| A | B |
|---|
| Revolve (def) | To orbit something |
| Rotate (def) | To spin on an axis |
| Approximate age of the Solar System | 4.6 Billion years old |
| Cause of Earth's Shape | Earth's Rotation |
| What causes winds to curve to their right in the northern hemisphere? | Coriolis Effect |
| 1st planet from sun | Mercury |
| 3rd planet from sun | Earth |
| A comet's tail always points | away from the sun |
| The same side of the Moon faces Earth because | Moon's rotation rate = the moon's revolution rate |
| The moon & sun rise in the east & set in the west because | Earth rotates west to east |
| 3 names given to a small rock in space, the rock burning in the atmosphere & the rock hitting Earth | Meteoroid, Meteor, Meteorite |
| Scientific explanation for the formation of the Universe | Big Bang Theory |
| Steps in the life cycle of our sun in order | Nebula, Protostar, Stable State, Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, White Dwarf, Black Dwarf |
| Examples of Jovian planets | Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune |
| The name of our galaxy | Milky Way |
| Geocentric | Earth centered model of the solar system |
What letter represents Rigel, a blue super giant?, 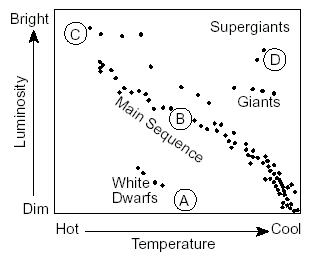 | C,  |
| Order of the moon phases from new to full | New, Waxing Crescent, 1st Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon |
| Moon phases for Spring tides | New & Full |
| Next stage in the life cycle of our sun | Red Giant |
| 2 moon phases that can produce spring tides | New & Full |
| 2 moon phases that can produce neap tides | 1st & 3rd Quarter |
| List the terrestrial planets | Mercury, Venus, Earth & Mars |
| How much later does the moon rise & set each day? | 50 minutes |
| Which planet is the hottest? | Venus, because of its thick atmosphere |
What season is it in the Northern hemisphere?, 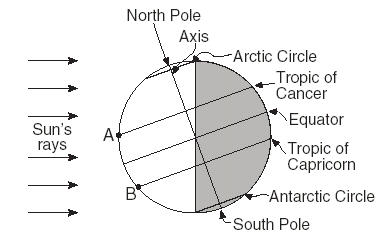 | Summer because the northern hemisphere is tilted toward the sun & above 66.5 degrees N has 24 hrs of daylight,  |
Which letter represents our sun?,  | B,  |
| 3 Reasons for seasons | Angle at which the Sun's rays strike the Earth's surface due to Earth’s tilt, parallelism of the Earth's axis aimed to Polaris, & Earth's Revolution around the sun |
| Red Shift (def) | Explains the Big Bang theory: Spectral lines move toward the Red end of the spectrum as an obj moves away from the observer, described by the doppler effect |
| The astroid belt is located between: | Mars & Jupiter |
| What is the shape of our galaxy? | Spiral |
| Only planet that has water as a solid, liquid & gas | Earth |
| Approximate scientific estimate of the age or our universe | 13.7 billion years |
| The Foucault pendulum is evidence of Earth's _______? | Rotation |
| How are gravity & mass related? | Directly; An increase in the mass of one of object causes the gravitation attraction between them to increase. |
| Person who found the 4 largest moons of Jupiter & was the 1st to use a telescope. | Galileo |
| Person who made long term sky observations with the naked eye. | Tycho Brahe |
| Person who stated the orbits of the planets are elliptical. | Kepler |
| Person who credited the moon's gravity for affecting tides. | Newton |
| Person credited with the heliocentric model of the solar sytem | Copernicus |
| Instrument that is used to break light into the colors of the rainbow & show spectra | Spectroscope |
| Most distant object in the universe | quasar |
| Nuclear fusion reaction converts ______ into Helium & Energy | Hydrogen |
| Longest Wave length of the electromagnetic spectrum | Radio |
| Millions of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity | galaxy |
| The daily rise and fall of the oceans caused by the moon’s gravitational pull is called: | Tides |
| A planet that is one Astronomical Unit (AU), or 150 million Km (93 million miles), from the sun: | Earth |
| Distances in outer space are measure in: | Light years |
| Planets found beyond our solar system are called: | Exoplanet or Extra Solar Planet |
| object so dense that nothing including light can escape its gravity field | black hole |