 |
Java Games: Flashcards, matching, concentration, and word search. |
 |
 |
| A | B |
|---|
transverse section view, 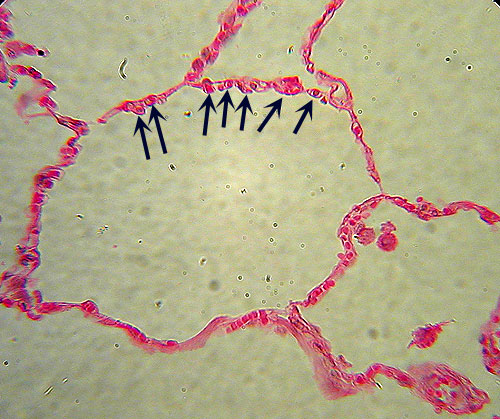 | Simple Squamous Epithelium-- Identification: Small, flat cells arranged around large, empty circles (air sacs). May be confused with Adipose Tissue, but note the multiple cells and nuclei (arrows). ---Features to Know: nuclei. |
cluster of 4 cells if laid out flat,  | Simple Squamous Epithelium--- Where Located: lung (air sacs or alveoli) and lining blood vessels . -- Function: diffusion (gas exchange). |
identify,  | Simple Cuboidal Epithelium-- Identification: Squarish cells with round nuclei in a single row (arrows), usually arranged in a circle (tubule). ---- Features to Know: nuclei. --- Where Located: kidney tubules (can also be seen in sweat glands of skin slide). --- Function: absorption and secretion. |
Identify?, 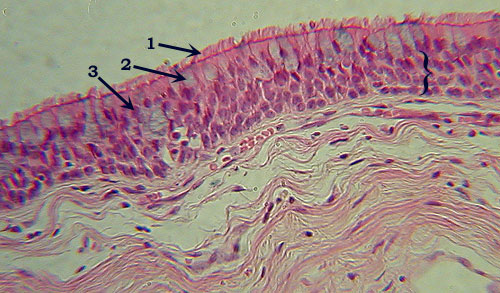 | Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium--- Identification: Tall rectangular cells, with multiple irregular rows of nuclei (bracketed; compare to simple columnar, above).---- Note also goblet cells, found only here and in Simple Columnar Epithelium.--- Features to Know: cilia (1), goblet cells (2), nuclei (3). -- Where Located: trachea.-- Function: secretion and movement of mucus. |
?-?,  | Stratified Squamous Epithelium-- Identification: Many layers (6 or more) of small, flattened cells. The only other epithelial tissue with so many layers is transitional (below), but note that stratified squamous epithelium typically has a more evenly contoured surface; with the uppermost layers of cells flattened.--- Features to Know: nuclei, if evident. --- Where Located: lining mouth and esophagus.--- Function: protection from abrasion and infection. |
?,  | Transitional Epithelium -- Identification: Numerous layers of cells of varying and often irregular shape, though generally not squamous (when unstretched as in the slides). Surface of tissue is folded (inside of ureter) or bumpy appearing (urinary bladder).-- Features to Know: nuclei. -- Where Located: ureter (and urinary bladder). -- Function: elasticity: stretch and retract. |
??,  | Areolar (or Loose) C.T.-- Identification: Loose arrangement of thin (elastic and reticular) and thick (collagen) fibers that criss-cross haphazardly.-- Features to Know: collagen fibers (1), elastic fibers (2), fibroblasts (3). Fibers Present: collagen fibers, elastic fibers, reticular fibers. -- Where Located: surrounding most organs, underneath epithelia.-- Functions: wraps, cushions, holds defensive cells, holds fluids. |
??, 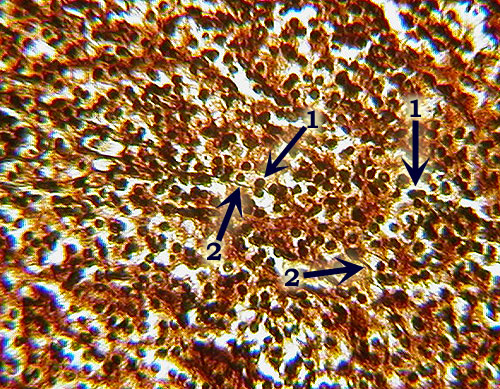 | Reticular C.T. -- Identification: Dark-staining reticular fibers (2) present, but may be obscured by the numerous nuclei of lymphoblasts and other cells (1). Overall brownish color is also distinctive. -- Features to Know: lymphoblasts (1). Fibers Present: reticular fibers (2). ---Where Located: spleen (also bone marrow, lymph nodes).-- Function: forms scaffolding to support loose cells. |
???, 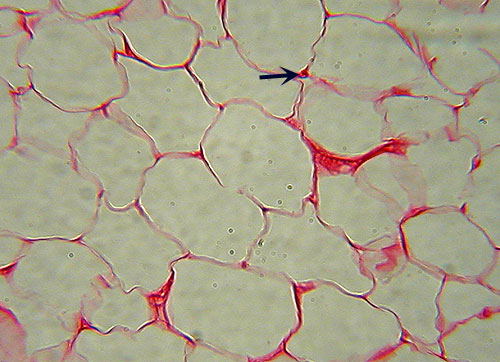 | Adipose Tissue Identification: Virtually no extracellular matrix visible due to greatly enlarged cells, nearly the entire volume of which is a fat vacuole (appears empty on slide). Most likely to be confused with simple squamous epithelium: note that the "open" areas are surrounded by narrow bands of cytoplasm, not multiple, nucleated cells. Few nuclei will be visible (arrow). -- Features to Know: adipocyte, nucleus.-- Fibers Present: none visible.-- Where Located: underneath skin, breasts, surrounding eyes & kidneys.--- Functions: energy storage, cushioning, insulation. |
