| A | B |
|---|
| What is A triplet code ? | A triplet code comprised of three nucleotide bases in a sequence., 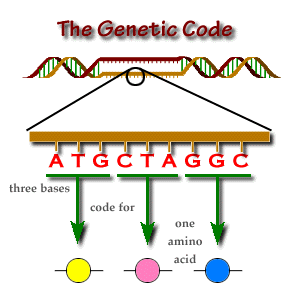 |
| How many different DNA triplet codes or RNA codons? | 64 different DNA triplet codes or RNA codons |
| What does the nucleus control? | Nucleus Controls Cell Structure and Function |
| Nucleus' Direct contol of Cell Structure and Function | Direct control through synthesis of: structural proteins secretions (environmental response) |
| Nucleus' InDirect contol of Cell Structure and Function | Indirect control over metabolism through enzymes |
| ***Genes are-- | are functional units of DNA contain instructions for 1 or more proteins,  |
| **Protein synthesis requires: | several enzymes, ribosomes, 3 types of RNA |
| **Protein synthesis requires: | several enzymes, ribosomes, 3 types of RNA |
| **What is a mutation? | Mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene |
| **What can a mutation do? | can change gene function |
| **mutation causes | Causes: exposure to chemicals exposure to radiation mistakes during DNA replication |
| How do things get in out of cells? | They have to overcome the cell barrier |
| The cell membrane is a ____, but nutrients must get in products and wastes must get out | barrier |
| ________ determines what moves in and out of a cell. A membrane that lets nothing in or out is impermeable, lets anything pass is freely permeable, restricts movement is ____ | Permeability, **selectively permeable** |
| Cell membrane is selectively permeable and allows some materials to move freely but _______ other materials | restricts |
| Transport through a cell membrane can be: | active (requiring energy and ATP) passive (no energy required), 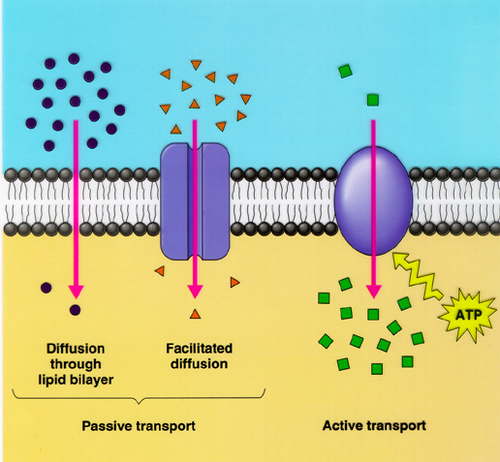 |
| 3 Categories of Transport | Diffusion (passive) Carrier-mediated transport (passive or active) Vesicular transport (active) |
| Diffusion: | molecules mix randomly solute spreads through solvent eliminates concentration gradient, 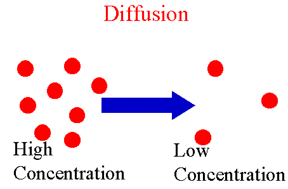 |
| Diffusion and concentration gradient | Solutes move down a concentration gradient,  |
| simple diffusion | small substances move directly through bilayer |
| materials which move directly thru bilayer (simple diffusion) | 1)lipid-soluble compounds (alcohols, fatty acids, and steroids) 2) dissolved gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) |
| Channel-Mediated diffusion | materials that pass thru channels-too large or wrong material for simple diffusion |
| osmosis | smosis simple diffusion of H2O; water moves TO highest particle concentration, 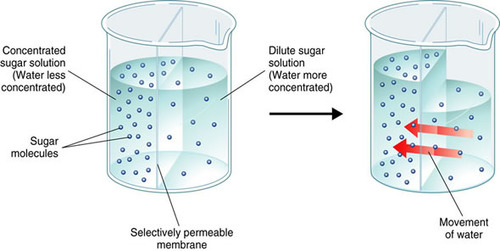 |
| tonicity | the ability of solution to change the shape of cell by altering intracellular water levels,  |
| Isotonic | Extracellular and intracellular concentrations are the same, 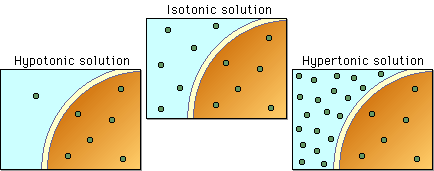 |
| solution that doesn't cause osmotic water flow in or out of cell | Isotonic, 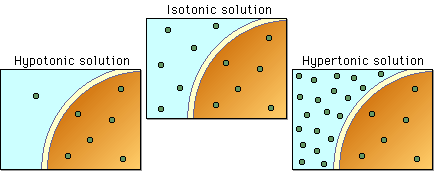 |