled and positioned properly, the smaller circumference of the matrix band should face what surface of the tooth | cervical |
| who has legal ownership of all patient records and radiographs | dentist |
| following removal of orthodontic brackets, which hand piece is used to remove the bonding material from the tooth | ultrasonic |
| an indicator that the final setting time of dental stone has been reached is that the model will be | cool and dry |
| a patient suffering from hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) may exhibit what symptoms | perspiration, confusion, increased anxiety and mood changes |
| the purpose of inverting the dental dam is to | prevent saliva leakage |
| upon completion of an amalgam restoration, excess amalgam should be disposed of in a | closed container |
| an advantage of a diamond bur compared to other dental burs is | superior cutting edge |
| a deficiency in this vitamins may contribute to night blindness | vitamin A |
| which teeth has 2 roots | maxillary first premolars, all other premolars have only one root |
| the purpose of attaching a ligature to a dental dam clamp is to | retrieve the clamp if it becomes dislodged and swallowed |
| patients requiring oral prophylactic antibiotics prior to a procedure should take the dose at what time | 30-60 minutes prior to the procedure |
| the injection technique most preferred by dentists on the mandibular arch is | inferior alveolar nerve block |
| which of the following gypsum products have the highest water-to-powder ratio and i the weakest product | type II; model plaster |
| aspiration allows the dentist to determine the | correct placement of anesthetic |
| which of the following is a way to make a correction on a patient's chart | place a single line throughout the incorrect information and enter the new information on the next line |
| what type of anesthesia is frequently used on mnadibular teeth and injected near a major nerve in order to numb the entrée area served by that nerve branch | block |
| what nutrient plays a major role in development of caries | carbohydrates |
| the purpose of applying a topical anesthetic prior to an injection is | desensitize the area |
| the examination technique that involves the operator using fingers and hands to evaluate soft and hard tissue is called | palpitation |
| what accessory is required to attach an abrasive disc to a handpiece | mandrel |
| this is a dental material which can be used as a desensitizer | fluoride |
| treatment for accidental fluoride overdose includes giving the patient | milk |
| when dry, properly etched surface material will appear | chalky |
| what is the primary advantage of adding base metals to nible metals in gold-noble alloy | increased resistance to wear |
| class II restoration are found on | posterior teeth, molars and premolars |
| which method of toothbrushing emphasizes placing the bristles at a 45 degree angle to the sulcus | Bass |
| decay located in the pits and fissures of the occlusal surfaces of the molars and premolars are considered which classification of caries | Class I |
| the material choice for Class III and IV restorations is | composite resin, for esthetic purposes on anterior teeth |
| what is the most appropriate indication for the placement of sealants | posterior teeth with pits and fissures |
| protective bases can be used to prevent | postoperative sensitivity and damage to the pulp |
| the purpose of retention pins in restorations is to | support core build ups |
| initial patient contact begins with | the patient calls for a new patient appointment |
| the significance of the smear layer in restorative dentistry is to decrease the bonding strength | decreases bonding strength |
| chronic overexposure to low concentrations of fluoride in children younger than 6 y/o will cause this | dental fluorosis |
| a good way to keep the mouth mirror from fogging while the operator is working | blow some air on it |
| using the universal numbering system, the maxillary right second premolars is tooth number | 4 |
