| A | B |
|---|
| 7 ways of transport | diffusion, osmosis, carrier facilitated diffusion,active transport,secondary active transport,endocytosis, extocytosis |
| Exocytosis | material exits the cell through vesicular transport, 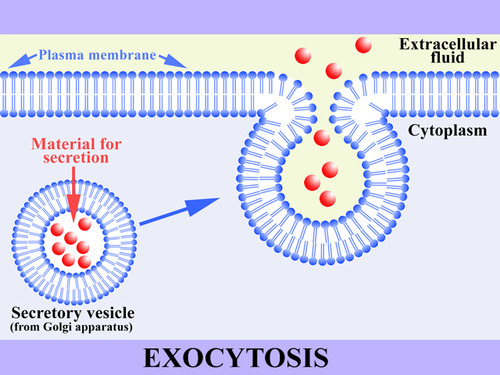 |
| Endocytosis | Materials enter the cell, such as with Phagocytes lysing bacteria, 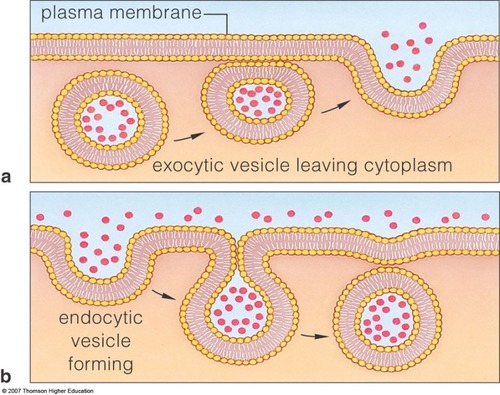 |
| Pinocytosis | cell drinking. A form of endocytosis, 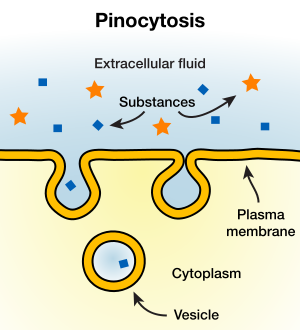 |
| Phagocytosis | cell eating. A form of endocytosis., 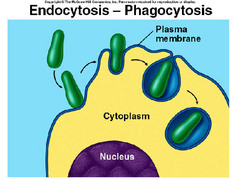 |
| Solvent | In a solution, the substance in which the solute dissolves. In the body this is typically water. |
| solute | the dissolved substance in a solution |
| transcription | (genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA, 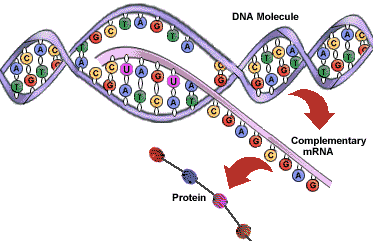 |
| translation | (genetics) the process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome in the cytoplasm, 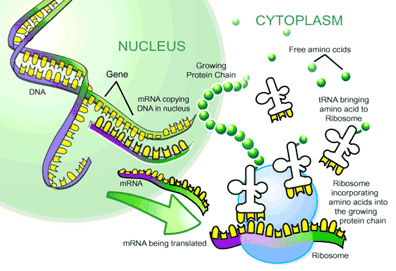 |
| Active transport | - for moving molecules from low to high concentration. Requires ATP., 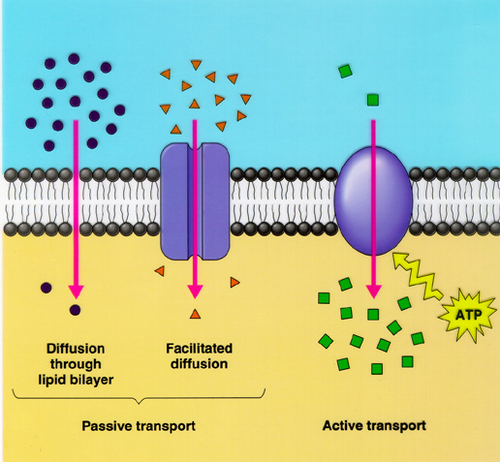 |
| Active processes | require energy to pass through the cell membranes, uses ATP |
| facilitated diffusion | diffusion using a carrier protein, uses no ATP and still requires concentration gradient & kinetic energy; to move molecules that are too large or insoluble (too charged), 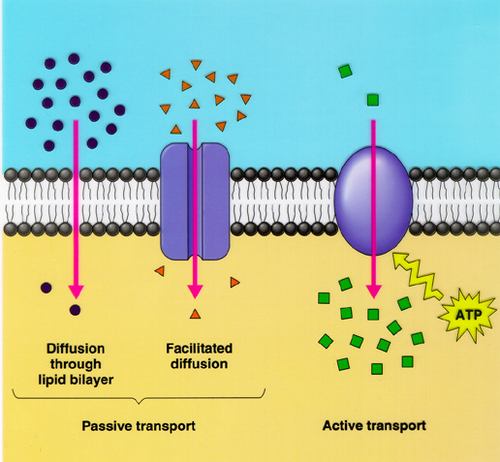 |
| diffusion | movement of substances down its concentration gradient from high to low concentration (passive) |
| semi permeable | only select substances pass through |
| hypotonic effect on cell | A cell in a hypotonic solution: gains water ruptures (hemolysis of red blood cells) |
| hypotonic solutions | f the solution is hypotonic to the cell, the cell expands, water moves INTO the cell towards the solute and cell will lysis (or burst), 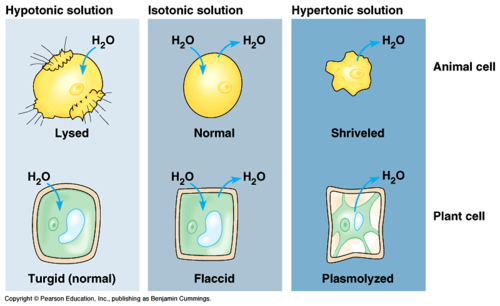 |
| hypotonic solute concentration | less solutes-gains water from osmosis, 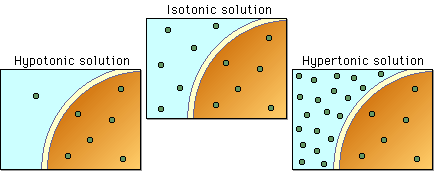 |
| hypotonic memory aid | Hypotonicity occurs when the concentration inside the cell is greater than outside the cell. Thus, water rushes into the cell and it swells. The way to remember that a cell swells under hypotonic conditions is to think of Hippo. Hippos are rather large and plump. |
| hypertonic memory aid | Hypertonicity occurs when the concentration outside the cell is greater than inside the cell. Thus, water leaves the cell and it shrinks. The way to remember that a cell shrinks under hypertonic conditions is to think of a hyper kid. Someone who is always hyper is constantly moving about and will most likely be skinny. |
| isotonic memory aid | Extracellular and intracellular concentrations are the same--Exactly like it should be--*I* like it *I*sotonic |