| A | B |
|---|
| How do DNA instructions become proteins? | Protein Synthesis |
| What are the steps to Protein synthesis? | Transcription, Translation, Processing |
Transcription,  | copies instructions from DNA to mRNA (in nucleus) |
| Translation | ribosome reads code from mRNA (in cytoplasm)---- assembles amino acids into polypeptide chain |
| Processing | by RER(rough ER) and Golgi apparatus produces protein |
Nucleosomes: DNA coiled around histones, 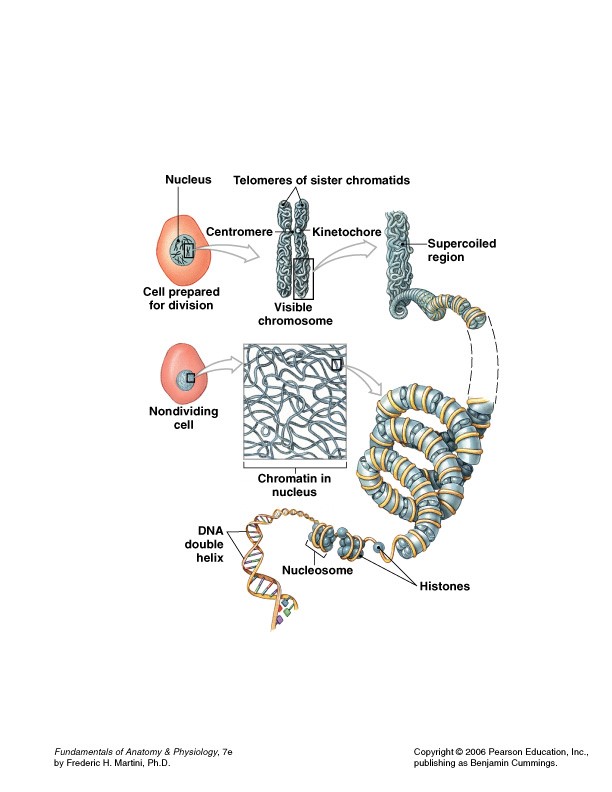 | Nucleosomes,  |
| Chromatin: | loosely coiled DNA (cells not dividing),  |
| Chromosomes: | tightly coiled DNA (cells dividing), 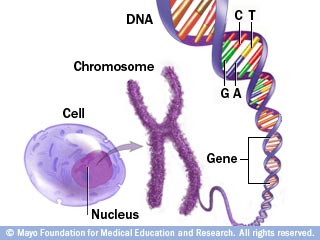 |
| What is genetic code? | involves DNA and genes, 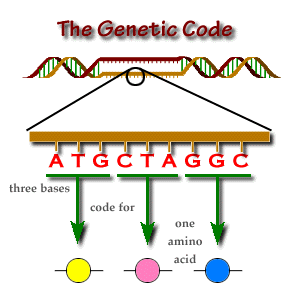 |
DNA:function,  | instructions for every protein in the body |
| Gene: function | DNA instructions for 1 protein, 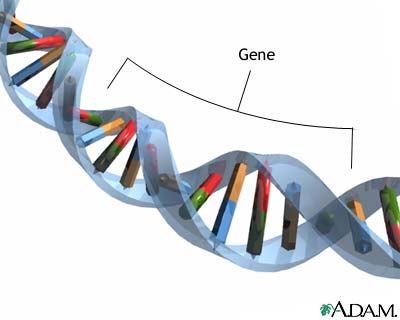 |
| Genetic Code | The chemical language of DNA instructions: sequence of bases (A, T, C, G),  |
| triplet code: 3 bases | 1 amino acid,  |
| ***Where are chromosomes located? | nucleus,  |
| What do chromosomes contain? | DNA |
| What does DNA store? | DNA stores genetic instructions for proteins |
| What do proteins determine? | Proteins determine cell structure and function |
| Explain transcription | remember DNA cannot leave nucleus--so during Trancription a genetic template for a protein is copied and carried out to the cytoplasm |
| transcibe (root of transcription) | to make an exact copy of (a document, text, etc.).Or in anatomy a copy of protein DNA |
| explain Translation - | RNA template serves as a series of codes for the amino acid sequence of the protein |
| translate (root of translation) | to turn from one language into another--in anatomy the RNA now translates as a code for the new protein to be made |
| steps of translation | 1. mRNA attaches to the ribosome 2. tRNA's attach to free amino acids in the cytoplasmic "pool" of amino acids 3. tRNA carries its specific amino acid to the ribosome |
| you tube translation video | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5bLEDd-PSTQ |
| you tube transcription video | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WsofH466lqk |
| Steps of Transcription | 1. DNA unwinds 2. One side of DNA "codes for a protein" 3. Genetic code of DNA is a triplet code of 3 nucleotides or bases 4. Each triplet is specific for the coding of a single amino acid |