| A | B |
|---|
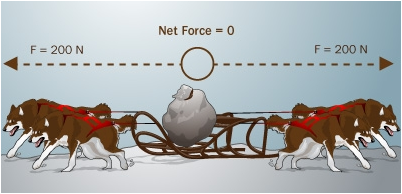 | Static equilibrium |
| equilibrium | balanced forces |
| disequilibrium | unbalanced forces |
| disequilibirum | object accelerates |
| newton | S. I. unit for force |
| kilogram | S. I. unit for mass |
| a push or a pull | Force |
| gravity | weakest of the 4 fundamental forces |
| strong nuclear | strongest of the 4 fundamental forces |
| Normal force | support force from a solid surface |
| Weight | Force due to gravity |
| momentum | mass times velocity |
| Force due to gravity | mass times acceleration of gravity |
| velocity | displacement / time |
| acceleration | velocity / time |
| density | mass /volume |
| meter | S. I. unit for length, distance, displacement |
| distance | How far? |
| displacement | How far? AND Which way? |
| speed | How Fast? |
| velocity | How Fast? AND Which Way? |
| Vector | requires magnitude AND direction |
| Scalar | Requires ONLY magnitude |
| Magnitude | number or amount |
| Volume | The amount of space an object occcupies |
| Static | Still |
| Dynamic | moving at constant velocity |
| mass | the amount of matter in an object |
| Momentum is conserved in a closed system. | Law of Conservation of Momentum |
| number of variables that can change in a valid experiment | ONLY ONE |
| Number of trials needed in a valid experiment | THREE |
| Heavy things DO NOT fall faster than light things. | TRUE |
| All accelerating objects get faster. | FALSE |
| Distance ____ path dependent. | IS |
| Displacement _____ path dependent. | IS NOT |
| Forces cause . . . | motion AND/OR deformation |