| treatment of alveoli tis includes | irrigation with saline solution |
| calcium hydroxide can be used for | temporary cement, base, restorative material |
| when assisting a right handed dentist, the dental assistant would use the right hand for | operating the HVE |
| a rapid change in body position, such as when the patient is suddenly placed in an upright position | postural hypotension |
| when placing a tofflemire retainer around a tooth, the diagonal slot should face toward the | gingival surface |
| what can be used as a visual aid to show the patient the areas in the mouth where debris remains after brushing and flossing | disclosing agent |
| to prevent the patient from accidentally swallowing the rubber dam place | a piece of dental floss around the clamp |
| on a prescription the abbreviation q.i.d means | four times a day |
| what instrument is used to remove caries during a restorative procedure | round cutting bur |
| what material would be placed into a prepared tooth FIRST for an amalgam restoration | calcium hydroxide |
| if the dentist is running behind schedule, patients that are awaiting for their appointments should be | informed of the situation |
| the cementum, alveolar bone, and gingiva are part of the | peridontium |
| antihistamines are used to treat | allergic reactions |
| bitewing radiographs show there is decay under the existing restoration, this type of caries is | recurrent caries |
| varnish is commonly used in amalgam cavity preparation to | seal and protect the dentin from migration of agents into the tooth |
| when teaching toothbrushing the emphasis should be on brushing | until complete removal of plaque regardless of time |
| during an amalgam restoration procedure, articulating paper is used to evaluate for | occlusion after carving |
| if all the normal treatments for angina do not relieve the pain the patient is experiencing, the dental team should assume the patient is suffering from | myocardial infarction (heart attack) |
| what is used in a crown and bridge preparation to displace the gingival tissue | retraction cord |
| which of the following may be seen in a patient with bulimia | erosion of the lingual surfaces of the teeth |
| after spraying an impression with disinfectant, the impression should be | sealed in a plastic bag |
| antibiotic premedication is recommend for a patient who may be susceptible to | developing infective endocarditis |
| what condition may occur if excess cement is not removed from the cervical margin after cementing a crown | inflammation of interdental papilla (gingival inflamation) |
| the surgical instrument used to trim alveolar bone and eliminate bony projections is a | rongeur |
| xerostomia refers to | dryness of the mouth |
| a veneer is applied to which surface of the prepared tooth | facial |
| the primary dentition contains how many premolars | 0- none |
| when placing dental cement for a crown or veneer, the assistant should coat the | restoration with a thin layer of material |
| which of the following instruments is used to carve the inter proximal portion of the amalgam restoration | hollenbach |
| which of the following is part of the full maxillary denture | post dam |
| what is the treatment for angina pectoris | nitroglycerin |
| what is used to determine the color of the composite resin material during the restorative process | shade guide |
| which filler type of composite resin has the strongest makeup and sis used commonly for posterior restorations | macrofilled |
| the goal of water fluoridation is to adjust the fluoride content to | 1.0 ppm |
| this instrument is used for carving amalgam | discoid cleoid |
the charting symbol between tooth number 28 and number 29 designates, 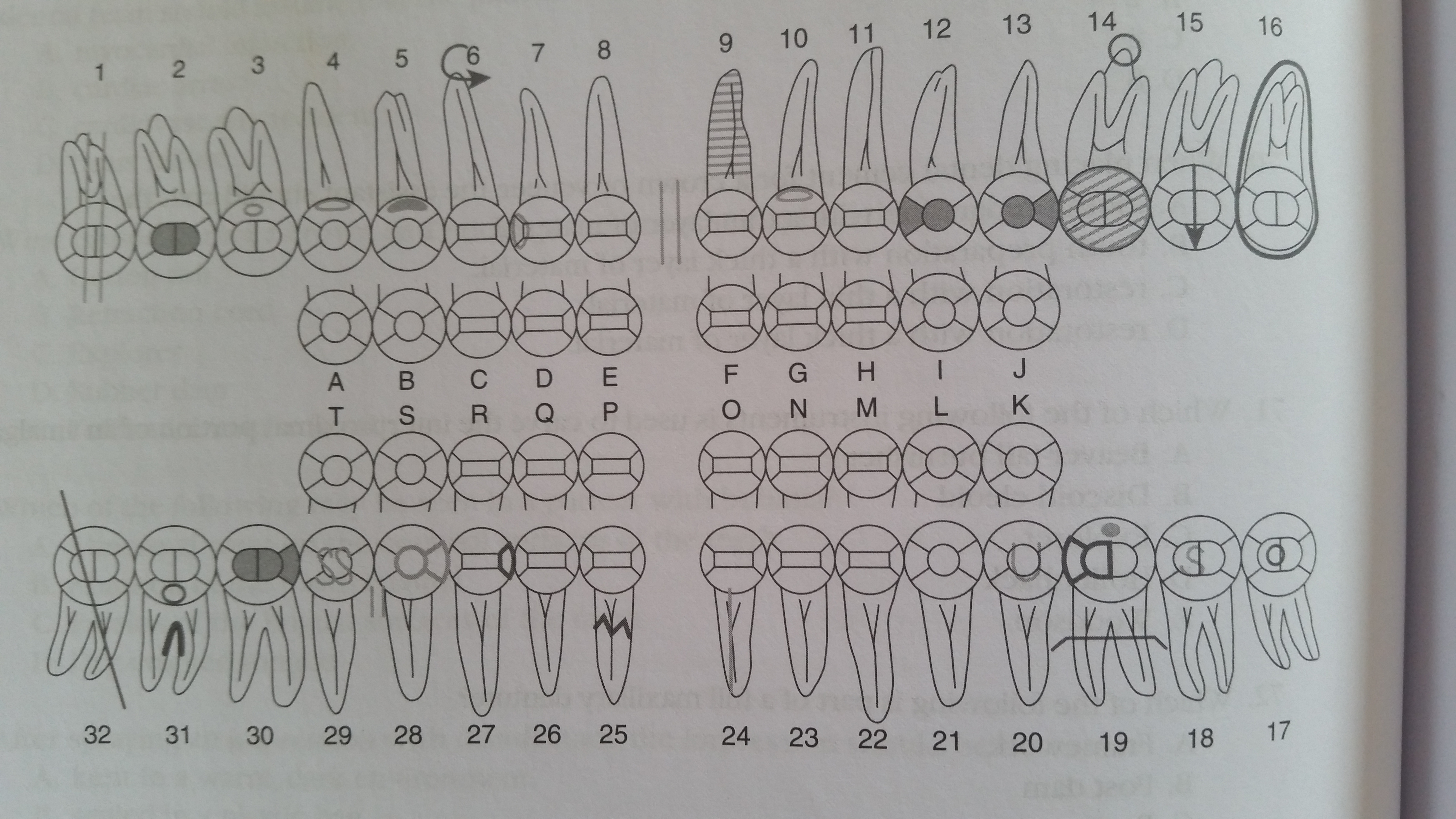 | open contact |
the charting symbol illustrated on tooth #24,  | root canal |
wich condition exists between tooth #8 and #9,  | diastema |
at restoration is charted on tooth #29,  | stainless steel crown |
what condition exist on the permanent maxillary left central incisor,  | implant |
