| A | B |
|---|
organelles,  | structures that perform specific functions in the cell |
| Basic components of a cell | Nucleus, cytoplasm, & plasma membrane |
cilia, 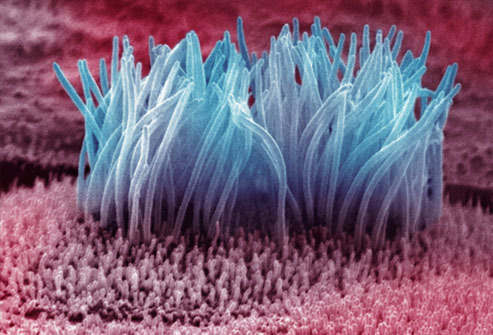 | hair-like processes from the surface of epithelial cells, such as those of the bronchi, that provide upward movement of mucus cell secretions |
Cytosol, 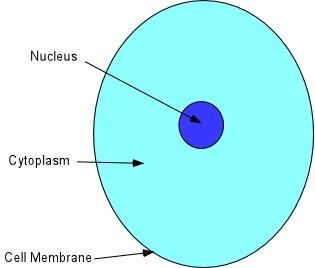 | intracellular fluid that contains water, solutes, enzymes & proteins. It has high levels of potassium and low levels of sodium |
cytoskeleton, 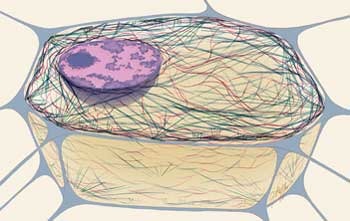 | collection of protein filaments that support the cell, function in cell movement, and move substances within the cel |
| Cytoplasm | "Material inside the cell" a jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended |
flagella, 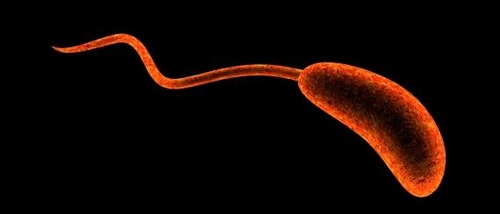 | whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement |
Golgi apparatus,  | Stack of flattened membranes and associated vesicles close to the nucleus. Packages, modifies, and sorts proteins for secretion from the cell, sends abnormal vesicle to lysosomes and normal to the membrane for exocytosis. |
hydrophilic, 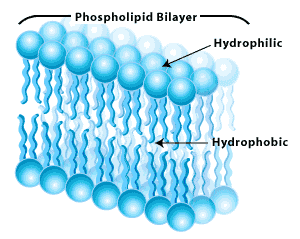 | water loving.....can dissolve in water. Polar. |
hydrophobic tails,  | nonpolar region of the plasma membrane. Water hating. |
Lysosomes,  | Membranous sacs containing acid hydrolases. Digest particles brought into the cell, old or abnormal organelles. |
Mitochondria, 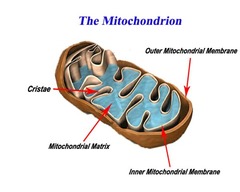 | double membrane structure, inner membrane folded into projection called cristae. Site of ATP synthesis. |
Nucleus, 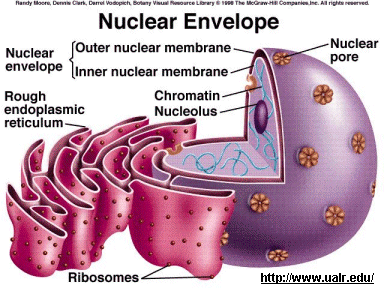 | Largest organelle. Surrounded by the nuclear envelope, contains nucleoplasm, nucleoli and chromatin. Control center; responsible for transmitting genetic info, and providing the instructions for making protein. |
Plasma Membrane, 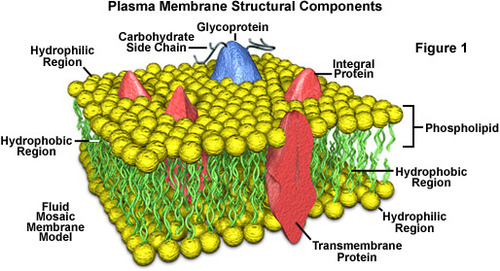 | Outer boundary of the cell composed of a phospholipid bilayer that controls what goes in/out of cell. Cell barrier |
Ribosomes,  | Site of protein synthesis in the cell (along with mRNA and tRNA and rRNA) |
Microvilli, 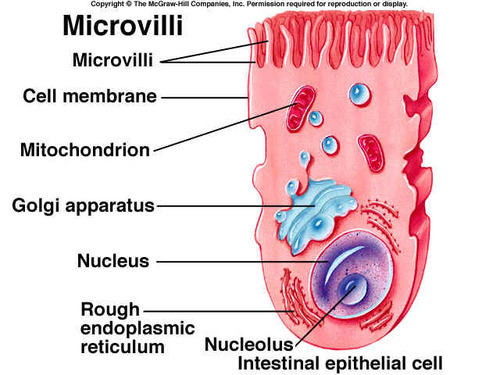 | finger-like extensions that increase surface area for increased absorption |
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, 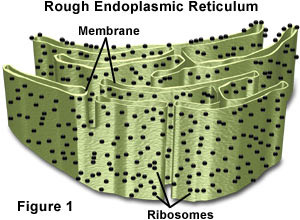 | Membrane enclosing a cavity, the cistern, and coiling thru the cytoplasm. Externally studded with ribosomes. |
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum,  | Membrane system of sacs and tubules that are free of ribosomes. Site of lipid and steroid (cholesterol) synthesis, lipid metabolism and drug detoxification. |
| What makes the mitochondria special ? | It has a double membrane structure and it's only maternally inherited.Makes ATP |
| Tonicity | the ability of solution to change the shape of cell by altering intracellular water levels,  |
| semi permeable | only select substances pass through |
Pinocytosis, 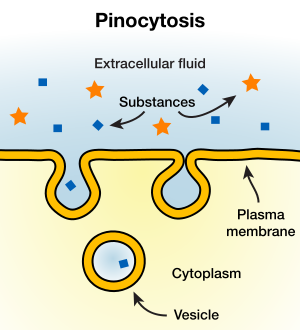 | cell drinking. A form of endocytosis |
Phagocytosis, 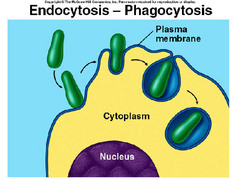 | cell eating. A form of endocytosis. |
hydrophobic tails,  | nonpolar region of the plasma membrane. Water hating. |
hydrophilic,  | water loving.....can dissolve in water. Polar. |