______,  | Dense IRRegular C.T. Identification: Densely packed parallel fibers. Note scattered cells (lack of lacunae distinguish this tissue from cartilages; compare especially to fibrocartilage). -- Features to Know: fibroblast (1). Fibers Present: collagen fibers. -- Where Located: ligaments and tendons. -- Function: attaches bone to bone or muscle; resists tensile (pulling) forces in single direction. |
__,  | Dense regular C.T. Identification: The collagen fibers are in distinct bundles, separated by space, giving an overall patchy or blocky appearance very dissimilar to other tissues. -- Features to Know: fibroblasts, if visible. --Fibers Present: collagen fibers. -- Where Located: dermis of skin. -- Functions: provides strength; can withstand tensile forces in many directions. |
__,  | (Dense Irregular) Elastic C.T. Identification: Similar to dense regular CT (densely packed collagen fibers), but with distinct dark, usually zigzagging, lines of elastic fibers (arrow). Although it has a similar name to Elastic Cartilage, these two tissues are not that similar (note the more parallel fibers and lack of lacunae here).-- Features to Know: fibroblasts. -- Fibers Present: collagen fibers, elastic fibers. Where Located: aorta.-- Function: elasticity (can stretch and return to original shape). |
++??,  | Hyaline Cartilage Identification: Distinctive lacunae (arrow) distinguish cartilages from other connective tissues. Lacunae often are paired. Note lack of fibrous appearance, instead an overall glassy appearance. Color varies. Features to Know: chondrocyte in lacuna (arrow). Fibers Present: collagen fibers (the thin, evenly dispersed fibers do not appear as fibers, but contribute to an overall glassy appearance). Where Located: articulating ends of long bones, nose, trachea, ends of ribs. Functions: structural support; cushions joints. |
----?, 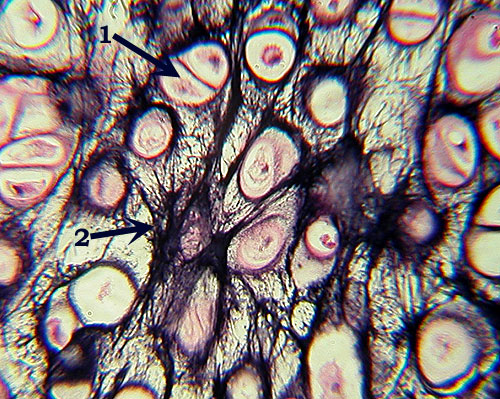 | Elastic Cartilage Identification: Distinctive large, often paired lacunae (similar to hyaline cartilage), but note extensive dark elastic fibers (2). Features to Know: chondrocyte in lacuna (1), elastic fibers (2). Fibers Present: elastic fibers (collagen fibers are also present but not visible). Where Located: ear lobe, epiglottis (remember those Es!). Function: flexibility, bendability. |
| fibrocartilage slide | Fibrocartilage Identification: Distinct, more or less parallel fibers visible. Distinguished from dense regular connective tissue by the distinct lacunae (arrow). Usually blue in color. Features to Know: chondrocytes in lacunae (arrow). Fibers Present: collagen. Where Located: intervertebral disks, pubic symphysis, menisci of knee joint. Function: resists compressive forces. |
--?, 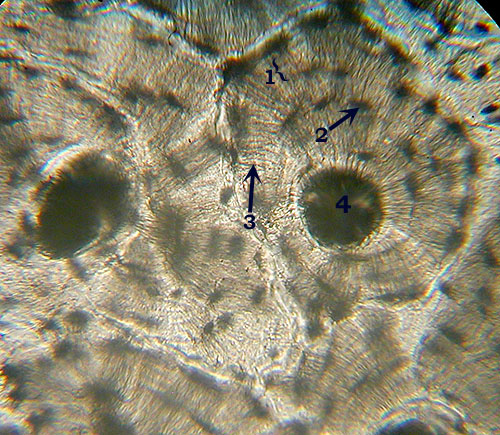 | (Compact) Bone Identification: Concentric rings (like tree rings) are unmistakable. Features to Know: lamellae (1), osteocytes in lacunae (2), canaliculi (3), Haversian canal (4). An entire set of concentric rings (lamellae) is called a Haversian System. Fibers Present: collagen fibers present but not visible. Where Located: bones . Functions: support, protection, act as levers, mineral storage. |
?-, 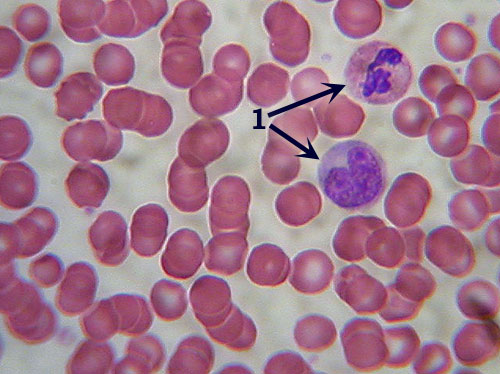 | Blood Identification: The numerous round, red blood cells in a featureless matrix are unmistakable. Features to Know: the liquid matrix is called the plasma. The numerous round, red cells are erythrocytes (or red blood cells) that lack nuclei (the center of the cell is depressed and thus may appear lighter colored). There are also smaller numbers of larger white cells with large, multi-lobed nuclei called leucocytes (or white blood cells; 1). Fibers Present: none visible. Where Located: within the circulatory system. Functions: transport of nutrients, gasses, wastes, etc. |
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
| |