| A | B |
|---|
| The element that forms the backbone of organic molecules is ___. | carbon |
| A reaction that gives off energy (loses energy) is called an _____ reaction | exothermic, 
|
| A reaction that requires more energy than it gives off is called an ___ reaction. | endothermic, 
|
Cellular respiration is an example of an ___ reaction, 
| exothermic, 
|
| Acidic solutions have a pH that is ____ seven. | below |
| Basic solutions have a pH that is ___ seven. | above |
| A(n) ______ is any substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction. | catalyst, 
|
A biological catalyst is known as a(n) ____., 
| enzyme, 
|
| Chemicals that have carbon and hydrogen in them and were produced by once living things are called ___ chemicals. | organic |
| Water and carbon dioxide are ____ molecules. | inorganic |
| The building blocks of larger molecules are known as ____. | monomers |
| Many monomers linked together form ____. | polymers |
| The root word "mono" means ___. | one |
| The type of macromolecule that is used primarily as a source of energy is ___. | carbohydrates, 
|
| Bread, pasta, cereal and fruits are high in which type of macromolecule? | carbohydrates, 
|
| The monomers of complex carbohydrates are ___. | simple sugars, 
|
| glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of ____. | simple sugars, 
|
| Sucrose is a type of carbohydrate made of glucose bonded to fructose. Therefore, it is a ___. | disaccharide |
| Lactose is a type of _____ found in milk (be specific) | disaccharide |
Plants store their carbohydrates as the polysaccharide known as ____., 
| starch |
Animals store carbohydrates in their liver and muscles as the polysaccharide known as ___., 
| glycogen, 
|
| The cell walls of plants are made of the polysaccharide known as ____. | cellulose, 
|
There is a lot of cellulose in the plant cell walls of grass. It is very difficult to break down into the simple sugars that make it up. Therefore, cows rely on _____ in their stomach to break it down for them., 
| bacteria |
| Sugars are classified in which macromolecule category? | carbohydrates, 
|
The type of macromolecule that is used mostly for building structures in an organism is called ___., 
| protein |
| The monomers of proteins are ___. | amino acids, 
|
A long straight chain of amino acids is called a ____., 
| polypeptide |
A polypeptide that folds into a 3-D structure that has a specific function is called a(n) ___., 
| protein |
Lean meat is highest in the macromolecule known as ____., 
| protein |
The most important quality of an enzyme is its ___., 
| shape. |
| A protein whose shape has been changed due to heat or harsh chemicals is known as a(n) ____ protein. | denatured |
Organic catalysts are known as ___., 
| enzymes |
| An enzyme ____ a chemical reaction without being changed itself. | speeds up |
| DNA and RNA are types of ____ | nucleic acids, 
|
| The type of molecule that stores genetic information is called ___. | DNA |
| The monomers of nucleic acids are ____. | nucleotides, 
|
| adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine are ____ | nucleotides |
The order of nucleotides in DNA determines the order of amino acids in a _______, 
| protein, 
|
A change in the order of nucleotides in DNA is known as a ____., 
| mutation |
| Fats, oils, and waxes are classified as ___. | lipids |
| The main function of ______ in an animal's body is to store energy. | lipids |
| Red meats, dairy and fried foods are high in the type of macromolecules known as ___. | lipids |
| The building blocks of most lipids are ___ . | 3 fatty acids and glycerol |
| Fats that are solid at room temperature and are not particularly good for you are a type called ___ fats | saturated |
| Fats that are liquid at room temperature and are considered healthy to eat are called ___ fats. | unsaturated |
| Cell membranes are made up of mostly ___. | phospholipids |
Enzymes are almost always made of ____., 
| proteins |
The chemical or chemicals that an enzyme works on is called the ___., 
| substrate |
| The part of the enzyme that the substrate fits into is called the ___. | active site |
| Lipids with a ring structure are called ______ | steroids., 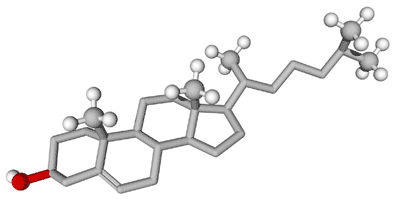 |
| Some steroids, like testosterone and estrogen, can act as ______. | hormones |
| The process by which organisms regulate their internal conditions to keep them fairly constant is called ___. | homeostasis |
| A group of organisms of the same type living in the same area is called a ___. | population |
| A group of many different types of organisms living together in the same area is called a ___. | community |
| The largest level at which organisms can be studied is at the level of the ___. | biosphere |
| The smallest thing that can be considered to be living is a ___. | cell |
| Changing form as an organism grows is called ___. | development |
| Something that an organism responds to is called a(n) ____. | stimulus |
| When one type of organism changes over very long periods of time (many many generations), it is called ____. | evolution |
| All the living and non-living things that interact in an area are called a(n)_____. | ecosystem |
| What are the tiny structures with specific functions called that are located in the cytosol of cells (mostly eukaryotic cells)? | organelles (Eukaryotic cells are the only type of cell that has membrane-bound organelles, like the nucleus, golgi, vacuoles, etc. These sac-like membranes form separate areas inside the cell where specialized functions can be carried out and specific substances can be stored. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes, which are often referred to as organelles also, but they are solid structures, not hollow sac-like structures like the membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells) |
| The small solid (not membrane-bound) organelle found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that helps the cell build different types of proteins is called a(n) _____. | ribosome |
| Prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells because they lack a(n) ______. | nucleus |
| Molecules like glucose and fructose that have the same chemical formula, but a different arrangement of atoms are called ______. | isomers |
| The root word "Poly" means ___. | many |