| A | B |
|---|
| Carbohydrates | compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1. |
| Polymerization | the process in which large compounds are built by joining smaller ones together |
| Monosaccharide | single sugar unit; the monomer of carbohydrates. |
| Polysaccharide | a long chain of monosaccharides joined together. |
| Cellulose | a polysaccharide used by plants that provides strength and rigidity. |
| Glycogen | a polysaccharide used by animals to store excess sugar. |
| Lipids | are fats, oils and waxes; generally not soluble in water and used to store energy. Made up of fatty acids bonded to a glycerol molecule. |
| Phospholipids | form biological membranes |
| Nucleic Acids | store and transmit hereditary information. |
| Two types of nucleic acids | DNA and RNA |
| Saturated fatty acid | has the maximum number of hydrogen bonds. |
| Unsaturated fatty acid | has less than the maximum number of hydrogen bonds (at least one double bond). |
| Protein | polymer that is made up of amino acids |
| Amino Acid | the monomer of proteins |
| Enzymes | biological catalyts; speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy |
| activation energy | the amount of energy required to get a reaction to start. |
| factors that affect enzyme funciton | temperature, pH, and concentration |
| active site | the part of the enzyme that the substrate binds to. |
| Substrate | the molecule acted on by an enzyme. |
| Products | the result of a chemical reaction. |
| polymer | large molecule formed by the joining of individual units or monomers. |
| monomer | simplest unit of a biological molecule. |
| DNA | dexoyribonucleic acid |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| Structure of a lipid | Looks like, 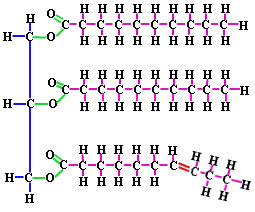 |
| structure of an amino acid | Looks like, 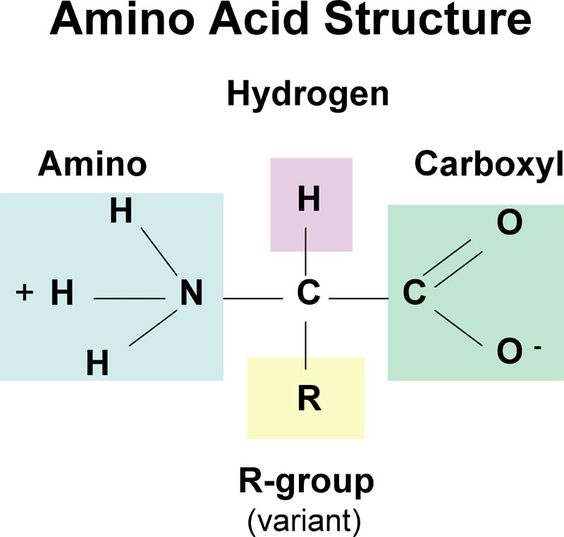 |
| structure of a protein | looks like, 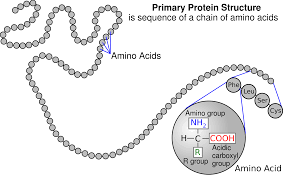 |
| structure of a starch | looks like, 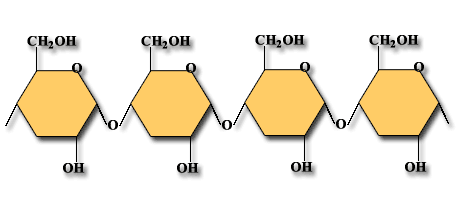 |