| A | B |
|---|
| adhesion | attraction of unlike substances,  |
| cohension | attraction of like substances such as water molecules, 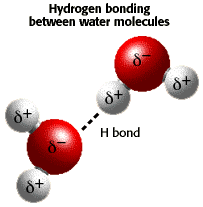 |
| capillarity | the ability of water to move up narrow tubes or through fine pores,  |
| hydrogen bond | weak attraction between the positive hydrogen regions and the negative regions of water molecules |
| polar | covalentlly bonded molecule with positive and engative regions |
| ATP | energy storage of all organisms |
| hydroxyl | funcitonal groups of alcohols |
| condensation/dehydration | removal of water after bonding two monomers |
| hydrolysis | the addition of a water molecule to break polymers into monomers |
| variable | a group of atoms that change on any a monomer |
| macromolecule | a very large polymer |
| organic compound | compound containing C and H in combo |
| polymer | a long chain of monomers linked by dehydration synthesis |
| amino acid | monomer of proteins, 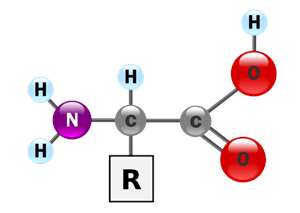 |
| monosaccharide | monomer of carbohydrates, 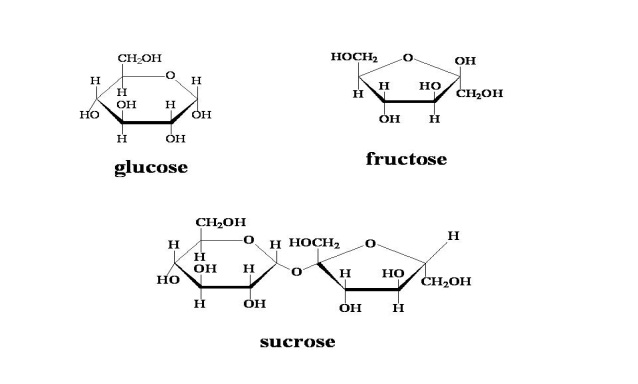 |
| fatty acids and glycerol | make lipids |
| steroid | four fused rings, 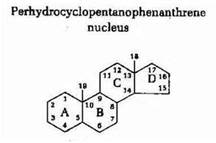 |
| dipeptide | two amino acids joined together |
| polypetide | many amino acids joined together |
| disaccharide | two monosaccharides joined together |