| A | B |
|---|
| Enzymes are c__________. | catalysts |
| catalysts: | proteins that lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction (speeds up process, takes less energy) |
| What happens to the catalyst during the chemical reaction | are not changed or used up in the reaction |
| Substrates: | reactants in enzymatic reactions |
| Active site: | a location on an enzyme that fits a particular substrate |
| How do enzymes work? Explain | Substrates bind to active site on enzyme--helped by enzyme, substrates inteact to form product, product is released from enzyme--enzyme is now ready to begin process again |
Explain this picture of enzymes at work., 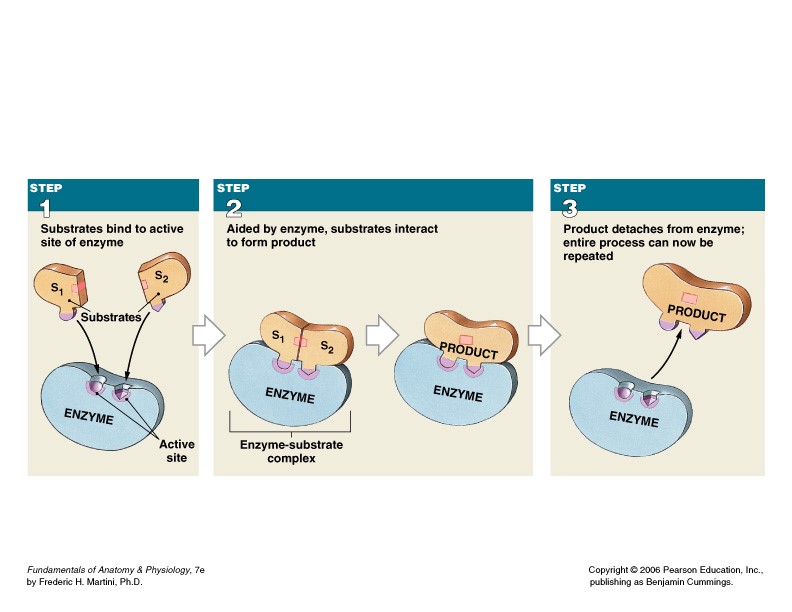 |  |
| Enzyme Characteristics | Specificity ,Regulation,Saturation limits |
| Regulation | the ability to turn off and on |
| Saturation limits | an enzyme’s maximum work rate |
| Specificity | one enzyme catalyzes one reaction |
| Nucleic Acids | Large organic molecules |
| Nucleic Acids | found in the nucleus |
| Nucleic Acids | ***store and process information at the molecular level |
| Nucleic Acids | DNA and RNA |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA),  | Determines inherited characteristics Directs protein synthesis Controls enzyme production Controls metabolism |
| Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) | protein synthesis |
| Complementary base pairs-DNA | AT GC-(at Grand Canyon) DNA: adenine (A) and thymine (T) and cytosine (C) and guanine (G) |
| Complementary base pairs-RNA | RNA: uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) |
| Nucleotides | Are the building blocks of DNA Have 3 molecular parts: sugar (deoxyribose) phosphate group nitrogenous base (A, G, T, C) |
| adenosine diphosphate (ADP): | High Energy Compounds -2 phosphate groups |
| adenosine triphosphate (ATP): | High Energy Compounds -3 phosphate groups |
| Adding a phosphate group to ADP to form the high-energy compound ATP is called- | Phosphorylation |
| ATPase | the enzyme that catalyzes phophorylation |