| A | B |
|---|
| "Iron Curtain" | the 'imagery' border declared by Churchill divining communist states and western Europe., 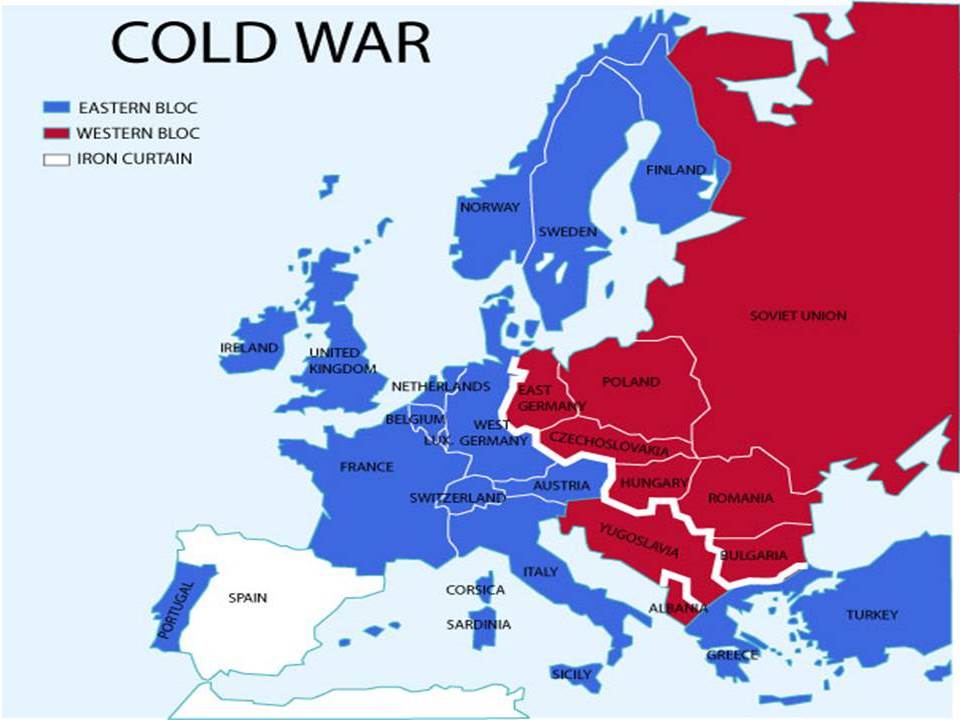 |
| arms race | a situation in which countries that are enemies each try to build or collect weapons faster than the other. |
| Berlin Airlift | a counter to the Berlin Blockade by the Western countries where planes dropped supplies to East Germany (it worked!). |
| Berlin Blockade | strategy by the Soviets to cut off supplies to East Berlin therefore pushing the west out to gain full control of Berlin. |
| capitalism | An economic system based on private property and free enterprise. |
| CIA | intelligence-gathering agency established in 1947 who also installed and/or supported anti-communist governments during the Cold War. |
| communism | the principle of common ownership of wealth and social equality. |
| containment | strategy of keeping communism boxed within its existing borders. |
| DMZ | heavily guarded military 'no man's land' along the 38th parallel dividing North and South Korea. |
| Domino Effect | the idea that if one country fell to Communism the surrounding countries would do so also. |
| GI | a bill that offered financial aid and government loans to veterans. |
| guerilla warfare | form of warfare that includes surprise, random attacks, often by fighters not in uniform. |
| Hollywood Ten | writers and directors in Hollywood who were thought to be radicals and called before House Un-American Activities Committee and they also refused to cooperate and were sentenced to short prison terms. |
| hot' conflict | a conflict where two sides actually took part in a military battle during the Cold (excluding the U.S. and USSR). |
| House of Un-American Activities Committee | a committee that was formed in the House of Representatives then later it came to focus on the threat of communism in the United States during World War II and the Cold War. |
| Joseph McCarthy | Wisconsin Senator who made a name for himself by accusing others of communist activity. |
| Joseph Stalin | Leader of the Communist Soviet Union from 1929-1953. |
| Korean War | War between South Korea (supported by the United States) and North Korea (supported by Communist China) from 1950 - 1953. |
| Mao Zedong | leader of the 1949 Communist Revolution in China.,  |
| Marshall Plan | a plan announced by U.S. Secretary of State George C. Marshall for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II. |
| Mutually Assured Destruction | arms build up to the point that both sides would annihilate the other if they faced off in war. |
| NASA | agency established in 1958 to compete with the Soviet space program. |
| NATO | an alliance, under U.S. leadership, between most of the Western Powers |
| Red Scare | fear that communist both inside and outside the united states would destroy the American/Capitalist way of life. |
| Rosenberg's | the couple that was convicted of passing atomic bomb secrets to the Soviets. |
| satellite states | smaller countries controlled by more the more powerful Soviet Union. |
| Sputnik 1 | the first artificial satellite launched in 1957 by the Soviets that caused a great interest and fear in science in the United States. |
| totalitarianism | a political system in which the state holds total authority over the society and seeks to control all aspects of public and private life wherever possible. |
| United Nations | International Organization founded in 1945 to promote peace, security, and economic development between all nations. |
| Warsaw Pact | treaty signed in 1945 that formed an alliance of the Eastern European countries behind the Iron Curtain (not completely voluntary. |
| Winston Churchill | British Prime Minister leader that helped the United Kingdom during World War II and during the Cold War.,  |