| A | B |
|---|
spherical or filamentous cells surronded by gelatinous sheath--photosynthetic pigments-(chloroplasts gree), 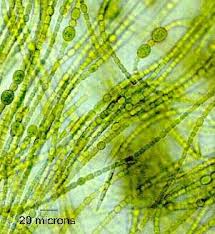 | -Cyanobacteriablue green algae |
fresh water-colonies of filamentous organisms-found in soil, on moist rock, bottom of lake---symbiont with plants providing NH3 (nitrogen) to its host, nitrogen fixator,  | nostec-blue green algae--plants can't use nitrogen-cyanobacteria converts to nitrogen that can be used (ammonia), plants absorb this form |
filamentous cyanobacteria--found as plankton-symbiont with plants providing nitrogen to its host, 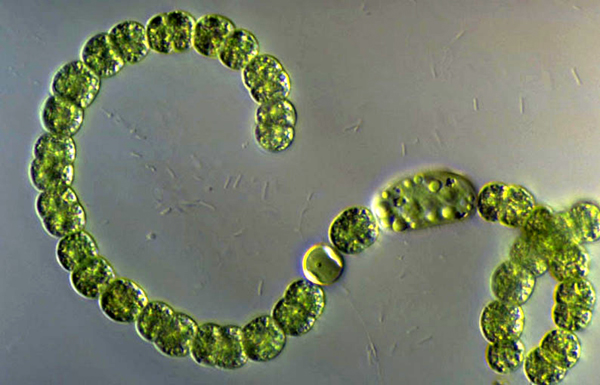 | anabaena |
filamentous cyanobacteria --prefers clear fresh water--some species prefer stagnant water,  | rivularia |
recently divided pairs seem to be one cell since the new cells cohere temporarily-halophile, 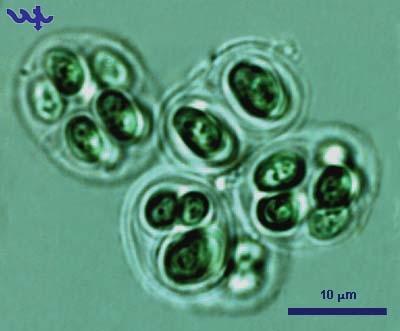 | gloecapsa---halophile-organism that can survive saline in enviroment |
| What is a byproduct of their photosynthesis? | By producing gaseous oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesi |
| Cyanobacteria | is a phylum of bacteria that obtain their energy through photosynthesis.[3] The name "cyanobacteria" comes from the color of the bacteria (Greek: κυανός (kyanós) = blue). They are often called blue-green algae |
| What is a "nitrogen fixer" bacteria? | Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are microorganisms present in the soil or in plant roots that change nitrogen gases from the atmosphere into solid nitrogen compounds that plants can use in the soil. |