| A | B |
|---|
Bacteria, 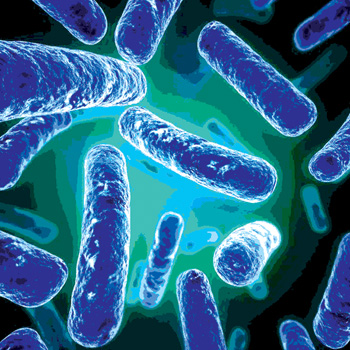 | Single celled prokaryotic organisms |
Cell, 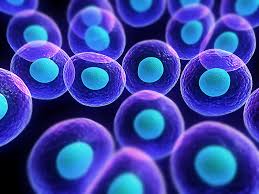 | Basic unit of structure and function in living things, the smallest unit of life |
Cell Membrane, 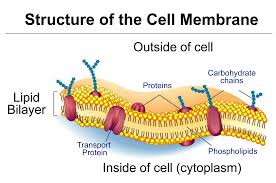 | Thin, flexible envelope that surrounds a cell and allows passage of materials in and out the cell |
| Cell Theory | Theory that all living things are made of cells, come from other cells, and that the cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. |
Cell Wall, 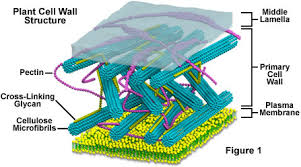 | Outermost boundary of plant cells that is made of cellulose (a carbohydrate) |
Chloroplast,  | Cell organelle containing chlorophyll that is involved in the process of photosynthesis |
Cytoplasm, 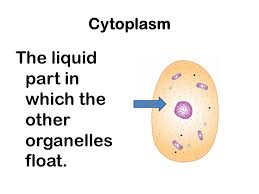 | Region between the cell membrane and the nucleus |
Endoplasmic Reticulum, 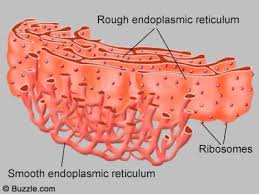 | Tubular passageways in the cell through which substances such as proteins are transported |
Eukaryote, 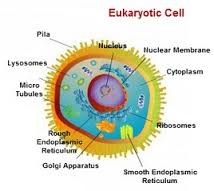 | Cell with a nucleus |
Mitochondria, 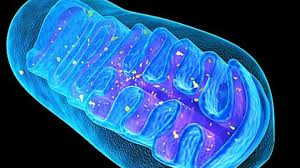 | Power houses of the cell in which cellular respiration occurs |
Multicelluar Organism, 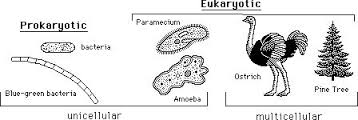 | organisms that consist of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organisms |
Nucleus, 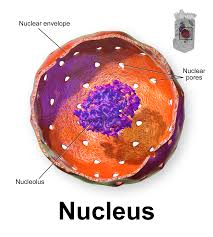 | Cell structure that directs all the activities of the cell |
Organelle, 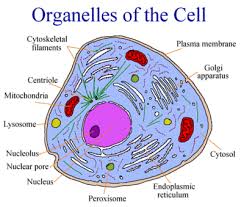 | “tiny organs” that make up a cell |
Prokaryote, 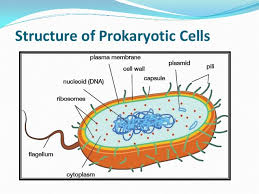 | Cell without a nucleus |
Ribosomes, 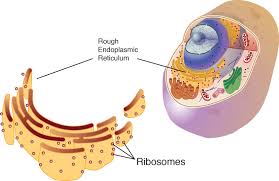 | Protein making site of the cell |
| Stimulus | Signal to which an organism reacts, change in the environment |
Unicellular Organism,  | Organism that consists of only one cell |
Vacuole, 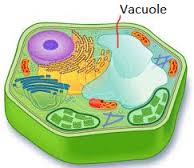 | Large, round sac in the cytoplasm of a cell that stores water, food, enzymes, and other materials |
| Respiration | Process in which simple food substances such as glucose are broken down and the energy they carry is released. |
| Digestion | Process by which food is broken down into simple substances |
| Reproduction | Process by which the cells divide to form new cells |
| Excretion | Process of getting rid of waste materials |
| Locomotion | Process by which a cell moves from one place to another |