| what action should be taken first in managing an office emergency | calling EMS |
| during a composite procedure, sectional matrices are used in conjunction with | tension ring |
| primary objective of amalgam polishing is | create a smoother surface with fewer irregularities |
| an accurate record of a patient's financial history with the dental office should deb recorded on | manual or electronic ledger |
| topical anesthetic given prior to a local injection in order to | desensitize the tissue at the injection site |
| in an emergency check th patients pulse at which artery | carotid |
| if a right handed operator is preparing a tooth #3 for a crown, the dental assistant would place the bevel of the HVE | parallel to the lingual surface of the tooth being prepared |
| the primary cause of syncope (fainting) in a dental office | allergic reaction to local anesthetic |
| during an amalgam procedure, which instrument is used to pack the amalgam firmly into the tooth preparation | condensor |
| which of the following is associated with the intake of sugar free sodas and entail carie | increase in acidity |
| the properly seated entail assistant is | 4 to 6 inches above the dentist |
| calcium hydroxide is used under new restorations to | stimulate reparative dentin |
| sublingual calculus is removed using a | curette |
| impression should be disinfected | at chair side upon removal |
| what is the greatest concentration of vasoconstrictor in local anesthetic | 1:20,000 |
| the attachments at the sides of the three-unit bridge are called | abutments |
| an allergic response that could threaten a patient's life | anaphylaxis |
| a patient with dental insurance is classified as a | subscriber |
| portion of the bridge that replaces the missing tooth | pontic |
| to minimize patient's gag reflex while taking maxillary alginate impression the dental assistant would use | hot water and fast set material |
| the operator has prepared an MO on tooth #3. The inter proximal box is rough and needs to be smoothed. what would you pass the operator | enamel hatchet |
| when are sealants placed on a tooth | as soon as the tooth is fully erupted |
| during an operative procedure the best way to keep the tooth from over heating and damaging the pulp is to | spray a mixture of air and water over the too |
| a patient who begins to breath deeply and rapidly is experiencing | hyperventilation |
| which wall of the cavity preparation is perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth | pupal wall |
| which classification of restoration does not require a matrix band | class I, there is no inter proximal area to restore |
| when punching a rubber dam for restorative procedure, the anchor tooth should be | 1 or 2 teeth to the distal |
| agents that provide a temporary numbing on nerve endings located on the surface of the oral mucosa | topical anesthetics |
| temperature hypersensitivity occurring for about a week after a restorative procedure and then subsiding is most likely | pulpal hyperemia |
| during an emergency the AED is used to provide what to the heart | electricity |
| what is achieved by injecting the anesthetic solution directly into the tissue at the site of the dental procedure | infiltration anesthesia |
| anaphylaxis is considered to be | life threatening allergic reaction |
| during the finishing of a class III composite restoration, which of the following instruments may be used to remove excess flash and smooth inter proximal area | abrasive strip |
| hardness of a material is ranked using what scale | mohs scale |
| when a patient fails to show for an appointment, the scheduling assistant should | call the patient and summarize the conversation in the chart |
| which instrument is not used in defining and finishing the cavity walls and margins of the cavity preparation | spoon excavators |
| in four handed dentistry the area of exchange is located | across the patient's chest near the chin |
| the dental team member most likely to be in charge of calling emergency medical services is the | business assistant |