| A | B |
|---|
| Work | Force times distance |
| Energy definition | the ability to do work |
| Work definition | the transfer of energy |
| E(GRAV) | energy of a mass due to its position in a gravitational field. |
| E(K) is increasing | getting faster |
| E(K) is decreasing | getting slower |
| E(GRAV) is increasing | moving up |
| E(GRAV) is decreasing | moving down |
| E(DISS) is large | A characteristic of an inefficient energy transfer. |
| E(DISS) | Unrecoverable energy |
| E(DISS) is small | A characteristic of an efficient energy transfer |
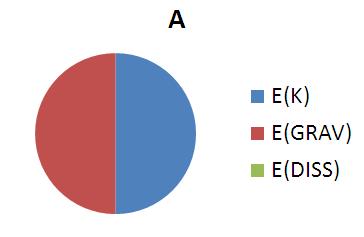 | Moving slowly, but is high above the ground. |
| Formula for E(K) | 1/2 m v v |
| Formula for E(GRAV) | m g h |
| If velocity doubles, | kinetic energy will quadruple. |
| If velocity triples, | kinetic energy will be 9 times larger. |
| If height doubles, | Gravitational Potential Energy will double. |
| If height decreases by half, | Gravitational Potential Energy will decrease by half. |
| S. I. Unit for Work and Energy | Joules |
| S. I. Unit for mass | kilograms |
| 81 Joules | Work done by a 9 newton force that moves a crate 9 meters. |
| 18 Joules | Work done by a 2 N force that lifts a crate 2 meters |
| 0 joules | Work done to move a 40 N box 3 meters to the right. |
| Conditions met for work to be done | A force must cause a displacement AND the force must be parallel to the motion it causes. |
| An object has no Kinetic Energy when | v = 0 |
| An object has no gravitational potential energy when | h = 0 |
| Mechanical Energy | The sum of the Kinetic and Potential Energies |
| E(K) = Max; E(GRAV) = 0 | moving fast at ground level |
| E(K) = 0; E(GRAV) = MAX | Rest at a position high above the ground |
| When E(K) = E(GRAV), | An object has fallen half the distance to the ground. |
| 25 Joules | The E(K) of a 2 Kg mass moving at 5 m/s |
| 100 Joules | The E(K) of a 2 Kg mass moving at 10 m/s |
| 400 joules | The E(GRAV) of a 4 Kg mass that is 10 meters above the ground. |
| 200 joules | The E(GRAV) of a 2 Kg mass that is 10 meters above the ground. |
| If an object's velocity gets 4 times faster, | the object's E(K) will be 16 times larger. |
| If an object's velocity gets 6 times faster, | the object's E(K) will be 36 times larger. |
| If an object's velocity gets 12 times faster, | the object's E(K) will be 144 times larger. |