| A | B |
|---|
| 2 types of cells | soma and sex(germ) cells |
| compare soma & germ cell size | germ cells small, somatic cells large |
| What is cell theory? | the cell performs all life functions |
| compare soma & germ cell-make up | somatic cells more complex with more organelles |
| compare soma & germ cell--purpose | germ cell-reproduction soma cell-all over body many purposes |
| Germ cells are | erm cells are cells that are able to produce and reproduce --male sperm, female oocytes (eggs), reproductive cells |
| somatic cells can be found--- | in blood, connective tissue, bones, skin, and internal organs. |
| somatic cell--meiosis or mitosis | A somatic cell is a body cell; it can only undergo mitosis |
| A germ cell-- meiosis or mitosis | A germ cell undergoes meiosis. |
| What are the components of the cell? (not individual organelles) | Contains lipids, carbohydrates, and functional proteins |
Phospholipid Bilayer(describe), 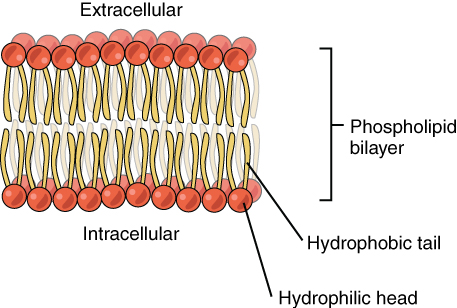 | Double layer of phospholipid molecules,  |
hydrophilic heads of Phospholipid Bilayer(describe),  | heads—toward watery environment, both sides,  |
hydrophobic fatty-acid tails of Phospholipid Bilayer(describe),  | hydrophobic fatty-acid tails—inside membrane--away from watery enviroment |
| function of Phospholipid Bilayer(describe) | barrier to ions and water soluble compounds |
Integral proteins: (membrane proteins), 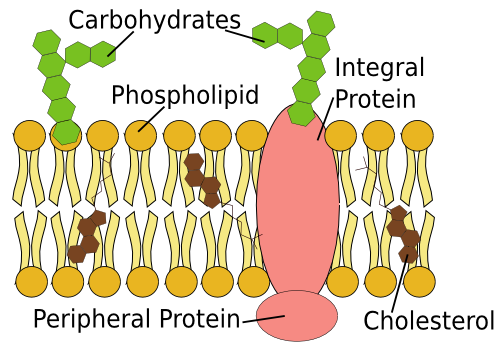 | within the membrane |
Peripheral proteins:(membrane proteins),  | inner or outer surface of the membrane |
| 6 Functions of Membrane Proteins | stabilizers,identifiers, catalyze reactions, bind and respond to ligands,transport , regulate |
| Membrane Protein Function- Anchoring proteins | (stabilizers): attach to inside or outside structures |
| Membrane Protein Function- Recognition proteins | (identifiers): label cells normal or abnormal |
| Membrane Protein Function- Enzymes | catalyze reactions |
| Membrane Protein Function-Receptor proteins | bind and respond to ligands (ions, hormones) |
| Membrane Protein Function- Carrier proteins | transport specific solutes through membrane |
| Membrane Protein Function- Channels | regulate water flow and solutes through membrane |
| functions of membrane carbohydrate | Lubrication and protection Anchoring and locomotion Specificity in binding (receptors) Recognition (immune response) |
glycocalyx (blue fuzzy component--this is a microscope picture), 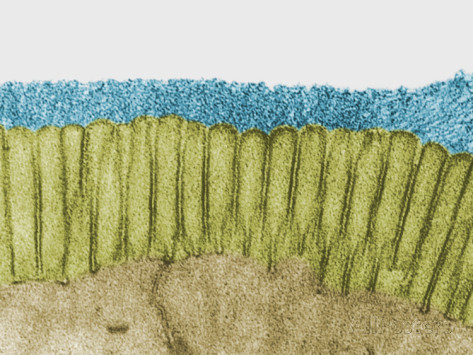 | membrane carbohydrates form sticky “sugar coat" that extends outside cell membrane,  |